Tor Browser, a beacon in online privacy, offers users an unparalleled browsing experience rooted in anonymity and security. Understanding its core features and benefits is essential for those who install Tor Browser on Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, or Debian 10 Buster. Unlike conventional browsers, Tor Browser, derived from “The Onion Router,” employs a unique multi-layered encryption approach, ensuring data remains shielded as it navigates through various Tor relays globally.
Key Features of Tor Browser:
- Complete Anonymity: Tor ensures users remain virtually untraceable by routing communications through a global network of servers.
- Dark Web Access: Tor is the sole gateway to .onion websites, a segment of the internet known as the “Dark Web,” hidden from standard browsers.
- Protection from Surveillance: While ISPs or other entities can monitor standard browsers, Tor safeguards users from intrusions.
- Bypassing Censorship: Tor adeptly circumvents regional website blocks or restrictions, granting unrestricted access.
- No Tracking: Unlike other browsers that may use cookies or store history, Tor ensures user privacy by erasing browsing history and cookies after each session.
While the Tor Browser is a bastion of privacy, users should be aware of potential vulnerabilities, such as malicious Tor exit nodes or browser exploits. However, with cautious usage, Tor offers a level of online security and anonymity that’s hard to rival.
This guide will provide a comprehensive walkthrough on how to install Tor Browser on Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, and Debian 10 Buster. We’ll delve into various installation methods, including Debian’s default apt repository, manual installation using the .deb package, and Flatpak installation from Flathub.
Install Tor Browser on Debian 12, 11, or 10 via APT
Step 1: Updating Debian Before Tor Browser Installation
Before installing the Tor Browser, make sure to update your Debian system. Regular updates provide the latest security patches and fix bugs, preventing software conflicts and improving system performance.
Use the following command to update:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThe apt update command fetches the package list from the repository, updating the local package index. On the other hand, apt upgrade upgrades all the upgradable packages on your system.
Step 2: Install Tor Browser on Debian via APT Command
After ensuring an updated system, we can now install the Tor Browser. For this method, we will use Debian’s default repository. The process is efficient and straightforward, facilitating seamless installation and updates.
To install Tor and the Tor Browser Launcher, input the following command into your terminal:
sudo apt install tor torbrowser-launcherIn this command, apt install is the package handling utility behind Debian. The packages tor and torbrowser-launcher are the specific applications you’re directing apt to install.
The
torpackage provides the underlying software that enables the Tor network’s anonymizing capabilities. Thetorbrowser-launcheris a helper program that will download, verify, install, and provide a system for updating the Tor Browser Bundle. The latter ensures the Tor Browser is up-to-date and authentic, reducing the risk of running counterfeit versions.
Install Tor Browser on Debian 12, 11, or 10 via Flatpak and Flathub
An Overview of Flatpak
Before we dive into installing the Tor Browser using Flatpak, let’s take a moment to understand what Flatpak is. Flatpak is a universal package management system that aims to solve the distribution, installation, and package compatibility issues across different Linux distributions. With a focus on sandboxing, Flatpak provides additional security for your system and the applications you install.
Step 1: Enabling Flathub For Tor Browser on Debian
Flathub is the primary repository for Flatpak applications. It contains many applications, including the Tor Browser. To install Tor Browser using Flatpak, first enable the Flathub repository. Here’s how:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoThe flatpak remote-add command adds the Flathub repository to your Flatpak configuration, while --if-not-exists ensuring the command won’t fail if the repository is already added.
Step 2: Install Tor Browser on Debian via Flatpak Command
With the Flathub repository enabled, we can install the Tor Browser. This process is carried out using the flatpak install command.
Here’s the command to install Tor Browser:
flatpak install flathub com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcher -yThe flatpak install command installs the specified application, in this case, the Tor Browser, from the defined repository, here being Flathub. The -y flag automatically confirms the installation prompt, expediting the process.
If your system doesn’t have Flatpak installed yet, kindly refer to our detailed guide on “How to Install Flatpak on Debian” for step-by-step instructions on installing the most recent supported version of Flatpak.
Section 3: Manually Installing Tor Browser
We will venture into a slightly more hands-on approach to installing the Tor Browser on your Debian system for this final method. This involves directly downloading the latest browser version from the official Tor Project website, guaranteeing you receive the most current build. Although the browser can typically self-update, substantial updates may still necessitate repeating this manual process.
