LXQt is a premier Linux desktop environment offering a harmonious blend of performance and features. Understanding its core attributes is essential for those aiming to install LXQt on Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, or Debian 10 Buster. Originating from the fusion of the LXDE and Razor-qt projects, LXQt delivers a seamless experience optimized for functionality and resource conservation.
Key Attributes of LXQt:
- Efficiency: Known for its swift performance, LXQt operates with minimal resource usage, making it ideal for high-end and older hardware setups.
- Customization: LXQt grants users extensive control over their desktops, ensuring a workspace tailored to individual preferences.
- User-Centric Design: With its intuitive interface, LXQt promotes easy navigation and efficient management of files and applications.
- Modern Framework: Built on the robust Qt application framework, LXQt adheres to contemporary design principles and standards, ensuring compatibility and forward-thinking operations.
- Streamlined Setup: The LXQt installation is straightforward, catering to Linux veterans and newcomers.
LXQt’s blend of speed, customization, and modern design makes it a top choice for Debian users. This guide will walk you through the steps to install LXQt on Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, or Debian 10 Buster, ensuring a hassle-free setup across these Debian versions.
Install LXQt on Debian 12, 11, or 10 via APT
Step 1: Refreshing Debian System Before LXQt Installation
To start with the LXQt installation, you must ensure your Debian system is current. Keeping your system updated helps in smooth installations by reducing potential software conflicts.
Update your Debian system by running these commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgradeThe sudo apt update command refreshes the package lists, letting the system recognize the newest software versions. The next command, sudo apt upgrade, upgrades any software on your system that’s out of date.
Step 2: Proceed to install LXQt on Debian via Task Command
LXQt, being a lightweight desktop environment, is readily found in Debian’s repositories. This means you can easily and quickly install it compared to desktop environments.
To install LXQt, run:
sudo apt install task-lxqt-desktopHere, sudo grants necessary permissions, apt install is the command to install software, and task-lxqt-desktop is the specific package for the LXQt desktop environment.
If you’re working with a server-focused Debian installation and want a minimalist setup, you can install LXQt with:
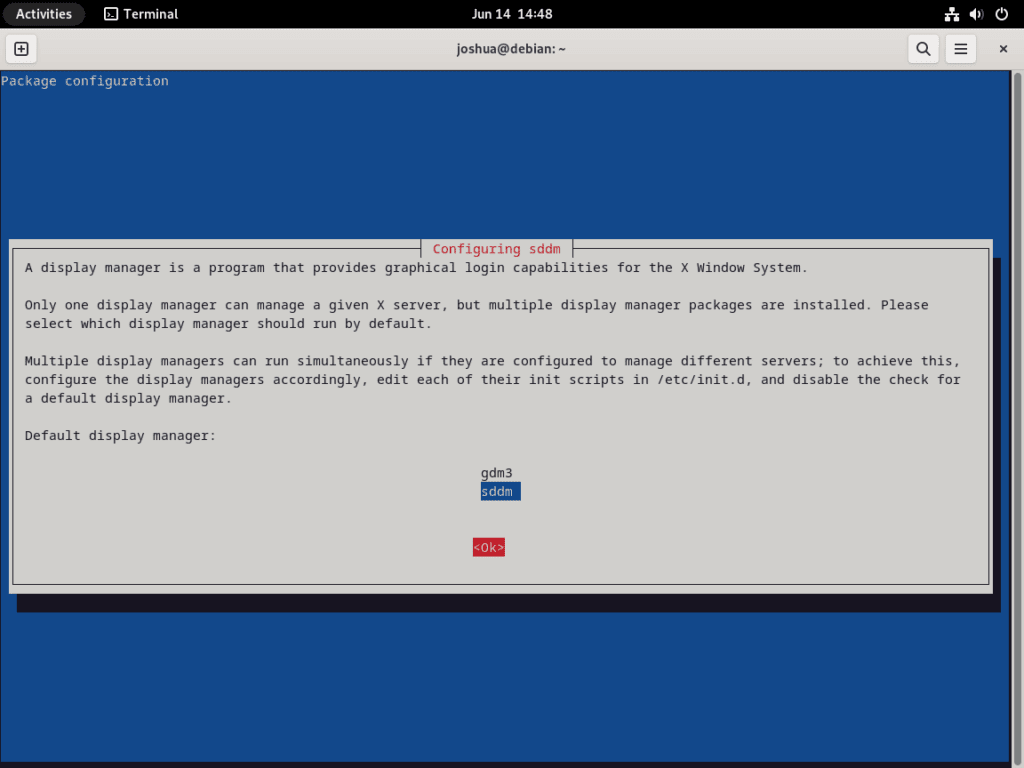
sudo apt install lxqtDuring installation, you’ll see the “Configuring sddm” prompt. LXQt uses the Simple Desktop Display Manager (SDDM) as its login screen. To proceed, highlight <Ok> using the TAB key and press ENTER.
Step 3: System Reboot Post LXQt Installation
After successfully installing LXQt, restart your system. This step ensures LXQt initializes appropriately for optimal performance.
Reboot your system by typing:
sudo rebootAfter your system restarts, LXQt will be fully operational on your Debian installation.
