Htop is an indispensable tool for system monitoring, offering a dynamic view of your system’s processes and resource usage. This guide will demonstrate how to install Htop on Fedora Linux, a crucial step for any system administrator or user looking to gain deeper insights into their system’s performance. Renowned for its user-friendly interface and detailed system metrics, Htop stands out as a powerful alternative to the traditional top command.
Key Features of Htop:
- Real-Time System Monitoring: Provides a live view of system processes, updating in real-time.
- User-Friendly Interface: Interactive and easy to navigate, making system monitoring more accessible.
- Customizable Display: Offers options to tailor the display to your specific needs.
- Resource Usage Insights: Clearly shows CPU, memory, and swap usage, helping identify resource-heavy processes.
- Advanced Process Management: Allows tasks such as process killing and renicing directly from the interface.
With Htop, you can easily delve into the details of your system’s operation, making it simpler to identify and manage the processes impacting your system’s performance. The installation on Fedora Linux is straightforward, and once completed, you’ll have a robust tool at your fingertips for effective system management.
Install Htop on Fedora Linux via DNF
Step 1: Update Fedora Linux Packages Before Htop Installation
Ensure your Fedora Linux system is up-to-date to prevent conflicts during the Htop installation. Updating packages is a crucial step, as it ensures compatibility and security.
To update your system, execute the following command in the terminal:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshThis command will check for available updates and apply them, keeping your system’s packages current.
Step 2: Install Htop via DNF Command
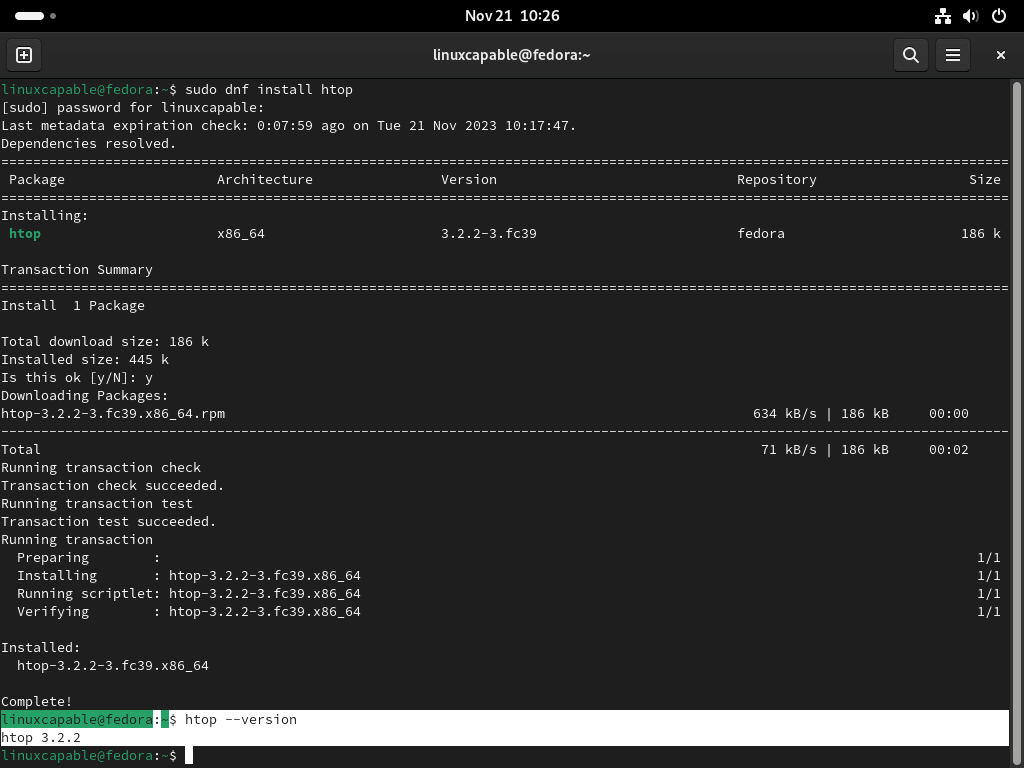
Once your Fedora Linux system is updated, you can proceed with the installation of Htop. Htop is installed using DNF, Fedora’s package manager, simplifying the installation process.
