This guide will demonstrate how to install LibreOffice on Fedora Linux, offering a straightforward approach to leveraging this powerful office suite on your system. LibreOffice stands out as a free and open-source software, equipped with a comprehensive set of tools suitable for personal and professional use. Its compatibility with various file formats and user-friendly interface make it a preferred choice for many.
Below are some key features of LibreOffice:
- Versatility: Supports a wide range of document formats, including Microsoft Office files, making it highly adaptable in different work environments.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrates with the Linux environment, offering a stable and efficient experience.
- Customizability: Users can personalize their experience with numerous templates and extensions.
- Community Support: Backed by a strong community, providing regular updates and helpful resources.
In this guide, you’ll find a step-by-step process to get LibreOffice up and running on Fedora Linux. The steps are designed to be clear and concise, ensuring a smooth setup experience even for those new to Linux. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a fully functional LibreOffice suite, ready to handle all your document, spreadsheet, and presentation needs. Let’s dive into the installation process and explore the capabilities of LibreOffice on your Fedora system.
Install LibreOffice on Fedora Linux via Default Appstream
Step 1: Refresh Fedora Packages
Before installing LibreOffice on Fedora Linux, it’s crucial to ensure that all the packages on your system are up-to-date. This step helps in maintaining system stability and security.
Execute the command below in your terminal to refresh and upgrade the packages:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshThis command combines two actions: ‘upgrade’ updates all installed packages to their latest versions, and ‘–refresh’ forces the system to ignore its cache and check for new updates directly from the repositories.
Step 2: Install LibreOffice via DNF Command
After updating the system packages, the next step involves installing LibreOffice. Fedora’s official repository, known for its stability and regular updates, hosts the LibreOffice package.
To install LibreOffice, use the following command in the terminal:
sudo dnf install libreofficeThis command instructs DNF, Fedora’s package manager, to install the LibreOffice suite. DNF automatically handles dependencies and installs all necessary components of LibreOffice, ensuring a seamless installation process.
Install LibreOffice on Fedora Linux via Direct Download
Step 1: Obtain LibreOffice RPM Archive on Fedora
Access the LibreOffice Download page to find the necessary download links. Use a command like wget to download the latest version of LibreOffice.
For instance, to download LibreOffice 7.6.4, use:
wget https://download.documentfoundation.org/libreoffice/stable/7.6.4/rpm/x86_64/LibreOffice_7.6.4_Linux_x86-64_rpm.tar.gzAlways check for the most recent download link, as the URL provided here may frequently change.
Step 2: Unpack the Downloaded LibreOffice Archive
Once the download completes, extract the LibreOffice package with the command:
tar xvf LibreOffice_*_Linux_x86-64_rpm.tar.gzThis command will decompress the file and ready it for installation.
Step 3: Transition to the Extracted Folder
Change to the directory containing the extracted RPM files:
cd LibreOffice*/RPMS/
This step is crucial to ensure that the installation commands are executed in the correct directory.
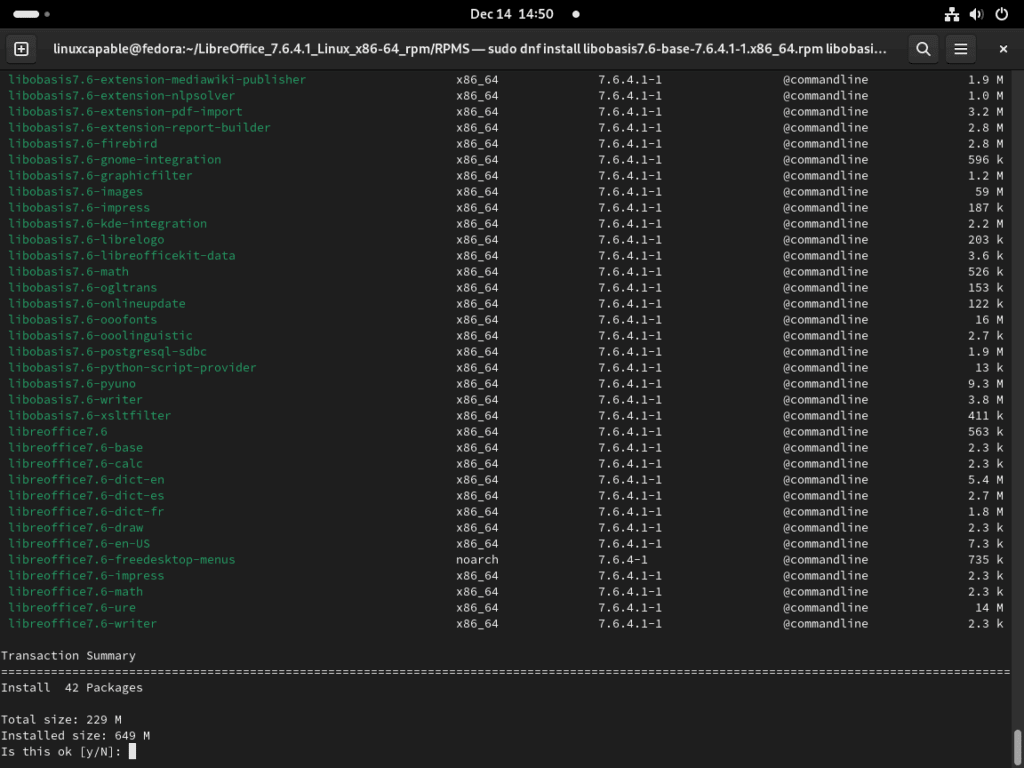
Step 4: Install LibreOffice RPM via DNF Command
First, remove any pre-installed LibreOffice versions to avoid conflicts. This can be done with:
sudo dnf remove libreofficeThen, install the latest version of LibreOffice that you’ve downloaded:
sudo dnf install *.rpmThis command will install all RPM files in the current directory, effectively setting up the latest version of LibreOffice on your Fedora system.