Step 1: Downloading the Tor Browser Archive
The Tor Browser’s up-to-date versions are available for download as .tar.xz files from the Tor Project’s official website. You can use the wget command to fetch these files, as shown below:
wget https://www.torproject.org/dist/torbrowser/{version}/tor-browser-linux64-{version}_ALL.tar.xzThe
{version}placeholder should be replaced with the actual version number of the Tor Browser you wish to download. Always check the Tor Project’s official download page to ensure you’re getting the latest version.
Step 2: Extract Tor Browser Downloaded Archive
Once the download is complete, the next step is to extract the archive’s contents. You can accomplish this using the tar command as shown:
tar -xvJf tor-browser-linux64-{version}_ALL.tar.xzAgain, remember to replace {version} with the actual version number of the Tor Browser that you have downloaded.
Step 3: Relocating the Tor Browser Directory and Registering as a Desktop Application
Before we register the Tor Browser as a desktop application, it’s prudent to relocate it to a directory more suited for such applications. In this case, /usr/local/share serves our purpose ideally, as it is generally used to store shared data from local, standalone applications.
Firstly, we need to move the tor-browser directory to /usr/local/share by issuing the following command:
sudo mv tor-browser /usr/local/share/Do note that we are using sudo for this operation, as modifying the contents of /usr/local/share typically requires root privileges.
After moving the tor-browser directory, navigate to this new directory by using the cd command:
cd /usr/local/share/tor-browserNow that we are in the correct directory, let’s register Tor Browser as a desktop application. Execute the following command:
./start-tor-browser.desktop --register-appThis command yields an output similar to the one below:
Tor Browser has been registered as a desktop app for this user in ~/.local/share/applications/
This marks your successful launch and initial interaction with the Tor Browser. You are now ready to browse the internet with enhanced privacy and security.
Initiate the Tor Browser on Debian 12, 11 or 10