To install Htop, use the command:
sudo dnf install htopStep 3: Confirm Htop Installation
After running this command, DNF will handle the download and installation of Htop. Once the installation is complete, it’s good practice to verify the installation.
To confirm Htop’s installation and check its version, use:
htop --version
This command will display the version of Htop installed on your Fedora Linux system, confirming that the installation was successful.
Htop Keyboard Shortcuts on Fedora Linux
Htop, a dynamic system-monitoring tool, provides keyboard shortcuts to enhance user interaction and efficiency. These shortcuts allow users to navigate and manage processes on Fedora Linux quickly. Below is a detailed list of the most commonly used shortcuts within Htop:
Navigation and Process Management
- Arrow Keys (←, ↑, →, ↓): Scroll through the process list to view different processes.
- Shift + U: Clears all process selections (removes all tags).
- Period (.) or Comma (,): Start an incremental search to find a process by its PID (Process ID).
- F1, ?, H: Access the help screen to view more information about Htop’s features.
- U: Display processes belonging to a specific user.
- F2, Shift + S: Open the settings menu to customize Htop’s appearance and behavior.
- Shift + H: Toggle the display of user threads on or off.
- F3, Shift + /: Initiate an incremental search by process name.
- Shift + K: Toggle the display of kernel threads on or off.
- F4, \: Apply a filter to list processes by name.
- Shift + F: Pin the cursor to a specific process for tracking.
Viewing and Sorting Options
- F5, T: Switch between the default list view and a tree view of processes.
- Plus (+), Minus (-): Expand or collapse branches in the tree view.
- F6, >: Choose a column to sort the process list.
- Shift + P: Sort processes based on their CPU usage.
- F7: Decrease the Nice value of a process, affecting its priority.
- Shift + M: Sort processes by memory usage.
- F8: Increase the Nice value of a process to lower its scheduling priority.
- Shift + T: Sort processes based on time.
Process Control and System Insights
- F9, K: Terminate the selected process or processes.
- L: Use the
lsofcommand to list open files for a process. - F10, Q, Ctrl + C: Exit Htop.
- S: Trace system calls using
stracefor selected processes. - Space Bar: Tag or select a process.
- Shift + L: Use
ltraceto track library calls of a process. - I: Monitor input/output statistics for processes.
These keyboard shortcuts are designed to streamline the monitoring and management of system processes, making Htop an efficient tool for system administrators and power users on Fedora Linux.
Basic Htop Command Examples on Fedora Linux
Below are some essential Htop command examples commonly used in Fedora Linux. These examples offer insights into Htop’s capabilities and how to leverage them for efficient system management.
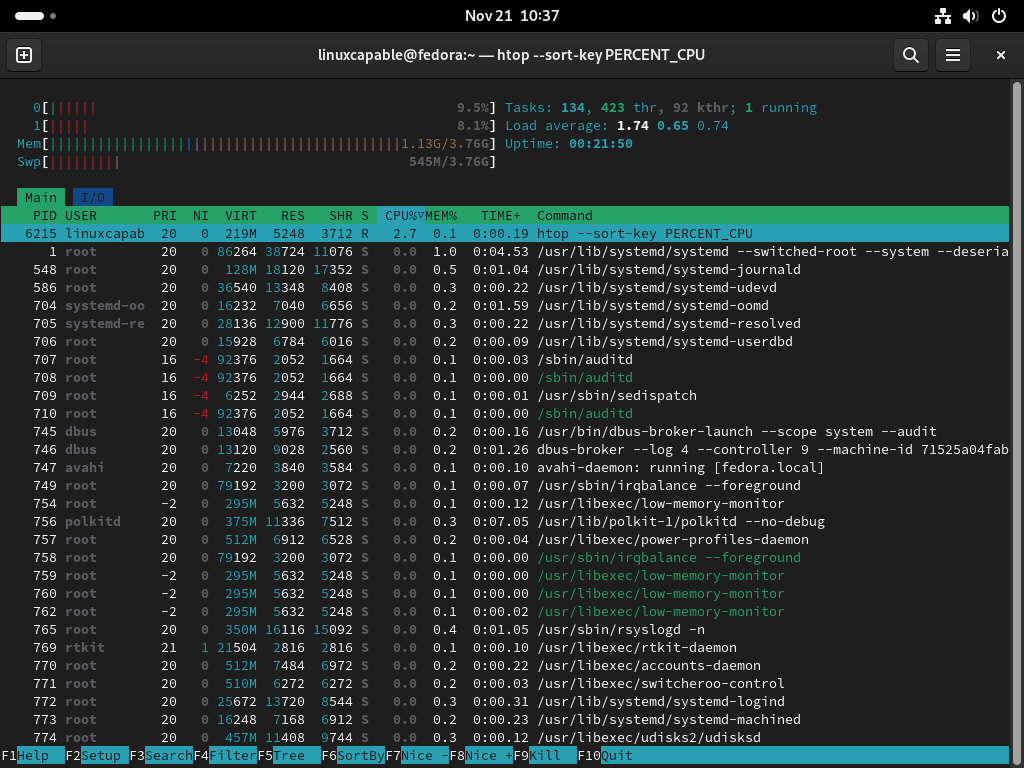
Sorting Processes by CPU Usage
htop --sort-key PERCENT_CPUThis command launches Htop and sorts processes based on their CPU usage. It’s beneficial for quickly identifying processes that are consuming significant CPU resources.
