This guide will demonstrate the process of installing Neofetch on Ubuntu 24.04, 22.04, or 20.04 LTS Linux releases with the command-line terminal and APT Package Manager.
Neofetch is a highly regarded open-source utility designed for system information fetching, showcasing a system’s capabilities in a visually appealing manner directly within the command-line interface. It stands out for its flexibility, offering extensive customization options to display exactly the information users find most relevant. From hardware details like the CPU and memory to software stats including the operating system and shell version, Neofetch compiles essential data into an easy-to-read format. Its lightweight nature ensures that it can run on a wide range of systems without impacting performance, making it a favorite among developers, system administrators, and desktop users alike.
Key features include:
- Customizable Output: Tailor the displayed information to meet your specific needs.
- Support for Various Operating Systems: Works seamlessly across Linux, macOS, Windows, and more.
- Easy Integration: Can be added to shell startup files for automatic system information display upon terminal launch.
- Screenshot Utility: Facilitates easy sharing of system configuration with others.
- Lightweight and Fast: Optimized for efficiency, it loads quickly without burdening the system.
- Extensive Software and Hardware Details: Displays comprehensive information on system resources.
- Theme Support: Allows for customization of the output with themes.
- Active Community: Benefits from a vibrant community for support and updates.
Transitioning from understanding Neofetch’s key features and benefits to the practical steps for installation, the following sections will equip you with the necessary knowledge to get Neofetch up and running on your Ubuntu system.
Update Ubuntu Before Neofetch Installation
To start with Neofetch, it’s crucial to prepare your system first. This preparation involves ensuring that all your Ubuntu packages are up to date. By doing this, you’ll avoid any conflicts arising from outdated packages.
Here’s how you update your Ubuntu packages:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeBy running this command, you’re doing two important tasks: updating the list of available packages with sudo apt update, and then upgrading your system’s packages to their latest versions with sudo apt upgrade.
Install Neofetch on Ubuntu via APT
Neofetch is readily available on the Ubuntu repository, simplifying the installation process significantly. This easy availability is one of the many benefits of open-source software and rich community-supported repositories like Ubuntu’s.
To install Neofetch, you need to use the following command:
sudo apt install neofetchOnce installed, verify the installation and build using the neofetch –version command.
neofetch --versionWhen you run this command, the sudo part executes the command as a root user, providing the necessary permissions. apt is the package handling utility in Ubuntu, and install neofetch is the instruction to apt to install the Neofetch package.
Verify Neofetch Installation on Ubuntu
After the installation, you must confirm that Neofetch was correctly installed and that you have the right build. Verifying your installation reassures you that everything went as expected, and you are ready to proceed.
To check your Neofetch installation, run the following command:
neofetchThis command will display the version of Neofetch currently installed on your system, confirming the success of the installation process. Now, you are all set to use Neofetch and enjoy its delightful combination of functionality and aesthetics!
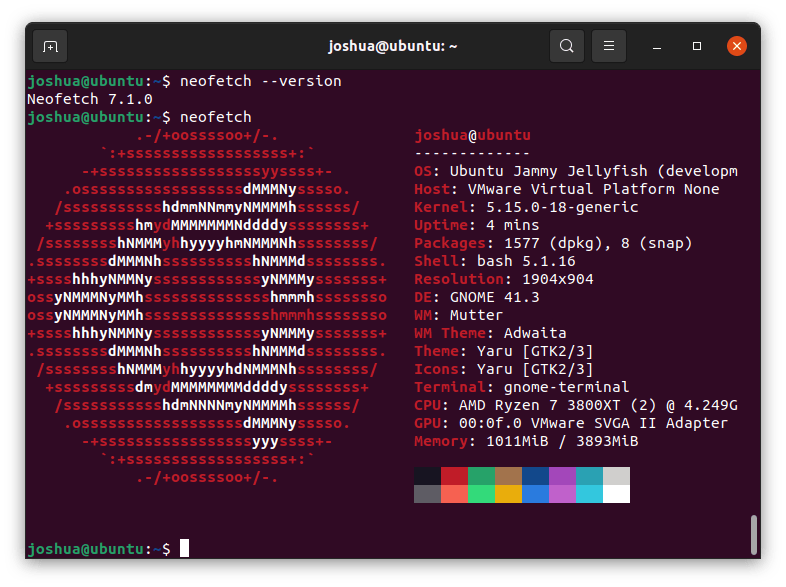
As mentioned above, the default information that is printed is as follows.
| OS: | Operating System Name and Version. |
| Host: | PC or Server Name. |
| Kernel: | The Linux Kernel version and build. |
| Uptime: | The system uptime since start/reboot. |
| Packages: | Installed Package Managers with package count. |
| Shell: | Installed shell version. |
| Resolution: | Monitor resolution. |
| DE: | The installed user interface (Desktop Environment). |
| WM: | Type of Window manager in use. |
| WM Theme: | The Windows Manager theme. |
| Theme: | The installed user interface theme. |
| Icons: | The installed Icon Pack. |
| Terminal: | The default terminal is in use. |
| CPU: | The processor and performance |
| GPU: | The installed graphics card. |
| Memory: | Memory amount used and available. |
Example Neofetch Commands on Ubuntu
Let’s break down Neofetch’s capabilities and illustrate how to manipulate the commands to yield the best results.
