This guide will demonstrate how to install Microsoft Edge on Fedora Linux using the command-line terminal with either the DNF package manager with the Microsoft Edge RPM or with Flatpak and Flathub.
Microsoft Edge, the modern web browser from Microsoft, has made significant strides since its inception, offering a plethora of features that cater to efficiency, security, and compatibility. It stands out as a robust choice for users seeking an alternative to traditional browsers on Linux platforms. Let’s delve into the key attributes that make Microsoft Edge a noteworthy contender in the browser space:
Here are some compelling features of Microsoft Edge:
- Performance: Optimized for speed, Edge ensures swift page loading, smoother browsing, and less lag time.
- Security: With state-of-the-art security features, Edge provides robust protection against phishing and malware.
- Compatibility: Edge supports a wide array of web standards, ensuring websites render correctly and consistently.
- Cross-Platform: Available on various platforms, Edge allows for seamless synchronization of bookmarks, passwords, and settings across devices.
- Extensions: A vast library of extensions enhances functionality and personalizes the browsing experience.
- Privacy Controls: Comprehensive privacy settings give users control over their data and browsing activities.
- Integration: Edge offers deep integration with Microsoft services, enhancing productivity and convenience.
- Innovation: Constant updates bring cutting-edge features and improvements, keeping Edge at the forefront of browser technology.
These attributes underscore why Microsoft Edge is an excellent choice for users looking to enrich their web experience on Fedora Linux.
Now, let’s transition to the technical aspects of installing Microsoft Edge on Fedora Linux.
Install Microsoft Edge on Fedora via Microsoft RPM
Update the Fedora Packages Before Microsoft Edge Installation
Before jumping in, ensuring your system is up-to-date is good practice. This step avoids potential conflicts and ensures a smooth installation process. Open your terminal and execute the following command:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshImport Microsoft RPM Repository
Before we install Microsoft Edge, we need to add its official repository to our system. However, we should import the GPG key for the RPM packages before doing so. This key verifies the authenticity and integrity of the packages we’ll install, adding an extra layer of security. To import the GPG key, run this command:
sudo rpm --import https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.ascThis command downloads and imports the Microsoft GPG key used to sign the RPM packages for Microsoft Edge. It ensures the packages are genuine and haven’t been tampered with.
Next, we will add the Microsoft RPM repository to our system. Use the following command to do so:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo https://packages.microsoft.com/yumrepos/edgeYou should see the output confirming the addition of the repository as below:
Adding repo from: https://packages.microsoft.com/yumrepos/edgeSelect Microsoft Edge Browser Version Installation
The introduction notes that Microsoft Edge offers three versions: stable, beta, and developer. Each serves a different need. The stable version provides a well-tested and reliable user experience. The beta version allows users to experiment with upcoming features but may not be as stable. The developer version is for those who don’t mind living on the Edge, using the newest (potentially unstable) features.
Option 1: Install Microsoft Edge stable build (Recommended)
For most users, we recommend installing the stable version of Microsoft Edge, which you can do using this command:
sudo dnf install microsoft-edge-stableYou can verify the version and build of Microsoft Edge installed on your system using the following command:
microsoft-edge -versionOption 2: Install Microsoft Edge Beta or Dev builds
Those interested in previewing upcoming features can install the beta or developer versions of Microsoft Edge. However, remember that these versions may have bugs and aren’t recommended for daily use. To install these versions, use the following commands:
Microsoft Edge Beta:
sudo dnf install microsoft-edge-betaMicrosoft Edge Dev:
sudo dnf install microsoft-edge-devRemember that installing these versions won’t replace your stable Microsoft Edge. They will be installed as separate applications.
You can check the versions of these installations with the following commands:
microsoft-edge-beta --versionmicrosoft-edge-dev --versionInstall Microsoft Edge on Fedora Linux via Flatpak and Flathub
There are multiple ways to accomplish any task in the world of Linux. In our case, there’s an alternative to the DNF package manager for installing Microsoft Edge on Fedora Linux: Flatpak in conjunction with Flathub. Flatpak, a software utility for application sandboxing and distribution, is an excellent way to access the most recent versions of various software. It serves as an efficient distribution framework for Linux. When used alongside Flathub, an extensive app store, and repository for Linux, it’s a method that many Fedora users may find quite convenient.
Activating the Flathub Repository for Microsoft Edge
Before installing Microsoft Edge, we must ensure your system’s Flathub repository is active. Flathub hosts a wide variety of applications, including Microsoft Edge. To add the Flathub repository to your system, you’ll need to run the following command in your terminal:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoThe flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists command checks if the Flathub repository is already present in your Flatpak configuration. If not, it adds the repository, giving you access to many applications available on Flathub. This is a crucial step in preparing your system for installing Microsoft Edge via Flatpak and Flathub.