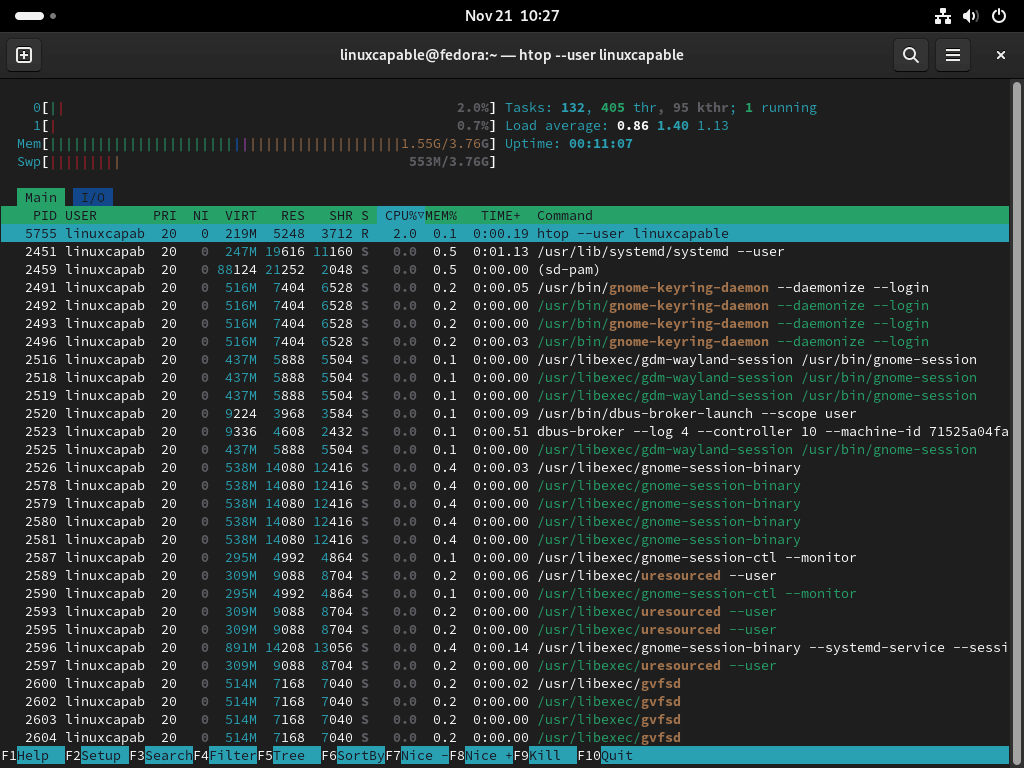
Displaying Processes of a Specific User
htop --user [username]Replace [username] with the actual username to filter and display processes running under that user. This command helps monitor the activities of a specific user.
