Vivaldi browser, crafted by Vivaldi Technologies, emerges as a vibrant alternative to the default Firefox Extended Support Release (ESR) familiar to Debian users. Boasting a wealth of customization options and distinctive features, Vivaldi presents itself as an enticing option for those desiring Firefox ESR. This guide will delve into Vivaldi’s standout attributes before illustrating how to install Vivaldi Browser on Debian 12 Bookworm or the older stable releases of Debian 11 Bullseye or Debian 10 Buster.
Vivaldi’s Distinct Advantages Over Firefox ESR:
- Tailored Experience: Vivaldi’s extensive customization capabilities, from themes to toolbars, offer a personalized browsing experience, contrasting with Firefox ESR’s more rigid setup.
- Enhanced Tab Management: Features like tab stacking, hibernation, and split-screen views in Vivaldi provide users with superior tab organization and navigation, a step up from Firefox ESR’s basic tab functionalities.
- Integrated Utilities: Vivaldi equips users with built-in tools such as note-taking, image capture, and a handy sidebar. In contrast, Firefox ESR necessitates additional extensions for similar features.
- Optimized Performance: Vivaldi’s adaptive interface and background tab hibernation ensure efficient resource usage, making it preferable for systems with constrained resources.
- Robust Privacy Measures: Vivaldi’s commitment to user privacy is evident in its non-tracking stance and integrated ad and tracker blockers. While Firefox ESR also champions privacy, Vivaldi’s approach resonates with many users.
- Regular Updates: Vivaldi’s rapid release cycle ensures users always have access to the latest features, contrasting with Firefox ESR’s less frequent update schedule.
Given its myriad features and user-centric approach, Vivaldi is a top choice for Debian users seeking a modern and customizable browsing experience. Now, let’s move on to installing the browser on your desktop.
Import Vivaldi APT Repository on Debian 12, 11 or 10
Step 1: Update Debian Before Vivaldi Installation
Before starting the installation process, update your Debian system to ensure all existing packages are up to date. This will minimize potential conflicts during the installation. Execute the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeStep 2: Install Vivaldi Initial Required Packages
To complete the installation, you will need to install specific software packages. These packages are commonly found on most Linux distributions and are necessary for the installation process. Run the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt install software-properties-common apt-transport-https curl ca-certificates -yRunning this command will only install packages that are not already present on your system.
Step 3: Import Vivaldi APT Repo
First, download the GPG key, which is used to verify the authenticity of the packages you are downloading and installing. Run the following command in your terminal:
curl -fsSL https://repo.vivaldi.com/archive/linux_signing_key.pub | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/vivaldi.gpg > /dev/nullNext, add the Vivaldi repository by executing the following command:
echo deb [arch=amd64,armhf signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/vivaldi.gpg] https://repo.vivaldi.com/archive/deb/ stable main | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/vivaldi.listStep 4: Refresh APT Index Cache
After importing the repository, update your repository list to reflect the new repository changes. Run the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt updateInstall Vivaldi Browser on Debian 12, 11 or 10 via APT Command
You can now install the stable or snapshot (nightly) version of the Vivaldi Browser. Note that you can install both versions simultaneously.
Step 1: Install Vivaldi Browser on Debian (Select Option)
Run the following command to install the stable version of Vivaldi Browser:
sudo apt install vivaldi-stableFor users or developers who want to test Vivaldi’s development version, run the following command:
sudo apt install vivaldi-snapshotStep 2: Verify Vivaldi Browser Installation on Debian
Confirm the version and build of the Vivaldi Browser installed on your operating system using the appropriate command:
For the stable version:
vivaldi-snapshot --versionThe snapshot (nightly) version:
vivaldi-snapshot --versionKeep in mind that the stable version is recommended for daily browsing. The development version should not be used for any serious browsing or transactions.
Launch Vivaldi Browser on Debian 12, 11 or 10
After successfully installing the Vivaldi Browser, you can launch it from the command line or via the graphical interface.
CLI Commands to Launch Vivaldi Browser
To launch the Vivaldi Browser directly from the terminal, use the appropriate command for the version you have installed:
For the stable version:
vivaldiSnapshot (nightly) version:
vivaldi-snapshotRunning these commands will open the Vivaldi Browser immediately from your command terminal.