Install Microsoft Edge via Flatpak Command
With the Flathub repository active on your system, we’re all set to install Microsoft Edge using the Flatpak package manager. Unlike the previous method that used the DNF package manager and Microsoft’s DNF repository, we can only install the stable and developer versions of Microsoft Edge via Flatpak. However, both versions can be installed side by side.
To install the stable version of Microsoft Edge, use the following command:
flatpak install flathub com.microsoft.Edge -yFor those looking to explore the latest features and improvements of Microsoft Edge, you can install the developer version using the following command:
flatpak install flathub com.microsoft.EdgeDev -yIf you encounter an error message reading, “error: Unable to load summary from remote flathub: Can’t fetch summary from disabled remote ‘flathub’,” it signifies that the Flathub repository is disabled on your system. To resolve this issue, you’ll need to enable the Flathub repository with the following command:
flatpak remote-modify --enable flathubAfter enabling the Flathub repository, try installing Microsoft Edge using the previous
Launch Microsoft Edge Browser on Fedora
You can launch the browser and explore its features after successfully installing Microsoft Edge on your Fedora Linux system using the DNF or Flatpak method. Depending on your comfort level, different methods exist to launch the Microsoft Edge browser using a command-line or graphical user interface (GUI).
Launching Microsoft Edge from the Command Line on Fedora
The terminal or command-line interface can be a powerful tool for managing and controlling your system, offering direct control over your software and files. Here, we provide the command-line instructions for launching Microsoft Edge.
DNF Method of launching Microsoft Edge
To launch the stable version of Microsoft Edge from your terminal, you can execute the following command:
microsoft-edgeIf you’ve installed the Beta or Developer versions of Microsoft Edge, you can also launch these versions using the respective commands:
microsoft-edge-betamicrosoft-edge-devFlatpak Method of launching Microsoft Edge
If you used the Flatpak method to install Microsoft Edge, you can run the following commands to launch the stable and Developer versions, respectively:
flatpak run com.microsoft.Edgeflatpak run com.microsoft.EdgeDevLaunching Microsoft Edge from the GUI on Fedora
Not all users are comfortable or familiar with using a command-line interface, and that’s perfectly fine. Fedora’s desktop environment provides a user-friendly graphical interface for managing your installed software.
To launch Microsoft Edge from the GUI, you can follow these steps:
- Click on Activities, located at the top left corner of your desktop.
- Click on Show Applications. This option is usually represented by a grid of dots at the bottom of the sidebar.
- Locate the Microsoft Edge icon. You can also use the search bar to type in “Microsoft Edge” to find the application quickly.
- Click on the Microsoft Edge icon to launch the browser. If you’ve installed multiple versions (stable, beta, or dev), click on the correct icon for the version you wish to use.
First-Time Setup Wizard on Microsoft Edge with Fedora
Upon launching Microsoft Edge for the first time, you’ll be greeted with an introductory screen designed to facilitate the initial setup and personalization of your browsing experience. This configuration process is straightforward and user-friendly, ensuring your browser is set up to meet your needs best.
The Welcome Screen
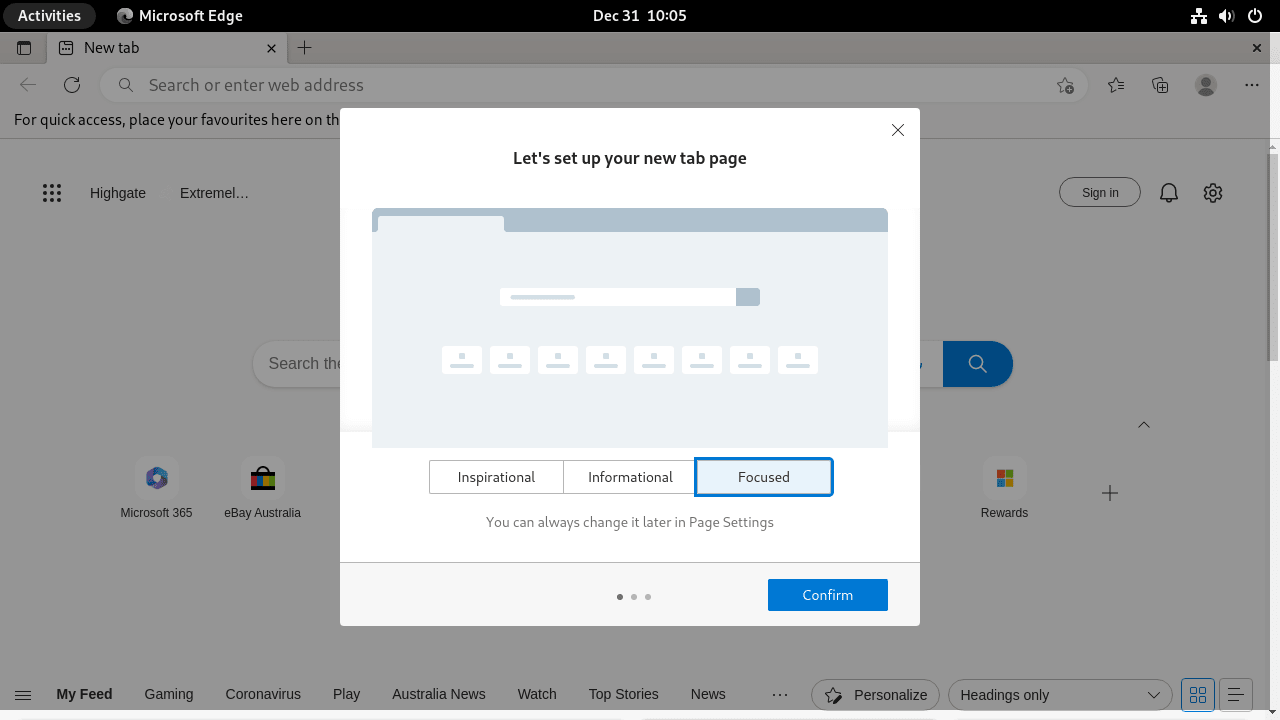
When you first open Microsoft Edge, a welcome screen will be presented. This screen is intended to help you understand some of the critical features of the browser and guide you through the initial configuration process.