Accessing LXQt on Debian 12, 11, or 10
Step 1: Navigating the Login Interface
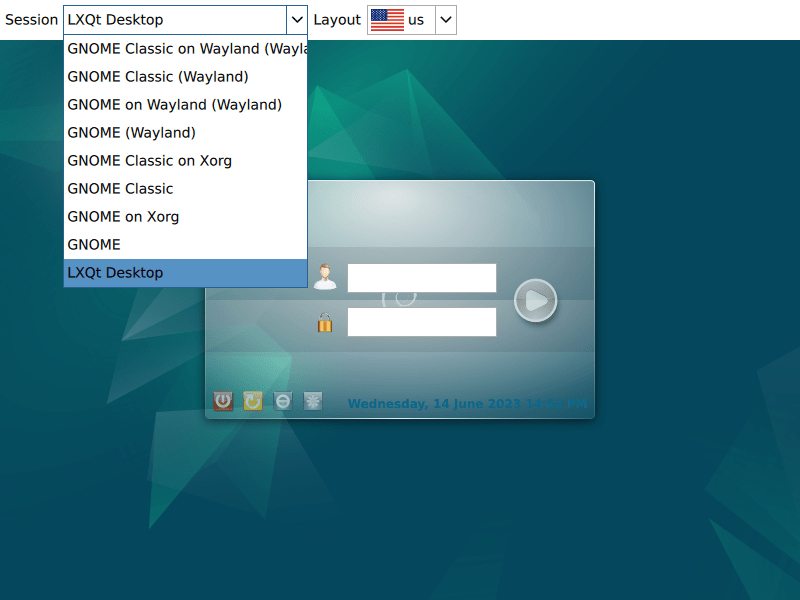
After you’ve installed LXQt and restarted your system, you’ll need to log into the LXQt desktop environment. Usually, LXQt becomes your default desktop environment automatically. If it hasn’t, you can choose it manually.
At the login screen, you’ll find a desktop environment selection option. Typically, it’s located in the top left corner. Click on this dropdown menu. From there, choose “LXQt” to set it as your desktop environment. Doing this will override other choices, like “GNOME (Wayland).”
Tips for Getting Started with LXQt on Debian 12, 11 or 10
It may seem a bit daunting when you first start using LXQt on Debian Linux due to its lightweight and minimal design. But don’t let that initial impression dissuade you. With a few helpful tips and insights, you’ll soon be able to navigate this desktop environment with ease and efficiency. Here are some tips to help you get the most out of LXQt.
General LXQt Tips with Debian
- Understanding the Layout: One of the first things to get familiar with in LXQt is its straightforward layout. It comprises a single panel at the bottom of the screen, similar to Windows. This panel houses the application menu, quick launch bar, and system tray.
- Customizing the Panel: To add, remove, or move items within the panel, right-click on the panel and select ‘Configure Panel.’ Add or remove widgets, change the panel size, and more.
- Knowing your Applications: LXQt comes with a selection of lightweight applications. You have PCManFM-Qt for file management, QTerminal for the terminal, and more. You can find these applications by clicking on the application menu.
Customization LXQt Tips with Debian
- Changing the Theme: LXQt supports changing themes. Go to ‘Preferences > LXQt settings > Appearance’ to explore the theme options.
- Altering the Wallpaper: Right-click on the desktop and select ‘Desktop Preferences.’ You’ll find options to change the wallpaper, icon themes, and more.
- Customizing Window Behavior: You can also customize window behaviors. Go to ‘Preferences > LXQt settings > Window Effects’ to tweak how windows interact.
These tips should help you get started with LXQt on Debian Linux, and remember, the LXQt community is always there to assist you further.
Management Commands for LXQt on Debian 12, 11 or 10
Switch Display Manager on Debian
If transitioning from LXQt to GNOME, start at the display manager selection. This process involves choosing a default display manager like GDM for GNOME. Initiate this by entering the command:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure sddmThis command kickstarts the reconfiguration for the SDDM display manager and lets you pick an alternate default display manager. Remember to restart your system after changing display managers or desktop environments to ensure your changes take effect. Use this command to restart:
sudo rebootRemove LXQt From Debian
If you ever want to remove LXQt, maybe try a different desktop environment, or return to your previous setup, use the following command:
sudo apt autoremove '^lxqt' task-lxqt-desktop --purgeThis command cleans LXQt and its associated files from your system.
Upon removing LXQt, you might need to reinstall the GNOME Desktop Environment. Some packages essential for GNOME might have been deleted during the LXQt uninstallation. To get GNOME back, first update your package list. Then, install the GNOME desktop environment with:
sudo apt install gnome gdm3 task-gnome-desktop --reinstallTo make sure you’ve fully implemented all changes, restart your system using:
sudo rebootClosing Thoughts
Throughout the course of this guide, we have traversed the intricacies of installing, navigating, and managing the LXQt desktop environment on Debian Linux distributions. This journey provided a comprehensive understanding of the tools and processes needed to tailor your desktop environment experience. From the first login experience with LXQt to transitioning back to GNOME, this guide aimed to facilitate your mastery of LXQt on Debian.