This guide will demonstrate how to install Timeshift on Manjaro Linux using the command-line terminal and the Pacman package manager to install the latest version and for future upgrades via cli commands.
Timeshift, a critical tool for system recovery and backup, represents a significant advancement in safeguarding Linux systems. Initially developed as an independent project, it has since been adopted and is now maintained by the Linux Mint team, ensuring continuous updates and improvements. Timeshift stands out for its ability to create incremental snapshots of the file system, akin to the System Restore feature in Windows and Time Machine in Mac OS.
Key Features of Timeshift:
- Incremental Snapshots: Timeshift takes periodic snapshots, allowing you to revert your system to a previous state, effectively undoing any recent changes.
- RSYNC and BTRFS Modes: It offers flexibility with RSYNC mode for using rsync and hard-links, and BTRFS mode, utilizing the BTRFS filesystem’s built-in features.
- Efficient Backup Management: Common files across snapshots share space, making it a space-efficient backup solution.
- Selective Backup: Unlike other backup solutions, Timeshift focuses on system files and settings, excluding personal files like documents and music. This specificity ensures system recovery without altering personal data.
This introduction to Timeshift sets the stage for exploring its installation on Manjaro Linux. Next, we delve into the technical how-to, guiding you through each step for a successful installation and configuration.
Install Timeshift via AUR on Manjaro
Step 1: Update Your Manjaro System Before Timeshift Installation
Start by updating your Manjaro system. This step is crucial to prevent compatibility issues, especially when dealing with the Arch User Repository (AUR). An up-to-date system ensures smoother installation and operation of new software.
Run this command in your terminal to update your package database and upgrade all existing packages:
sudo pacman -SyuThe time this process takes depends on the number and size of the updates. If this update includes the Linux Kernel, reboot your system to maintain stability and performance.
Step 2: Install Timeshift via Pacman Command
Proceed to install Timeshift using the following command in your terminal:
sudo pacman -S timeshiftThis command installs Timeshift directly from Manjaro’s official repositories, ensuring you receive a version compatible with your current system setup.
Launch Timeshift on Manjaro Linux
Open Timeshift via Command Line
Once you have installed Timeshift on your Manjaro Linux system, accessing it through the command line is an efficient method, particularly suited for quick accessibility. To open Timeshift, type the following command in your terminal:
timeshift-launcherThis direct approach is ideal for those who are comfortable with terminal commands and wish to quickly navigate to Timeshift’s functionalities.
Launch Timeshift from the Desktop Environment
For users who favor a more visual interaction, Timeshift can be launched from the application menu of your desktop environment. The method to locate and start Timeshift varies slightly depending on your desktop environment:
- For KDE and Xfce Users: Navigate to the Taskbar, go to ‘System’, and then select ‘Timeshift’. In both KDE and Xfce environments, Timeshift is typically grouped under the ‘System’ category, aligning with its system management and backup features.