The welcome screen may include options to customize your privacy settings, set up your new tab page, and import bookmarks from your previous browser.
Account Sign-In and Synchronization
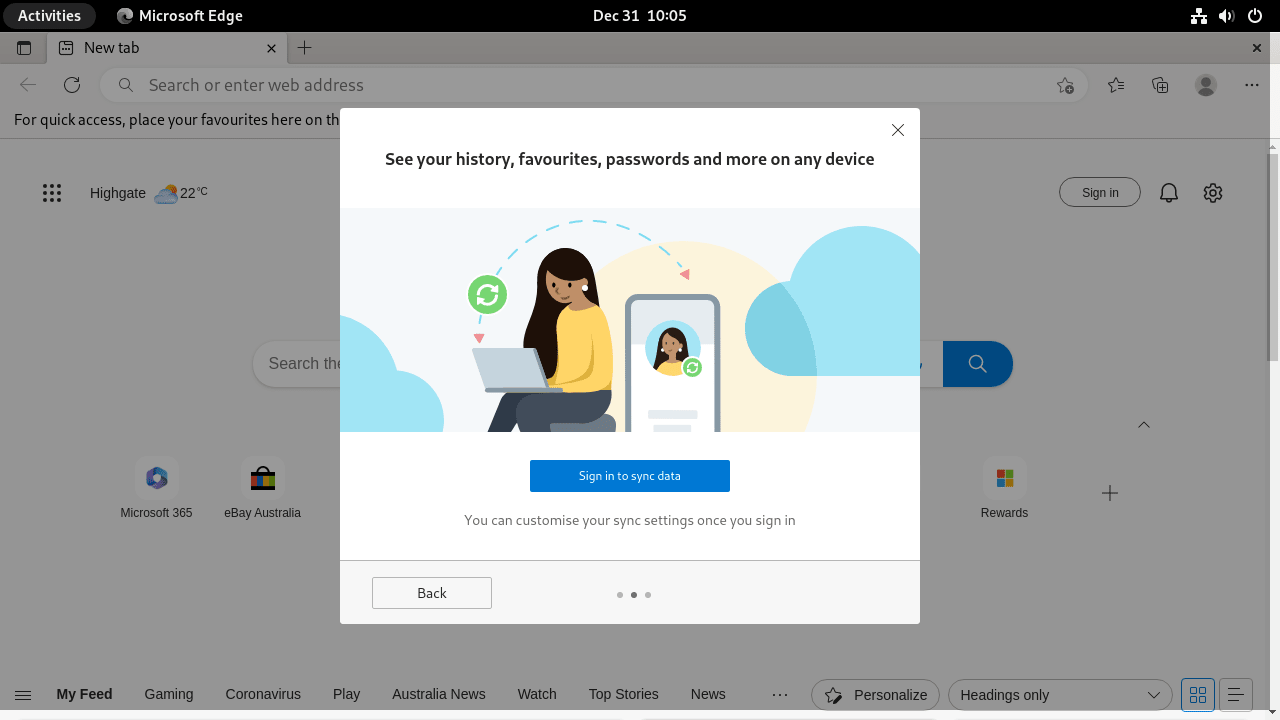
Microsoft Edge offers a synchronization feature that allows you to access your browsing history, bookmarks, extensions, and more across multiple devices. This is particularly useful if you use multiple computers or other devices and want to maintain a consistent browsing experience.