GUI Method to Launch Vivaldi Browser
For most desktop users, you can launch the Vivaldi Browser through the graphical user interface (GUI) by following these steps:
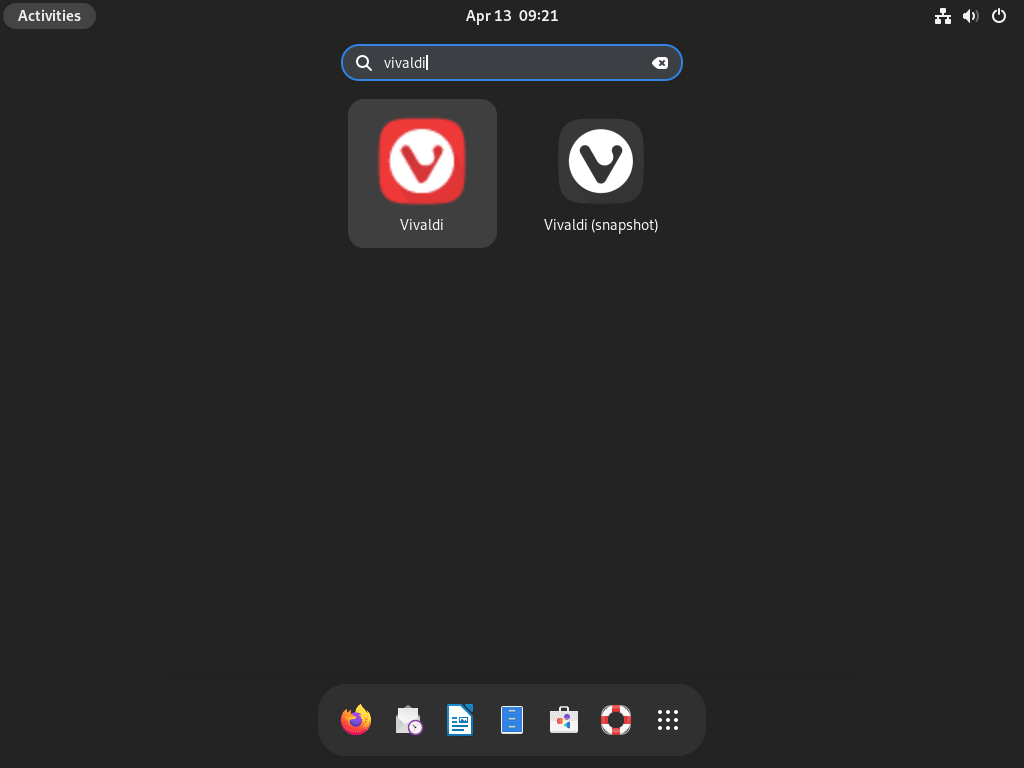
- Open the Activities menu (usually located in the top-left corner of the screen).
- Click on Show Applications (represented by a grid of dots icon).
- Search for “Vivaldi” in the search bar, or scroll through the list of installed applications.
- Click on the Vivaldi icon corresponding to the version you want to launch (either Vivaldi for the stable version or Vivaldi Snapshot for the nightly version).
Getting Started with Vivaldi Browser on Debian 12, 11 or 10
In this section, we will explore some tips and tricks to help you get started with the Vivaldi Browser on Debian Linux. We will cover general tips, customizations, and other helpful insights to enhance your browsing experience.
General Vivaldi Browser Tips with Debian
- Quick Commands: Vivaldi offers a powerful feature called Quick Commands, which allows you to access various browser functions quickly using keyboard shortcuts. Press
F2to open the Quick Commands menu, and type in your desired action (such as opening a new tab, searching your browsing history, or managing your bookmarks). - Web Panels: Vivaldi’s Web Panels enable you to view multiple websites simultaneously in a split-screen view. To add a new Web Panel, click the “+” button on the sidebar, and enter the URL of the website you want to add. This feature is particularly useful for monitoring social media feeds, news websites, or chat applications while browsing other sites.
