If you’re using Linux Mint and need a versatile document viewer, Okular stands out as a top choice. This KDE project creation brings a rich set of features and extensive format support to the table, making it a comprehensive solution for various document viewing needs. In this guide, we will walk you through the steps to install Okular on Linux Mint 21 or Linux Mint 20, ensuring you have access to this powerful tool regardless of your Linux Mint version.
Key Strengths of Okular:
- Versatile Format Support: Okular isn’t limited to PDFs; it supports many document and image formats, providing a one-stop solution for all your viewing needs.
- Robust Annotation Tools: From highlighting text to adding notes and geometric shapes, Okular’s annotation capabilities are extensive.
- Accessibility-Focused: With features like text-to-speech, Okular ensures it’s accessible to a diverse user base.
- Bookmarking Ease: Navigate and mark specific sections of your documents easily using Okular’s bookmarking feature.
- Extract Text and Images: A handy feature for researchers and students, Okular allows for extracting text and images directly from documents.
- Comprehensive Review Tools: Okular’s range of review tools facilitates thorough content assessments, enhancing your document interaction experience.
Choosing Okular on Linux Mint
While Linux Mint comes with its PDF viewer, Xreader, Okular’s advanced capabilities and extensive format support make it a superior choice for users with diverse and demanding document interaction needs. Its alignment with KDE’s design principles makes it an excellent option for those who prefer the KDE desktop environment, ensuring a seamless and integrated user experience.
Embracing the open-source ethos, Okular is a fitting choice for the Linux Mint community, offering a powerful, user-friendly, and free document-viewing solution. To get started with Okular and unlock its full potential on your Linux Mint system, follow the detailed installation guide provided in the next sections.
Install Okular on Linux Mint 21 or 20 via APT
Step 1: Update Linux Mint Packages Before Okular Installation
Ensuring your system’s packages are up-to-date is crucial for both security and successful software installation. An updated system guarantees compatibility and reduces the risk of conflicts when installing new software. It is a widely accepted best practice to refresh your system’s package list and upgrade the installed packages before adding new software.
To update your Linux Mint system, utilize the Advanced Package Tool (APT), a robust command-line utility designed to manage packages. Run the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThe sudo apt update command refreshes your system’s package list, acquainting it with the latest software versions. Following that, the sudo apt upgrade command updates the installed packages to their most recent iterations.
Step 2: Install Okular via APT Command on Linux Mint
Okular can be installed in various ways, but for newcomers, the most accessible and straightforward approach is through the default APT repository. This repository provides a stable and secure version of Okular, positioning it as the preferred installation method. However, it is essential to note that the version available in the APT repository might not be the latest due to its slower update cycle.
To proceed with the installation of Okular using the APT package manager, input the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt install okularIn this command, you instruct the APT package manager to fetch the Okular package from the repository and initiate the installation process on your Linux Mint system.
Install Okular on Linux Mint 21 or 20 via Flatpak and Flathub
Step 1: Ensuring Flathub is Enabled for Okular Installation
Before installing Okular, it’s imperative to confirm the activation of the Flathub repository. Flathub is a comprehensive hub for applications available via Flatpak, a package management system natively integrated into Linux Mint. The Linux Mint community and its developers show a clear preference for Flatpak over Snap, making it a reliable choice for software installation.
To enable Flathub on your Linux Mint system, execute the following command in your terminal:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoThis command ensures the addition of the Flathub repository as a Flatpak source only if it isn’t already present. The --if-not-exists flag is crucial here, as it prevents the creation of duplicate repository entries, maintaining a clean and efficient system configuration.
Step 2: Install Okular with Flatpak Command on Linux Mint
With Flathub now active, you are set to proceed with the Okular installation.
To install Okular via Flatpak, input the following command in your terminal:
flatpak install flathub org.kde.okular -yIn this command, flathub specifies the repository from which to fetch the package, org.kde.okular is the unique identifier for the Okular package within the Flathub repository, and the -y flag ensures an uninterrupted installation by automatically affirming all prompts.