Install LibreOffice on Fedora Linux via Flatpak and Flathub
Step 1: Activate Flathub Repository for LibreOffice
Begin by integrating the Flathub repository with Flatpak on your Fedora system. This is essential for accessing LibreOffice through Flatpak.
Execute the command below in your terminal:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoThis command registers the Flathub repository with your Flatpak package manager, allowing you to install LibreOffice and other Flatpak applications from Flathub.
Step 2: Implement LibreOffice Installation via Flatpak
Proceed to install LibreOffice using the following Flatpak command:
flatpak install flathub org.libreoffice.LibreOfficeThis command fetches and installs LibreOffice from Flathub. Depending on your internet speed, the download and installation process may vary in duration.
Troubleshooting: Addressing Flatpak Installation Issues
In cases where you encounter an error like:
"error: Unable to load summary from remote flathub: Can't fetch summary from disabled remote 'flathub,"You can fix this by re-enabling the Flathub repository with the command:
flatpak remote-modify --enable flathubThis action reactivates the Flathub repository, solving the issue and allowing the installation of LibreOffice to continue successfully.
Starting LibreOffice on Fedora Linux
CLI Commands to Launch LibreOffice
If you’ve just finished installing LibreOffice and your terminal is still open, you can start LibreOffice immediately. The command varies slightly depending on your installation method.
For installations done through Fedora’s repository or manually with RPMs, use:
libreofficeFor LibreOffice installations via Flatpak, the command changes to:
flatpak run org.libreoffice.LibreOfficeGUI Method to Launch LibreOffice
After installing LibreOffice, you can also launch it through Fedora’s graphical interface:
- Click on the “Activities” button, located in the top-left corner of your desktop.
- In the search bar that appears, type “LibreOffice” and press Enter.
- The search results will display the LibreOffice suite along with its individual components.
- Choose the desired application or the entire suite to launch by clicking on it.
First-Time Tips with LibreOffice on Fedora Linux
Now that you have successfully installed LibreOffice on Fedora, it’s time to delve into the nuances of this powerful suite. Tailored for the Fedora environment, these tips are crafted to elevate your productivity and user experience, specifically focusing on aspects unique to the Linux version of LibreOffice.
General Tips for Optimizing LibreOffice on Fedora
- Familiarize with the Interface: Spend some time exploring the LibreOffice interface. Although it might look overwhelming at first, understanding where each tool is located can significantly streamline your workflow.
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Learning and customizing keyboard shortcuts can drastically improve efficiency. LibreOffice allows you to set your own shortcuts, which can be a great timesaver.Example: To customize shortcuts, navigate to
Tools > Customize > Keyboard. - Use Styles and Formatting: LibreOffice’s powerful styling options can help maintain consistency in your documents. Familiarize yourself with the Styles and Formatting sidebar (
F11) for quick formatting options.
Customization Tips for a Personal Touch
- Theme and Icon Customization: Personalize your LibreOffice experience by selecting a theme that suits your taste. You can change the icon style under
Tools > Options > View. - Template Usage and Creation: Templates can significantly speed up document creation. Explore the pre-installed templates or create your own for repeated use.Example: To create a template, design a document as usual, then save it as a template via
File > Templates > Save As Template. - Extension Installation: Enhance LibreOffice’s functionality by installing extensions. Visit the LibreOffice Extension Center for a range of tools that can add extra features to your suite.Note: Ensure the compatibility of extensions with your version of LibreOffice and Fedora.
Other Essential Tips
- File Compatibility: While LibreOffice offers excellent compatibility with various file formats, always double-check formatting when sharing files with users of other office suites, especially for complex documents.
- Regular Backups: Make it a habit to back up important documents regularly. While this is a general tip, it’s particularly crucial when adjusting to a new software environment.
- Explore Calc and Impress: Don’t limit yourself to Writer. LibreOffice’s spreadsheet and presentation tools, Calc and Impress, are equally robust and offer many features tailored for Linux users.
- Utilize LibreOffice Help: The built-in help system is a valuable resource. It’s specifically tailored for Linux users and can be accessed by pressing
F1or navigating toHelp > LibreOffice Help.
Managing LibreOffice on Fedora Linux
Remove LibreOffice From Fedora
DNF Method to Remove LibreOffice
For users who installed LibreOffice using the RPM method or Fedora’s official repository, the removal process involves a simple command. Execute the following in your terminal:
sudo dnf remove libreoffice*This command uninstalls LibreOffice from your system. It is recommended to run this command if you wish to clear up space or install a different version of LibreOffice.
Flatpak Method to Remove LibreOffice
In cases where LibreOffice was installed using Flatpak, the removal process differs slightly. Use this command:
flatpak uninstall --delete-data org.libreoffice.LibreOfficeExecuting this command will not only uninstall LibreOffice but also remove all related data and configuration files. This is particularly useful when you want a clean removal without leaving behind any residual files.
Final Thoughts
In this guide, we’ve navigated through the straightforward yet crucial steps of installing, launching, and managing LibreOffice on Fedora Linux. Whether you chose the direct RPM method, Fedora’s repository, or Flatpak for installation, each route was tailored to ensure an efficient setup. Our journey didn’t just stop at installation; we also covered how to smoothly launch LibreOffice and, when necessary, cleanly remove it from your system.
Remember, keeping your software updated and opting for the installation method that best suits your needs is key. Most importantly, don’t hesitate to explore and make the most out of LibreOffice’s robust features on your Fedora system.