Filtering Processes by Name
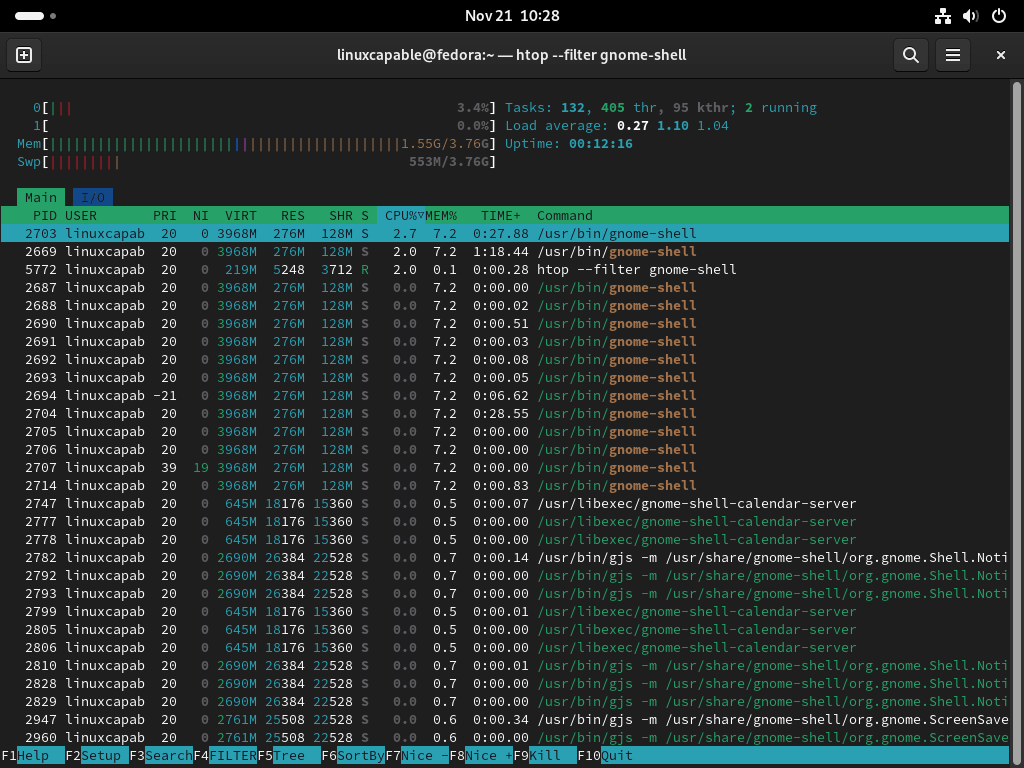
htop --filter [process_name]This command allows you to start Htop with a filter applied to display only processes that match [process_name]. It is handy for focusing on specific applications or services.
Running Htop in Tree View
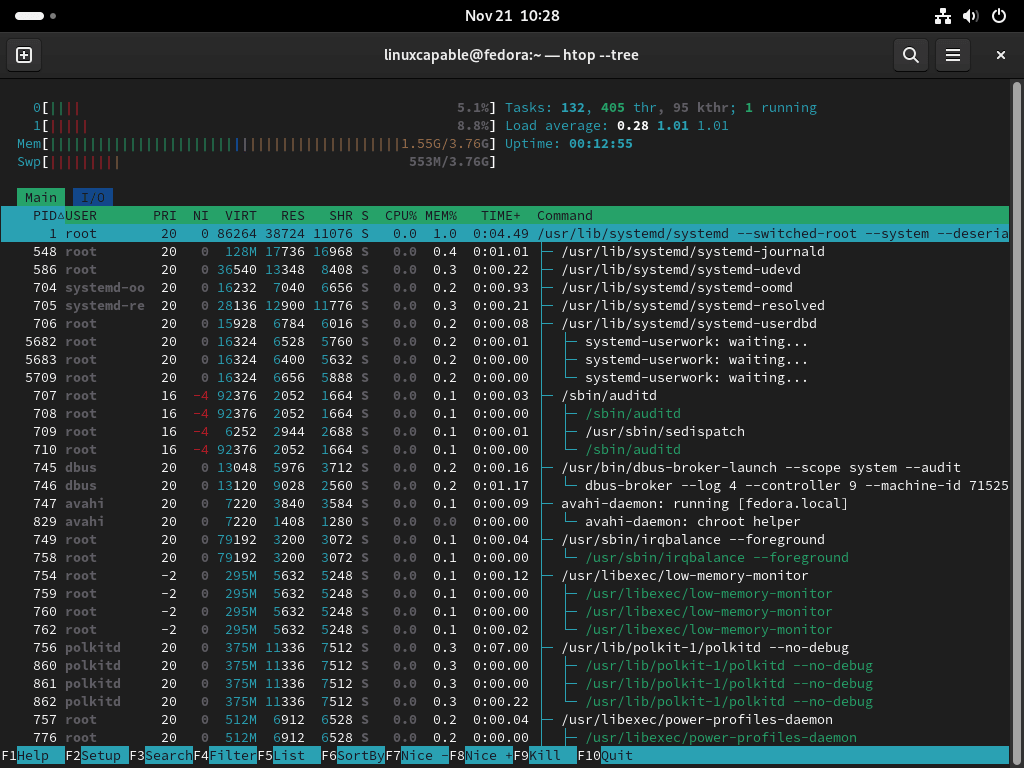
htop --treeThis command starts Htop in a tree view, showing the hierarchy of processes. It’s beneficial for understanding the parent-child relationships between processes.