If you installed the Tor Browser using the Debian Repository or the Manual Method, launch it using the terminal. Enter the following command:
tor-browserFor those who have opted for the Flatpak installation, the command to start the Tor Browser from the terminal differs slightly. Here’s the command:
flatpak run com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcherYou can also easily access the Tor Browser through the application menu if you prefer to navigate the system using the Graphical User Interface (GUI). Follow this path:
- Click on ‘Activities’.
- Move to ‘Show Applications’.
- Search for and select ‘Tor Browser’.
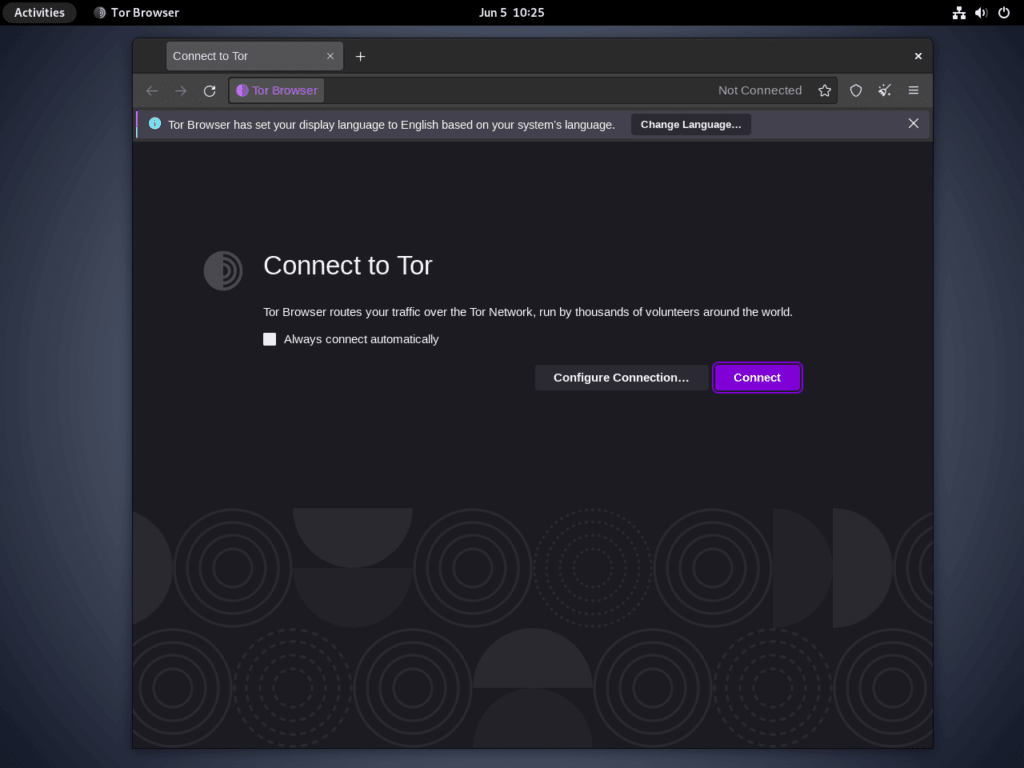
First Interaction with the Tor Browser
The first time you launch the Tor Browser, you will be presented with a window carrying two options: “Connect” and “Configure Connection…”
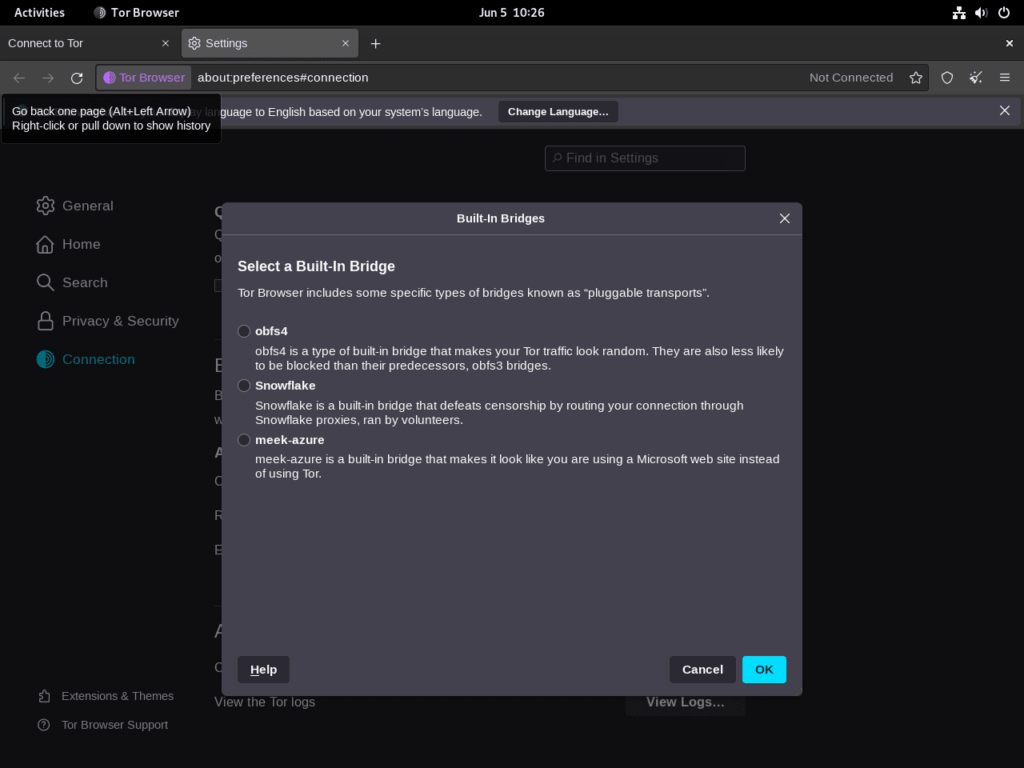
Most users will be inclined to choose the default “Connect” option, which suits a broad range of general browsing requirements. However, for countries with strict internet restrictions or users requiring advanced privacy features, the “Tor Network Settings” option offers the ability to configure proxy settings. Tor also enables the setup of bridges for users who need better connections or are facing difficulties accessing certain websites.
After you’ve selected “Connect,” connecting to the Tor network will commence. This could take anywhere from 15 to 60 seconds, depending on your geographic location and the destination you are connecting to.
Once the connection process is completed, you will be directed to the default landing page of the Tor Browser. The default search engine employed by the Tor Browser is DuckDuckGo, known for its robust privacy features.

Tips on Getting Started with Tor Browser on Debian 12, 11 or 10
While the Tor Browser operates seamlessly once installed, understanding its key features and how to optimize your user experience can enhance your overall journey. The following tips, tailored explicitly for Linux-based installations, provide a comprehensive overview to help you master Tor Browser on your Debian system.