Getting Started with Neofetch Commands
Before we delve into the examples, let’s take a brief look at the basic structure of a Neofetch command:
neofetch func_name --option "value"Let’s now explore a series of powerful and popular Neofetch command examples.
Display Only Uptime Information with Neofetch
Here, we’ll use Neofetch to display only the system’s uptime:
neofetch uptime --uptime_shorthand tinyThe uptime function name indicates that we want to fetch the uptime information of the system. The --uptime_shorthand option followed by tiny is used to shorten the displayed uptime.
Displaying Memory, Disk, and Window Manager Information with Neofetch
We list the desired function names to fetch and display specific system information.
neofetch uptime disk wm memoryDisabling Specific Info Lines with Neofetch
You can disable specific lines from appearing in the Neofetch output. For instance, to disable the CPU and GPU lines, use:
neofetch --disable cpu gpuDisplaying the OS Architecture with Neofetch
To display the OS architecture, we use the --os_arch option:
neofetch --os_arch onChanging the CPU Speed Display Type with Neofetch
Neofetch allows changing the type of CPU speed to display. Here’s how to set it to max:
neofetch --speed_type maxDisplaying the Number of CPU Cores with Neofetch
To show the number of logical CPU cores, use:
neofetch --cpu_cores logicalDisplaying CPU Temperature with Neofetch
To display the CPU temperature in Celsius, use the following command:
neofetch --cpu_temp CShortening the Output of Uptime with Neofetch
To shorten the output of the uptime display, we use the --uptime_shorthand option:
neofetch --uptime_shorthand onDisplaying GPU Type with Neofetch
To display the type of the GPU, use the following:
neofetch --gpu_type allDisplaying Shell Version with Neofetch
To show the shell version, use the --shell_version option:
neofetch --shell_version onThe --shell_version on option allows Neofetch to fetch and display the version of the shell currently in use.
Displaying Disk Usage with Neofetch
To showcase the disk usage, use:
neofetch --disk_show on --disk_quiet onIn this command, --disk_show on enables the display of disk usage, while --disk_quiet on limits the output to only the disks with your home directory on them.
Displaying Disk Usage in Percentage with Neofetch
If you prefer viewing disk usage as a percentage, use the following:
neofetch --disk_percent onThe --disk_percent on option will display the disk usage in terms of the percentage used.
Displaying Battery Information with Neofetch
Neofetch can also fetch and display the battery status:
neofetch --battery_display on --battery_shorthand tinyHere, --battery_display on enables the battery information, and --battery_shorthand tiny presents the battery status in a simplified manner.
Displaying Network Information with Neofetch
To display network information, use the following:
neofetch --ip_host on --ip_local onIn this command, --ip_host on displays the public IP address, while --ip_local on reveals the local IP address.
Displaying the Current Song with Neofetch
If you have a music player running, Neofetch can display the current song:
neofetch --song_shorthand tinyThe --song_shorthand tiny option will show the current song in a compressed format.
Changing the Display Image with Neofetch
Neofetch allows changing the displayed image using the --source option:
neofetch --source path_to_your_imageIn this command, replace path_to_your_image with the actual path to your desired image.
Displaying a Custom ASCII Art with Neofetch
To display custom ASCII art, use:
neofetch --ascii path_to_your_ascii_artReplace path_to_your_ascii_art with the actual path to your ASCII art file.
Changing the Image Size with Neofetch
You can also adjust the size of the displayed image:
neofetch --size widthxheightReplace widthxheight with the dimensions you desire.
Altering the Display Colors with Neofetch
To change the colors of the displayed information, use:
neofetch --colors 1 2 3 4 5 6Each number from 1 to 6 corresponds to a specific display aspect, and you can assign different color codes to each.
Saving Neofetch Output to a File with Neofetch
Finally, you can save the Neofetch output to a file:
neofetch > filename.txtIn this command, replace filename.txt with the desired file name.
Additional Learning: Remove Neofetch on Ubuntu
Uninstalling Neofetch from your Ubuntu system starts by issuing a simple command on your terminal. To commence the process, you need to type the following command:
sudo apt remove neofetchTyping this command, you instruct your Ubuntu system to remove Neofetch using the apt package handling utility with administrative privileges. Once the command is issued, your system will prompt you to confirm the uninstallation.
Closing Thoughts
In wrapping up, we’ve walked through the essentials of installing Neofetch on Ubuntu, specifically for versions 24.04, 22.04, or 20.04 LTS. Our guide aimed to simplify the installation process, providing clear, actionable steps to enhance your Linux experience with Neofetch. Along the way, we touched on its key features, installation methods, and even how to remove it if needed. This concise tour was designed to bolster your confidence in managing your system’s software, making Neofetch a valuable addition to your Ubuntu toolkit. Remember, keeping your system updated and exploring Neofetch’s customization options can significantly enrich your user experience. Here’s hoping you found this guide helpful and that it serves you well in your Ubuntu adventures!