This guide will demonstrate how to install Nvidia Drivers on AlmaLinux 9 or 8 using the command-line terminal and the Nvidia CUDA repositories designed for Enterprise Linux 9 or 8, ensuring access to the latest Nvidia and CUDA builds.
Nvidia graphics cards are pivotal for a wide range of computing tasks, from professional graphic design and video editing to scientific computing and deep learning. These powerful processors rely on Nvidia drivers to effectively communicate with the operating system, unlocking their full potential. Key highlights of Nvidia drivers include:
- Optimized Performance: Tailored to enhance the capabilities of Nvidia GPUs, ensuring smoother and more efficient operation across various applications.
- Advanced Feature Support: Enables the latest graphics features, including ray tracing and AI-enhanced graphics, for cutting-edge visual experiences.
- Stability and Reliability: Regular updates provide fixes for bugs and compatibility issues, contributing to a stable computing environment.
- Wide Compatibility: Supports a broad spectrum of Nvidia products, making it easier to maintain systems with different Nvidia GPUs.
- Enhanced Security: Regular patches and updates to address vulnerabilities, protecting systems from potential threats.
- Customizable Settings: Allows users to tweak graphics settings for optimal performance and visual quality according to their preferences.
- Energy Efficiency: Drivers include power management features that help reduce power consumption during idle or low-load conditions.
- Direct Support for CUDA: Direct integration with CUDA platforms for those engaged in computational work, ensuring efficient execution of parallel computing processes.
Transitioning seamlessly from understanding the importance and capabilities of Nvidia drivers, the following sections will guide you through the technical steps required to install these drivers on AlmaLinux.
Nvidia Drivers Installation Prerequisites on AlmaLinux
Update the AlmaLinux System Before Nvidia Drivers Installations
Any installation process should ideally be preceded by updating your system. An updated system minimizes the possibility of encountering conflicts caused by outdated packages during the installation. You can perform a system update using the following command:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshDetermine the Installed Nvidia Graphics Card
In the next step, it is beneficial to identify the specific Nvidia Graphics card that your system is equipped with. This knowledge aids in verifying compatibility and assuring a smooth installation process. However, users with newer graphics card models can bypass this step, as more recent models are commonly supported.
The command to identify your graphics card model is:
lspci | grep -e VGAAn exemplary output might look like this:
03:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation TU117 [GeForce GTX 1650] (rev a1)
If your system hosts an older graphics card, it is advisable to visit Nvidia’s official website to check compatibility. Installing legacy drivers might be necessary for older cards that are no longer supported by the latest Nvidia drivers.
Check the Secure Boot Status
If secure boot is enabled on your system, you might experience difficulties during the Nvidia driver installation. In such scenarios, you may need to turn off the secure boot or undertake additional measures to circumvent conflicts. Consequently, checking the secure boot status is a crucial step.
The command to check if secure boot is enabled is as follows:
mokutil --sb-stateThis command will display the status of the secure boot on your terminal. Depending on this output and your system configuration, you might need to adjust your setup. For any issues related to secure boot, refer to your system documentation or the relevant troubleshooting guides.
Integrating EPEL Repository into AlmaLinux
Add EPEL Repository
The initial step for setting up Nvidia drivers on AlmaLinux includes incorporating the EPEL repository. It’s beneficial to have both repositories for the best results. Furthermore, ensuring that the chosen EPEL repository aligns with your specific AlmaLinux distribution is vital.
Configuring EPEL for AlmaLinux 9
Your first task involves activating the CodeReady Builder (CRB). You can achieve this by executing the following command:
sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crbWith the CRB activated, you’re now prepared to install both versions of the EPEL. You can accomplish this by running the command below:
sudo dnf install \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-next-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm
Configuring EPEL for AlmaLinux 8
To set up the EPEL for AlmaLinux 8, you can employ the following command:
sudo dnf install \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-next-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm
These steps involve activating and incorporating an additional repository of software packages into your AlmaLinux distribution. This process expands the range of software you can install while ensuring compatibility with your specific version of AlmaLinux, such as the case with installing the Nvidia Drivers packages.
Install Nvidia Drivers on AlmaLinux via DNF Commands
Add Nvidia Drivers RPM on AlmaLinux
The forthcoming procedure necessitates installing the Nvidia drivers repository, sourced directly from Nvidia. This approach is advantageous as it provides immediate access to the latest updates.
It’s crucial to ensure the compatibility of the repository with your specific AlmaLinux distribution while integrating it into your system.