Tips for Tor Browser with Debian
- Safety First: Remember, the Tor Browser is designed for privacy and security but isn’t bulletproof. Avoid downloading files or opening documents online, as other apps can open them outside Tor, which may compromise your anonymity.
- Updates Matter: Ensure you’re using the latest version of Tor Browser. Regular updates provide new features and address security vulnerabilities, enhancing your protection level.
- Bookmark Wisely: Tor Browser does allow for bookmarking your favorite sites. However, be mindful of the bookmarks you create. Avoid bookmarking sites that might reveal personal information or preferences that could compromise your anonymity.
- HTTPS Always: While Tor encrypts your traffic within the network, it doesn’t encrypt it end-to-end. Utilize HTTPS versions of websites whenever possible to maintain data encryption beyond the Tor network.
Customizing the Tor Browser with Debian
A personalized browser can significantly enhance your browsing experience. Here are a few steps to customize your Tor Browser:
- Personal Security Settings: Navigate to the Torbutton (an onion icon), select ‘Privacy and Security Settings’, and adjust according to your needs. Be aware that higher security levels may impact website functionality.
- Modify Display Settings: You can customize your browser’s look and feel to suit your preferences. Click on the three horizontal bars at the top right corner, select ‘Customize…’, and drag your preferred items onto the toolbar.
Other Tor Browser Useful Tips with Debian
- Tor Network Settings: If Tor is censored in your country or network, go to the Torbutton > ‘Tor Network Settings’. You can configure a bridge or a local proxy to bypass censorship.
- No Torrents: Don’t use Tor for torrenting. The Tor network isn’t designed to handle high-bandwidth traffic, and torrenting can expose your IP address, negating Tor’s anonymity.
- Avoid Personal Information: Even while using Tor, avoid sharing sensitive information like your real name, address, or phone number.
Remember, the primary purpose of the Tor Browser is to enhance your online privacy.
Managing Tor Browser on Debian 12, 11 or 10
Once you have set sail on your journey of digital privacy with the Tor Browser, it’s paramount to understand how to maintain your course by regularly updating your browser and, if necessary, removing the browser.
Updates for Tor Browser on Debian
APT Update Method for Tor Browser:
For those who chose the APT method, the command you’ll need to enter in your terminal window to update your browser is:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThis command instructs the system to fetch the latest information regarding available packages (apt update) and then upgrade any packages where newer versions are available (apt upgrade).
Manual installations must follow the original process if a new binary is required.
Flatpak Update Method for Tor Browser:
On the other hand, if you selected the Flatpak installation method, your update command would look slightly different:
flatpak updateWith this command, your system will look for updates within the Flatpak application and apply them accordingly.
Remove Tor Browser From Debian
While the Tor Browser is an excellent tool for secure browsing, there may come a time when you wish to uninstall it. As with updating, uninstalling the Tor Browser depends on your original installation method.
APT Remove Method for Tor Browser:
To uninstall Tor Browser using the APT method, the following command should be used:
sudo apt remove tor torbrowser-launcherManual Remove Method for Tor Browser:
Unregister the application icon and delete the directory if you’ve opted for a manual installation. Here’s how:
First, navigate to the application directory:
cd ~/.local/share/applications/Then remove the Tor Browser desktop file:
rm tor-browser.desktopFinally, remove the Tor Browser directory:
rm -rf /usr/local/share/tor-browser/Flatpak Remove Method for Tor Browser:
For those who installed the Tor Browser via Flatpak, use the following command to uninstall:
flatpak remove --delete-data com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcherConclusion
You’ve learned how to install, launch, use, and manage the Tor Browser on Debian Linux 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, and Debian 10 Buster. With this knowledge, the Tor Browser gives you improved privacy and security when browsing the web.
In today’s digital world, online privacy is essential. The Tor Browser helps you browse confidently, reducing your online footprint.






Worthless guide, nothing worked.
Well, this comment without being rude I find useless, as I got nothing to go on. What Debian version did you try this on? What Arch was it? Did you try all three methods or just a single one and then gave up?
I just tested on Debian 12, worked fine. So without feedback that has a shred of information for me to narrow down a test environment to see if something else is going on I need to update, reflect or change methods for certain things, I will just take this comment as a pinch of salt.
Best Regards,
J.J