Since its inception in 2008, Google Chrome has emerged as a leading web browser, capturing over 60% of the global market share. Renowned for its cutting-edge design and rapid performance, this guide will elucidate the steps to install Google Chrome on Linux Mint 21 or the older stable release of Linx Mint 20.
Before we dive into the main article, for users curious as to why Google Chrome is the most popular browser, this has much to do with the Chromium engine, an open-source framework also utilized by browsers like Microsoft Edge and Brave. While Linux Mint defaults to Firefox, there are compelling reasons to consider Google Chrome:
Key Features of Google Chrome:
- Optimized Performance: Especially beneficial for web applications and online gaming.
- Intuitive Interface: A modern, user-centric layout.
- Robust Security: Features like safe browsing and sandboxing protect users from threats.
- Personalization: Tailor Chrome with themes, extensions, and apps from the Chrome Web Store.
- Seamless Synchronization: Effortless syncing of bookmarks and settings across devices.
- Integrated Google Services: Enhances the browsing experience.
- Efficient Bookmark Management: Equipped with tagging and description features for easy organization.
This guide now proceeds to detail the steps to install Google Chrome on Linux Mint 21 or Linux Mint 20 using the command line terminal, covering various installation methods.
Import Google Chrome APT Repository on Linux Mint 21 or 20
Step 1: Update Linux Mint Before Google Chrome Installation
Start by updating your system to ensure that all packages are current. This step is essential because installing the latest software updates on your system can help prevent potential compatibility issues when installing Google Chrome. It also helps to ensure a smooth and problem-free installation process.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeStep 2: Install Initial Packages for Google Chrome Installation
Next, you need to install the following packages. Execute this command to do so. It’s important to note that these are common dependencies that may already be installed on your system.
sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl -yStep 3: Import Google Chrome APT Repository on Linux Mint
The initial step in installing Google Chrome involves importing the GPG key for the digital signature. Without this crucial step, the installation will not be completed successfully.
curl -fSsL https://dl.google.com/linux/linux_signing_key.pub | sudo gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/google-chrome.gpg >> /dev/nullUpon successfully importing the GPG key, you must import the Google Chrome repository.
echo 'deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/google-chrome.gpg] http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main' | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.listStep 4: Refresh APT Index After Google Chrome Repository Import
The final step in importing the Google Chrome repository involves updating the repository list with the “apt update” command to incorporate the new additions to the apt sources list.
sudo apt updateInstall Google Chrome on Linux Mint 21 or 20 via APT Command
Step 1: Install Google Chrome Browser – stable build
Now that the Google Chrome repository has been imported, it is recommended that all users install the stable edition of Google Chrome. This is the preferred choice because the stable edition is thoroughly tested and deemed the most reliable and secure version for general use.
sudo apt install google-chrome-stableStep 2: Install Alternative Google Chrome Browser builds on Linux Mint
As an alternative, you can choose to install the Google Chrome Beta or the Unstable version. It is important to note that these versions are not recommended for regular, daily use, particularly not on a primary desktop or production server. However, they may appeal to tech-savvy individuals looking to try out new features and are comfortable with potential instability.
Use one of the following commands in your terminal to install the beta or unstable version of Google Chrome.
sudo apt install google-chrome-betasudo apt install google-chrome-unstableIt is possible to install all three branches of Google Chrome, as they each have separate installations. However, you will need to delete the imported sources.list file imported by Google, which is explained in the Additional Tips section at the end of the guide.
Launch Google Chrome on Linux Mint 21 or 20
With Google Chrome installed, you can launch the browser using the appropriate command in your terminal. You have the option to launch the stable, beta, or unstable version of Google Chrome by using one of the following commands:
google-chrome-stablegoogle-chrome-betagoogle-chrome-unstableMost desktop users can launch the browser by navigating to the application icon through the following path. It’s important to note that the exact location may vary based on the desktop environment that was initially installed.
Taskbar > Internet > Google Chrome {version}
Upon opening Google Chrome for the first time, you will encounter a pop-up asking you to create a password for the keychain. Additionally, Google Chrome will ask if you want to set it as the default browser for your desktop and if you consent to send data back to Google.