Importing Nvidia Repository RPM for AlmaLinux 9
Execute the command below to integrate the Nvidia repository into AlmaLinux 9:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel9/$(uname -i)/cuda-rhel9.repo
Adding Nvidia Repository RPM for AlmaLinux 8
For AlmaLinux 8, the command alters slightly as follows:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel8/$(uname -i)/cuda-rhel8.repo
Following the repository’s integration, installing the required dependencies is recommended. While some of these might already be installed, executing the command below ensures their presence:
sudo dnf install kernel-headers-$(uname -r) kernel-devel-$(uname -r) tar bzip2 make automake gcc gcc-c++ pciutils elfutils-libelf-devel libglvnd-opengl libglvnd-glx libglvnd-devel acpid pkgconfig dkmsOnce this is done, proceed to integrate the latest Nvidia drivers using the following:
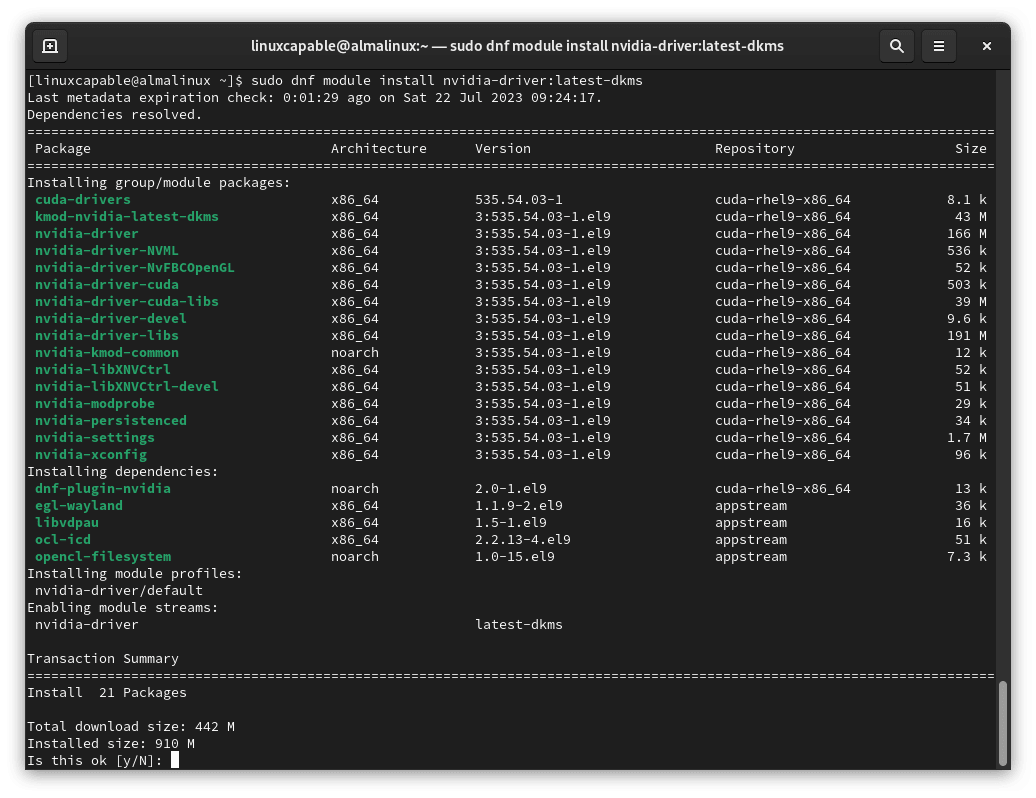
sudo dnf module install nvidia-driver:latest-dkmsAlternatively, Nvidia RPM modules can be listed using the command:
sudo dnf module list nvidia-driver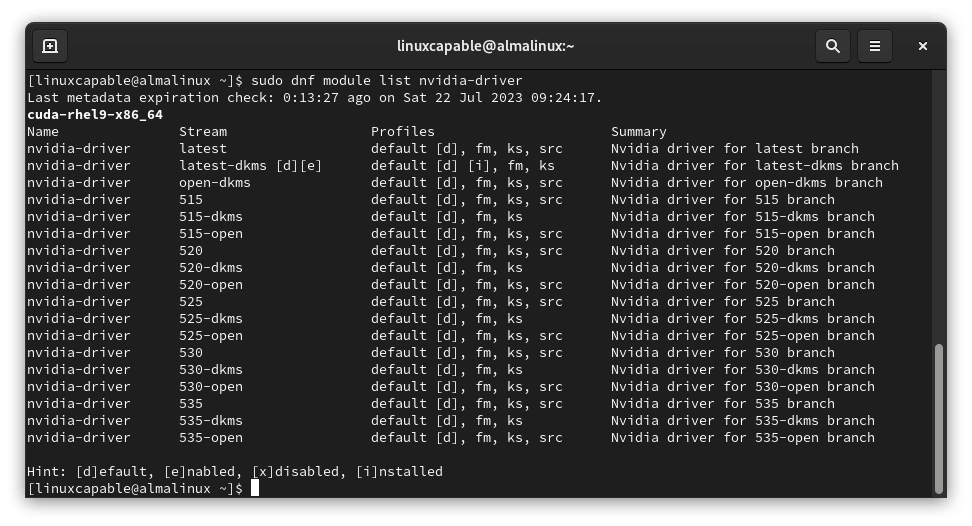
If you’re an open-source user, you might consider installing this module instead of the proprietary one. However, feedback suggests open-source users may run into bugs depending on the graphics card. If this happens, switch to the proprietary drivers, which typically resolves the issue.