Showing Only Active Running Processes
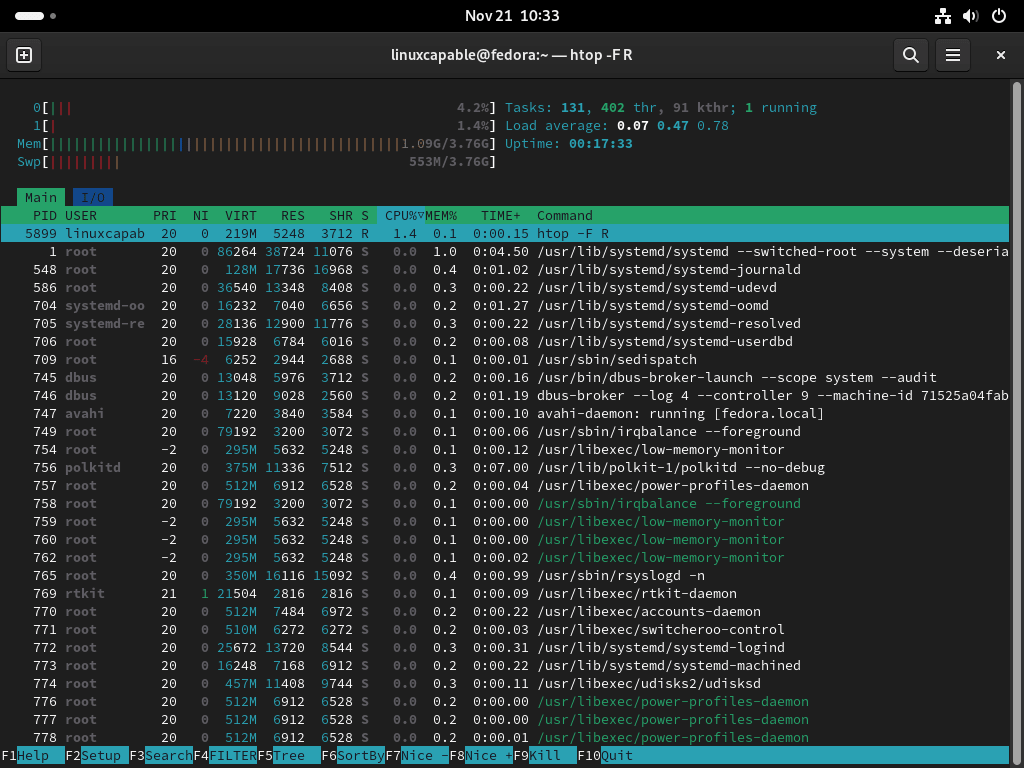
htop -F RThis will show all processes with the “R” state corresponding to running processes. You can also use the following regular expressions to match other activity states:
R: RunningS: SleepingT: StoppedZ: Zombie
Managing Htop on Fedora Linux
Remove Htop from Fedora
When you no longer need Htop on your Fedora Linux system or plan to replace it with a different monitoring tool, you can easily uninstall it. The process involves a simple command that removes Htop from your system entirely.
sudo dnf remove htopAfter running this command, Htop and its configuration files will be entirely removed from your Fedora system. This action frees up resources and makes room for the installation of other software if needed.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
To wrap up, we’ve covered the essentials of getting Htop up and running on Fedora Linux. From installation to mastering key shortcuts and basic commands, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge to efficiently use Htop for monitoring system processes. As you continue to explore Htop, remember its versatility and the value it adds to system management. Keep experimenting with its features to harness its potential in your system monitoring tasks.