- Mouse Gestures: Vivaldi supports Mouse Gestures, which allow you to perform common browser actions using simple mouse movements. To enable this feature, go to
Settings > Mouse > Mouse Gestures, and toggle the feature on. You can also customize your own gestures or modify the default ones.
Customization Vivaldi Browser Tips with Debian
- Themes: Personalize your Vivaldi Browser by applying a custom theme. Go to
Settings > Themes, and choose from the available presets or create your own unique theme by selecting the “Create New Theme” button. - Tab Management: Vivaldi offers various ways to manage your open tabs, including Tab Stacking, Tab Tiling, and Tab Hibernation. To stack tabs, simply drag one tab over another. To enable Tab Tiling, right-click on a tab stack and select “Tile Tab Stack.” For Tab Hibernation, right-click on a tab and choose “Hibernate Background Tabs” to save system resources.
- Customizing Toolbars: Rearrange, add, or remove buttons from the Vivaldi toolbars to suit your preferences. Right-click on any toolbar, and select “Customize.” From there, you can drag and drop buttons or access additional customization options.
Other Helpful Vivaldi Browser Tips with Debian
- Built-in Note-taking: Vivaldi has a built-in note-taking feature that allows you to save notes, links, and screenshots directly in the browser. To create a new note, click the “Notes” icon in the sidebar, and then click the “+” button.
- Capture Tool: Vivaldi’s built-in Capture Tool lets you take screenshots of entire web pages or selected areas. To use this feature, click the “Capture” icon in the status bar at the bottom-right corner of the browser window, and choose your desired capture option.
- Privacy and Security: Vivaldi offers various privacy and security features, such as a built-in ad and tracker blocker. To enable this feature, go to
Settings > Privacy > Tracker and Ad Blocking, and choose your preferred blocking level (none, moderate, or strict).
These tips should help you get started with the Vivaldi Browser on Debian Linux and make the most of its unique features and customizations.
Additional Commands For Vivaldi Browser on Debian 12, 11 or 10
This section will cover how to update and remove the Vivaldi Browser on your Debian system using terminal commands. We will also discuss the removal of the Vivaldi repository and GPG key if you no longer plan to use the Vivaldi Browser on your system.
Update Vivaldi Browser
Although most desktop users rely on automatic updates or auto-update notifications, you can also update the Vivaldi Browser manually using terminal commands. This method allows you to check for updates for your entire system.
To check for updates, run the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt updateIf an update is available, you can upgrade the Vivaldi Browser by executing the following command:
sudo apt upgradeNote this will update all packages that require updating, making it simple to check and keep Vivaldi and your entire system updated.
Remove Vivaldi Browser From Debian
If you decide to uninstall the Vivaldi Browser, use the following command that matches your installation method of stable or snapshot:
sudo apt remove vivaldi-stablesudo apt remove vivaldi-snapshotRemove Vivaldi Repository and GPG Key
If you no longer plan to use or install the Vivaldi Browser on your system, follow these steps to remove the Vivaldi repository and GPG key:
Step 1: Delete the Vivaldi Repository
To remove the Vivaldi repository, run the following command:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/vivaldi.listStep 2: Delete the GPG Key
Finally, delete the GPG key by executing this command:
sudo rm /usr/share/keyrings/vivaldi.gpgFollowing these steps, you can keep your Vivaldi Browser up to date, remove it if necessary, and delete the Vivaldi repository and GPG key if you no longer plan to use the browser on your Debian system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, installing the Vivaldi Browser on Debian Linux is a straightforward process that provides a powerful and customizable alternative to the default Firefox ESR browser. Vivaldi offers many features, such as Quick Commands, Web Panels, and Mouse Gestures, and advanced customization options, like themes, tab management, and toolbar adjustments. Following the steps outlined in this guide, you can easily install, update, and remove the Vivaldi Browser on your Debian system, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable browsing experience.



Hi…it does not work from the repository any more:
W: GPG error: http://repo.vivaldi.com/stable/deb stable Release: The following signatures couldn’t be verified because the public key is not available:
Hi Zajdan,
I just re-tested this right now, snapshot and stable both installed fine together with no gpg error.
Did you install the initial required packages and run the gpg import command? then run a quick apt update after to refresh the package index?