Executing this command prompts the Flatpak package manager to retrieve the latest version of Okular from Flathub and initiate the installation on your Linux Mint system, ensuring you have access to the most recent features and updates.
Launching Okular on Linux Mint 21 or 20
Using Command-Line Interface (CLI) to Start Okular
Launching Okular After APT Installation
Post-installation via the APT package manager, you can swiftly initiate Okular with the following terminal command:
okularThis command prompts the system to open Okular, providing immediate access to its features through the graphical user interface (GUI).
Starting Okular After Flatpak Installation
For installations done using Flatpak, the command to launch Okular varies:
flatpak run org.kde.okularHere, flatpak run is the standard command to initiate applications installed via Flatpak, with org.kde.okular serving as Okular’s unique identifier.
Utilizing Graphical User Interface (GUI) to Open Okular
For those preferring a more visual approach, launching Okular through the GUI is straightforward.
Navigate through the following steps:
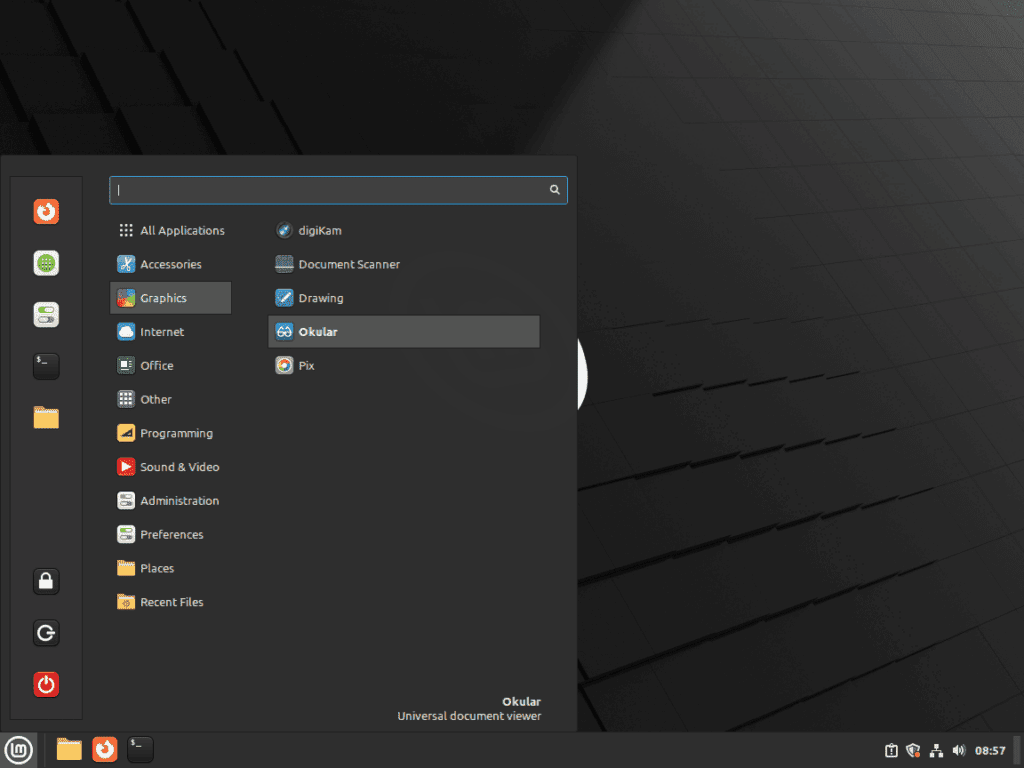
- Access the ‘Taskbar’
- Select ‘Show Applications’
- Locate and click on ‘Okular’
This process opens the Linux Mint menu, where ‘Show Applications’ unveils all installed software. Searching and selecting ‘Okular’ from this compilation will launch the application, providing a user-friendly method for those less inclined to use the CLI.