The sign-in screen will appear as follows:
You will be prompted to sign in with your Microsoft account to enable this feature. If you don’t have an account, you’ll have the option to create one.
However, you can continue without signing in if you do not wish to synchronize your browser data across devices. This can be done by clicking “X” in the pop-up window’s upper right corner.
Finalizing Your Configuration
Once you’ve navigated through the welcome screen and decided on the synchronization option, your initial setup of Microsoft Edge is complete. You’re ready to explore the web with your newly installed browser.
Congratulations! You have successfully configured Microsoft Edge on your Fedora Linux system.

First-Time Tips with Microsoft Edge with Fedora
When using the Microsoft Edge browser on Fedora Linux, there are several tips and features you should be aware of to enhance your browsing experience. Here, we’ll outline some general advice, customization tips, and additional pointers to help you get the most out of your new browser.
General Microsoft Edge Tips
Microsoft Edge is packed with several features designed to streamline your browsing. Understanding these features can make your browsing experience more effective and enjoyable.
- Incognito Mode: Just like other browsers, Microsoft Edge also provides an Incognito Mode, known as InPrivate mode. This feature ensures that browsing data, such as cookies and history, are not saved once you close the browser. To access it, you can use the
Ctrl+Shift+Nshortcut. - Reading View: If you’re reading an article or blog post and want a cleaner view without ads or other distracting elements, Microsoft Edge’s Reading View can be beneficial. Click the book icon in the address bar or press
Ctrl+Shift+Rto activate it. - Developer Tools: Microsoft Edge offers a robust suite of developer tools. Access them by pressing
F12or right-clicking on a webpage and selecting ‘Inspect Element’. These tools are essential for web developers for debugging and website testing. - Favorites: Organize your most visited sites using the Favorites feature. Click the star icon on the address bar to add a website to your Favorites.
Microsoft Edge Customization Tips
Microsoft Edge provides various customization options that let you tailor your browsing experience to your preferences.
- Choose Your Theme: Microsoft Edge allows you to select between a light and a dark theme. You can change this by going to
edge://settings/appearance. - New Tab Customization: You can customize what you see when you open a new tab. Go to
edge://settings/onStartupto set your preference. - Extensions: Enhance your browsing capabilities by adding extensions. Microsoft Edge supports many extensions available on the Microsoft Store and even the Chrome Web Store.
Other Microsoft Edge Tips
Here are a few additional tips to enhance your browsing experience with Microsoft Edge on Fedora Linux.
- Update Regularly: Regularly updating your browser ensures you have the latest features and security patches. Microsoft Edge will automatically update itself, but you can also manually check for updates by going to
edge://settings/help. - Privacy Settings: Microsoft Edge offers flexible privacy settings, allowing you to choose what data is collected. Review these settings by going to
edge://settings/privacy.
By implementing these tips, you can customize and optimize your browsing experience on Microsoft Edge.
Managing Microsoft Edge with Fedora
When using Microsoft Edge on Fedora Linux, there may come a time when you need to uninstall the browser from your system. Whether transitioning to a new browser or simply wanting to declutter your digital space, the process is straightforward and can be executed with a few commands.
DNF Remove Commands for Microsoft Edge
If you’ve used the DNF package manager to install Microsoft Edge, it can also remove the browser from your system. Here’s how to do it:
For the stable version, use the following command:
sudo dnf remove microsoft-edgeFor the Beta version, you can use:
sudo dnf remove microsoft-edge-betaAnd if you’ve installed the Developer version, execute the following:
sudo dnf remove microsoft-edge-stable-devRemoving the associated repositories is also recommended if you’ve decided to cut ties completely with Microsoft Edge and have no intention of reinstalling it later. However, note that if you wish to reinstall Microsoft Edge later, you will have to re-import these repositories and follow the installation steps again.
To remove the repositories, use this command:
sudo rm /etc/yum.repos.d/microsoft-edge*It’s important to note that executing these commands will remove all three versions of the Microsoft Edge repositories from your system. If you only want to remove the Beta or Developer version while retaining the stable one, you must modify the commands accordingly. Otherwise, the stable version will not receive any necessary updates.
Flatpak Remove Commands for Microsoft Edge
The removal process is slightly different if you install Microsoft Edge using Flatpak. Here’s how to uninstall the stable version of Microsoft Edge:
sudo flatpak uninstall com.microsoft.EdgeAnd for the Developer version:
sudo flatpak uninstall com.microsoft.EdgeDevConclusion
We’ve walked through the steps to install Microsoft Edge on Fedora Linux, highlighting the simplicity and versatility of the process, whether using DNF or Flatpak. Now that you’ve got Edge up and running, dive in and explore its rich features – from enhanced security to seamless cross-platform integration. Give those extensions a whirl and tweak the privacy settings to your liking. Remember, staying updated with the latest version will keep your browsing experience smooth and secure. Happy browsing!