For instance:
sudo dnf module install nvidia-driver:open-dkmsUpon successful completion, a system restart is necessary. Execute the command:
rebootVerifying the Nvidia Drivers Installation on AlmaLinux
Execution of the NVIDIA-SMI Command
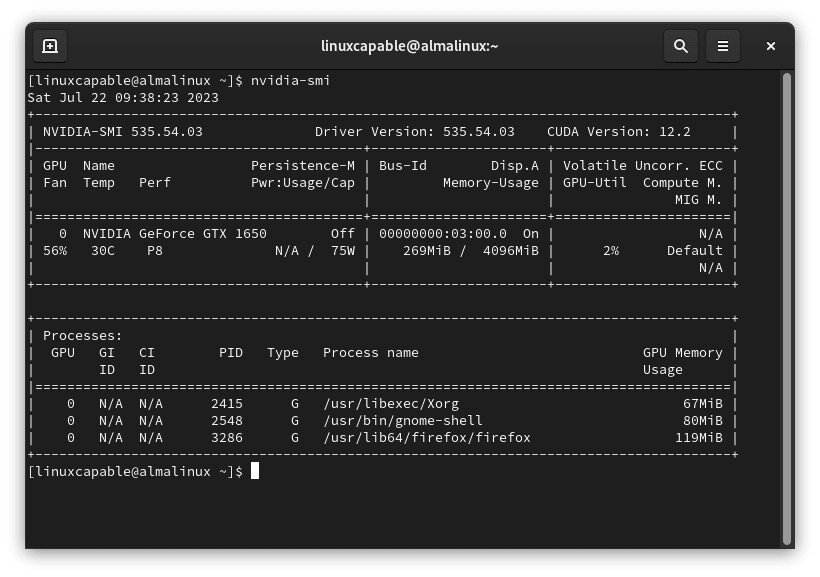
To confirm the successful installation of the Nvidia drivers, you need to execute the NVIDIA-SMI command. This command should produce an output that indicates a successful installation. You can run this command as follows:
nvidia-smiThe following is a placeholder for an image, giving you an example of what your output might look like upon a successful installation:
Accessing Nvidia Settings
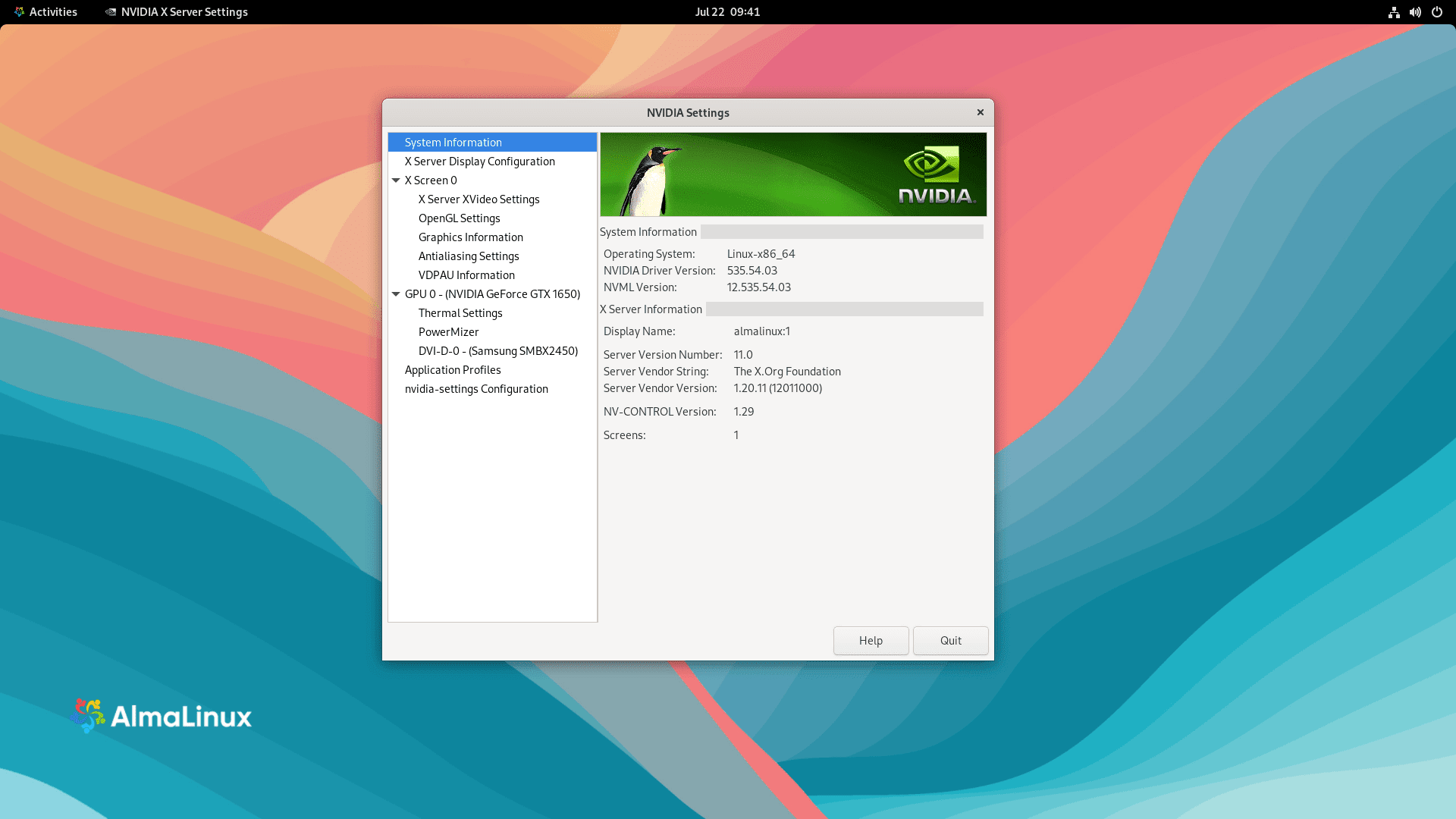
Another method for verifying the installation involves accessing the Nvidia settings graphical user interface (GUI). This can be done either from the application icon menu or by executing the following command:
nvidia-settingsLocating the GUI Application Icon
There’s also an option to verify the installation by locating the GUI application icon. You can achieve this by navigating the path Activities > Show Applications > NVIDIA X SERVER in the application menu.
Below is a placeholder for an image illustrating what a successful Nvidia driver installation should look like:
As of the time of writing this tutorial, NVIDIA 535 is the latest version. By installing directly from the Nvidia repository, you should see that this version is installed. However, remember that this version number may change quickly as time progresses, but the process remains the same.
Resolving Issues: Step-by-Step Guide to Troubleshooting
Handling Secure Boot Challenges with Nvidia Driver Installation
If you are experiencing problems due to Secure Boot after installing the Nvidia drivers, these steps may provide a resolution without requiring you to disable Secure Boot.
Disabling Nouveau Drivers
Conflicts may arise between Nouveau and Nvidia drivers. Therefore, you should prevent these conflicts by blacklisting Nouveau drivers. To do this, execute the following commands:
echo "blacklist nouveau" | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf
echo 'omit_drivers+=" nouveau "' | sudo tee /etc/dracut.conf.d/blacklist-nouveau.confUpon completing these modifications, regenerate all Dracut initramfs images and update the module dependency list using the following commands:
sudo dracut --regenerate-all --force
sudo depmod -aEnabling Secure Boot
If Secure Boot is enabled on your system, it’s necessary to import the Machine Owner Key (MOK) public key, which signs the Nvidia kernel module. To accomplish this, utilize the mokutil command as shown:
sudo mokutil --import /var/lib/dkms/mok.pubThe mokutil command will prompt you to create a password, which will be required when your system reboots.
Next, proceed to reboot your system:
sudo rebootDuring the reboot, your system may request key enrollment. Accept this request and input the password you generated with the mokutil command.
Validating the Driver Installation
To ascertain that the Nvidia drivers are successfully installed, execute the nvidia-smi command:
nvidia-smiTroubleshooting Post-Windows Update
A firmware update might reset the TPM chip in a dual-boot environment with Windows. In such a situation, you must re-import the Machine Owner Key (MOK). To rectify this, rerun the mokutil command:
sudo mokutil --import /var/lib/dkms/mok.pubThese instructions offer a detailed guide to troubleshooting and resolving any potential issues you may encounter while installing the Nvidia drivers on AlmaLinux.
Conclusion
Our exploration into installing Nvidia drivers on AlmaLinux has proven to be insightful. We have walked through the necessary steps, ensuring clarity at every stage, from verifying the Nvidia drivers’ successful installation to troubleshooting potential issues. This process enhances your system’s graphics capabilities and overall computing experience.
As a parting recommendation, remember to keep your drivers updated to ensure optimal performance. Regular updates typically offer enhancements and bug fixes, which can substantially increase your system’s stability and efficiency.