First-Time Tips with Okular on Linux Mint 21 or 20
Starting with a new software can be exciting yet intimidating, given the array of features and customization options that come with it. Okular is no different. As you embark on your journey with Okular, here are some tips and tricks to help you harness the full potential of this powerful tool.
General Okular Usage Tips with Linux Mint
- Document Navigation: Use the scroll wheel on your mouse or the arrow keys on your keyboard for easy navigation through documents. Pressing
Ctrl + +/-will zoom in or out of the document. - Multiple Document Interface: Okular supports opening multiple documents in the same window, which can be useful for cross-referencing. Go to
File > Open New Tabor use the shortcutCtrl + Tto open a new document tab. - Search Functionality: Okular’s search functionality is a powerful tool for quickly locating information within a document. Press
Ctrl + Fto open the search bar. - Annotations: Okular allows you to make annotations in the documents, a feature especially useful when reviewing or studying documents. Click on
Tools > Reviewto access the annotation tools. - Export Notes: Your annotations are not permanently attached to the PDFs, but you can export them. Go to
File > Export As > Document Archive.
Okular Customizations Tips with Linux Mint
- Toolbar Customization: You can customize the toolbars to suit your workflow better. Right-click on the toolbar and select
Configure Toolbarsto customize. - Theme Customization: Okular allows you to choose between light and dark themes. Navigate to
Settings > Configure Okular > Accessibilityand under ‘Change Colors’ select ‘Use color scheme’. - Shortcut Customization: Okular allows you to customize the shortcuts. Go to
Settings > Configure Shortcutsto assign custom shortcuts to various functions.
Tips for Okular Advanced Usage with Linux Mint
- Document Archiving: Okular allows the exporting of documents in the archive format (.okular file). This format stores both the document and the annotations, which can be useful when sharing annotated documents with peers.
- Command-line Options: Okular supports a range of command-line options for advanced usage. Running
okular --helpin terminal will display the options available. - Shell Script Integration: As a command-line runnable application, Okular can be integrated into shell scripts for advanced automation tasks.
The tips above should help you start with Okular more profoundly and efficiently, but true mastery comes from exploring and using the software. So, don’t hesitate to explore Okular’s menu and settings to get a feel for all the functionality it offers.
Additional Okular Commands with Linux Mint 21 or 20
Update Okular on Linux Mint
APT Update Command Method for Okular
To ensure optimal performance and security, regularly updating Okular is crucial. Execute the following command to refresh your package list and ensure you have the latest information on available updates:
sudo apt updateThis command updates the package index, a crucial step before upgrading the application.
Flatpak Update Command Method for Okular
For installations done via Flatpak, use the update command to ensure Okular is up-to-date:
flatpak updateThis command checks for updates across all installed Flatpak applications, including Okular, and applies them as needed.
Remove Okular From Linux Mint
APT Remove Command Method for Okular
If you need to uninstall Okular installed via APT, the following command will remove the application while preserving configuration files:
sudo apt remove okularThis action ensures that if you decide to reinstall Okular later, your settings remain intact.
Flatpak Remove Command Method for Okular
For Okular installations done with Flatpak, use the following command to uninstall the application and delete the associated data:
flatpak remove --delete-data org.kde.okular -yThis command ensures a clean removal, erasing the application and its data from your system. The -y flag confirms the action, streamlining the process.
Final Thoughts
In recapping what the how-to article has gone over, we have aimed to demystify installing, using, and managing Okular on Linux Mint, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the application. Whether you choose APT or Flatpak for installation or prefer using the command line or GUI for launching, you now have the tools at your disposal to navigate Okular with confidence. Remember, mastering these commands is a crucial step towards becoming proficient with your Linux system, and embracing Okular is about more than just viewing PDFs—it’s about leveraging the power and flexibility of open-source software.



This was an impressive document. Meticulous attention to the many options available and tips to avoid pitfalls. I am very grateful for the time spent to develop this page.