- For GNOME Users: Click on ‘Activities’, then select ‘Show Applications’. Search for ‘Timeshift’, which is sorted alphabetically among your installed applications. This method in GNOME is straightforward and user-friendly, making it easy to find and initiate Timeshift.
First-Time Tips with Timeshift on Manjaro
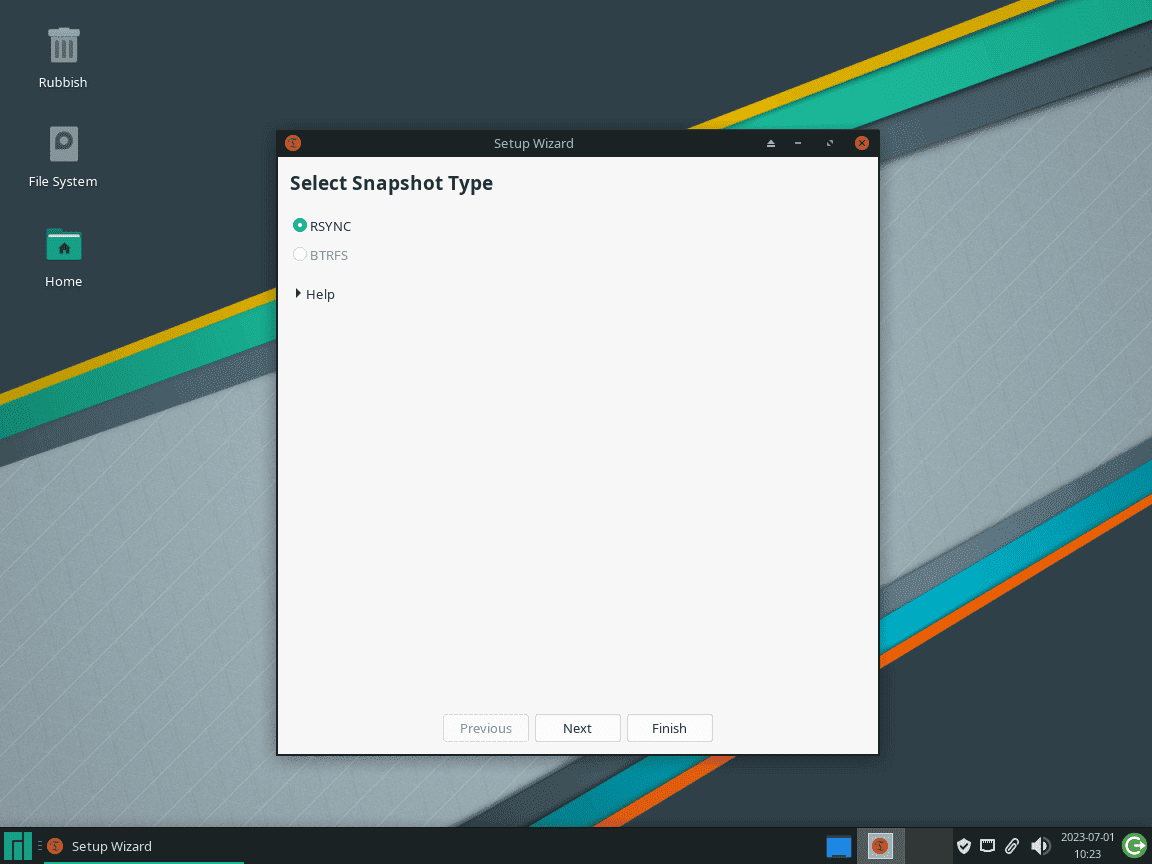
Select the Appropriate Snapshot Type on Manjaro
Understand the snapshot types available in Timeshift: RSYNC and BTRFS. Use RSYNC for compatibility with all systems, especially if you have a conventional partition layout. Opt for BTRFS if your system uses the Btrfs filesystem, as it leverages subvolumes for efficiency.
Allocate Sufficient Storage Space on Manjaro
Ensure you have enough storage for your snapshots, as they can be sizeable. Consider dedicating a separate partition or an external hard drive for snapshot storage. This foresight prevents storage issues and maintains system performance.
Customize Snapshot Levels for Comprehensive Coverage on Manjaro
Configure Timeshift to create snapshots at various intervals – hourly, daily, weekly, and monthly. This customization provides thorough coverage. A balanced approach could be maintaining daily snapshots for a week and weekly snapshots for the preceding month.
Test Your Snapshots on Manjaro
Regularly test your snapshots to ensure they are both correctly created and restorable. This verification is vital for reliable system recovery in the event of a failure.
Exclude Non-Essential Directories on Manjaro
Timeshift focuses on system files by default. Customize your snapshot settings to exclude non-essential directories, saving storage space and enhancing snapshot efficiency.
Employ Scheduled Snapshots and Regular Maintenance on Manjaro
Set Timeshift to automatically create snapshots according to a schedule. This automation ensures consistent backup availability. Regularly review and delete obsolete snapshots to manage storage efficiently.
Remain Informed on Timeshift Updates on Manjaro
Staying current with Timeshift updates is essential. Regular updates not only bring new features but also important security enhancements. Regularly check for Timeshift updates, or better yet, configure your system to update Timeshift automatically. This practice ensures you always have the most recent and secure version of the tool.
Managing Timeshift on Manjaro
Update Timeshift via AUR on Manjaro
Regularly updating Timeshift is crucial to access new features and maintain backup security. Manjaro Linux uses the pacman package manager for this task.
Checking for Timeshift Updates
To check for updates, use the command:
sudo pacman -SyuThis command scans all repositories, including the AUR (Arch User Repository), for available updates, ensuring you don’t miss any critical improvements.
Remove Timeshift
If you need to uninstall Timeshift from your Manjaro Linux system, the process depends on how it was initially installed.
Uninstalling Binary Package
To remove Timeshift installed as a binary package, use the command:
sudo pacman -R timeshiftThis command uninstalls Timeshift from your system.
Conclusion
We’ve walked through the essential steps for managing Timeshift on Manjaro Linux, from installation and updates to efficient usage and even uninstallation. Remember, keeping Timeshift updated is key to ensuring robust system protection. Regularly check for updates and allocate sufficient storage for your backups. Timeshift is a powerful tool for safeguarding your system, and with these tips, you’re well-equipped to make the most of it.