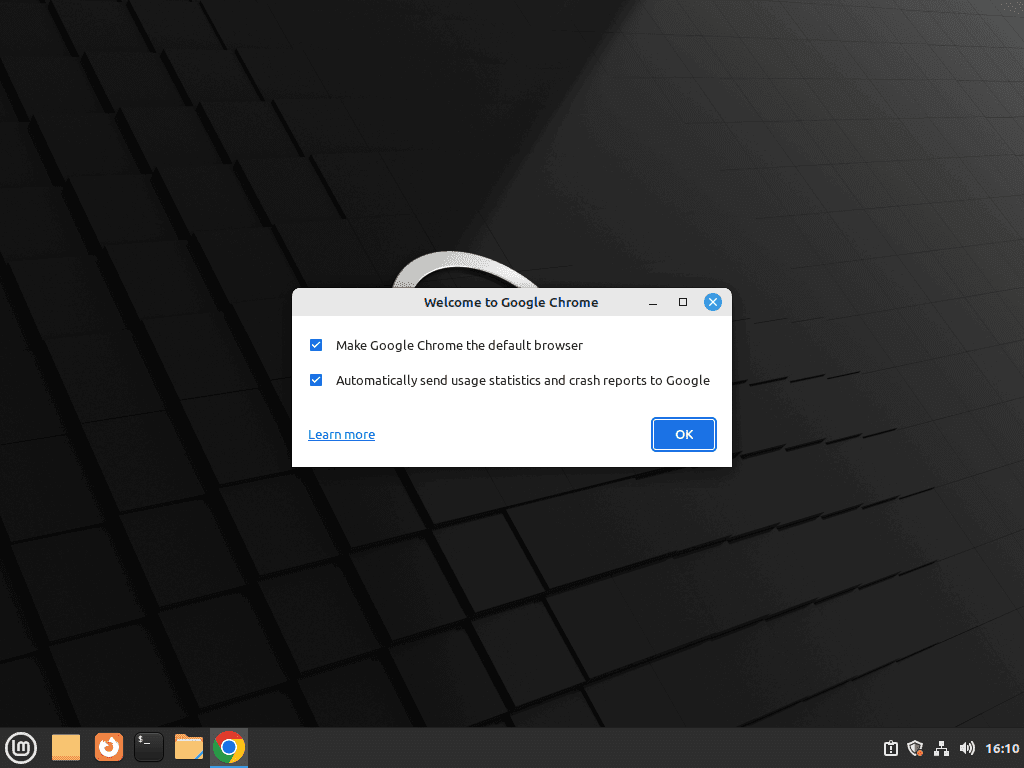
When presented with the option to make Google Chrome the default browser over the typical default, Firefox, you can either uncheck this option or leave it as is. You will also have the option to allow Google to receive data and crash reports. Click the “OK” button to proceed.
The next step will be to sign in to Google Chrome, but you can skip this step. If you skip, click the “X” in the Chrome browser tab.
First-Time Tips with Google Chrome on Linux Mint 21 or 20
After installing Google Chrome on Linux Mint, a vast world of features and capabilities await you. For those new to Google Chrome, the following tips can provide valuable insights into getting started and making the most of your browsing experience.
Sync with a Google Account on Google Chrome with Linux Mint
New to Chrome? Consider syncing with a Google Account. This will:
- Synchronize bookmarks, history, extensions, and more across devices.
- Provide access to saved passwords and payment methods.
- Allow you to resume browsing sessions from other devices.
Google Chrome Keyboard Shortcuts to Enhance Efficiency on Linux Mint
Utilize Chrome’s powerful keyboard shortcuts for a more efficient browsing experience:
- Ctrl + L: Highlight the URL in the address bar.
- Ctrl + T: Open a new tab.
- Ctrl + W: Close the current tab.
- Ctrl + Shift + N: Open a new incognito window.
- Ctrl + Shift + T: Re-open the last closed tab.
Customize Your Google Chrome on Linux Mint
Personalize your Chrome experience:
- Themes: Visit the Chrome Web Store to find a wide range of themes that can change the appearance of your browser.
- Extensions: Enhance functionality with extensions from the Chrome Web Store. Examples include ad-blockers, password managers, and productivity tools.
Set Up Google Chrome Bookmarks with Linux Mint
Frequent a lot of websites? Set up bookmarks for easy access:
- Use the star icon in the address bar to add bookmarks quickly.
- Right-click on the bookmarks bar to create folders and organize your bookmarks.
Dive into Google Chrome Settings on Linux Mint
Explore the settings panel to:
- Adjust privacy settings to control what data Chrome saves.
- Customize the appearance, including font size and zoom levels.
- Manage passwords, payment methods, and addresses.
Use the Google Chrome Built-In Task Manager on Linux Mint
If you ever feel Chrome is slowing down:
- Press Shift + Esc to bring up Chrome’s Task Manager. It displays information about each tab and extension, including memory and CPU usage.
Google Chrome Privacy with Incognito Mode on Linux Mint
For more private browsing sessions, use Incognito Mode:
- No browsing history, cookies, or search history are saved.
- Access it via Menu > New Incognito Window or Ctrl + Shift + N.
Additional Commands for Google Chrome on Linux Mint 21 or 20
Update Google Chrome on Linux Mint
It is essential to regularly check for updates of Google Chrome using the terminal, as the GUI update notifications may not always effectively update the browser. To ensure you have the latest version, run your terminal’s “apt update” and the “apt upgrade” commands.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeUninstall (Remove) Google Chrome on Linux Mint
To uninstall the Google Chrome browser, use the following command if you no longer want to use the stable version.
sudo apt remove google-chrome-stable --purgeUse the following commands to remove the beta or unstable version of Google Chrome.
sudo apt remove google-chrome-beta --purgesudo apt remove google-chrome-unstable --purgeTo altogether remove the Google Chrome repository that was previously imported, execute the following set of commands.
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.listTroubleshooting Tips with Google Chrome on Linux Mint 21 or 20
Google Chrome Multiple Sources.list on Linux Mint
When installing all three editions of Google Chrome (stable, beta, and unstable), it’s important to note that each one will create its own separate sources list in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory. This can cause a conflict when using the apt update command as multiple sources.list files for Google Chrome will exist, and the system will ignore some of them.
Example of the error you may have in your terminal:
W: Target Packages (main/binary-amd64/Packages) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target Packages (main/binary-all/Packages) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target Translations (main/i18n/Translation-en_AU) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target Translations (main/i18n/Translation-en) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target DEP-11 (main/dep11/Components-amd64.yml) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target DEP-11 (main/dep11/Components-all.yml) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target CNF (main/cnf/Commands-amd64) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target CNF (main/cnf/Commands-all) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target Packages (main/binary-amd64/Packages) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target Packages (main/binary-all/Packages) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target Translations (main/i18n/Translation-en_AU) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target Translations (main/i18n/Translation-en) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target DEP-11 (main/dep11/Components-amd64.yml) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target DEP-11 (main/dep11/Components-all.yml) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target CNF (main/cnf/Commands-amd64) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target CNF (main/cnf/Commands-all) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target Packages (main/binary-amd64/Packages) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target Packages (main/binary-all/Packages) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target Translations (main/i18n/Translation-en_AU) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target Translations (main/i18n/Translation-en) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target DEP-11 (main/dep11/Components-amd64.yml) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target DEP-11 (main/dep11/Components-all.yml) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target CNF (main/cnf/Commands-amd64) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target CNF (main/cnf/Commands-all) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.list:3
W: Target Packages (main/binary-amd64/Packages) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target Packages (main/binary-all/Packages) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target Translations (main/i18n/Translation-en_AU) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target Translations (main/i18n/Translation-en) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target DEP-11 (main/dep11/Components-amd64.yml) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target DEP-11 (main/dep11/Components-all.yml) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target CNF (main/cnf/Commands-amd64) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
W: Target CNF (main/cnf/Commands-all) is configured multiple times in /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list:3 and /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.list:3
So when installing Google Chrome from the source you imported from this guide, the beta and developer installations added extra sources, so, for example, you can remove these with the following command.
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-beta.list
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome-unstable.listOr remove all Chrome repositories.
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome*Then, re-add the one repository.
echo deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/google-chrome.gpg] http://dl.google.com/linux/chrome/deb/ stable main | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/google-chrome.listRemember to run an APT update.
sudo apt updateThis should fix the issue in the future, and you will still receive updates for all three browsers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, installing Google Chrome on Linux Mint is a simple process that requires adding the Chrome repository, updating the package manager, and finally installing the Google Chrome browser. Users can choose to install the stable version of Google Chrome, recommended for daily use, or the beta or developer versions for those who want to live on the edge. It is also essential to check for updates frequently and to remove any extra sources that may cause conflicts in the /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ directory. With simple steps, users can enjoy a seamless browsing experience with Google Chrome on Linux Mint.


