Flatpak, a groundbreaking software utility, offers a streamlined method to install, manage, and execute containerized applications on Linux systems, including Debian distributions. For those aiming to install Flatpak on Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, or Debian 10 Buster, understanding its core features and advantages is essential.
Key Attributes of Flatpak:
- Robust Sandboxing: Flatpak enhances security by running applications in isolated environments, minimizing potential system vulnerabilities.
- Universal Deployment: With Flatpak, users can seamlessly install applications, bypassing the typical dependency and system requirement hurdles. This universality ensures compatibility across various Linux distributions.
- Efficient App Management: Flatpak offers a hassle-free approach to application lifecycle management, from installation to updates and removal. It also supports managing multiple application versions concurrently.
- Consistent Experience: Regardless of the underlying Linux distribution, Flatpak ensures a uniform application appearance and behavior.
Flathub: The Go-To Flatpak Repository: Flathub stands as the primary hub for Flatpak applications, offering diverse software. By integrating the Flathub repository with Debian, users can access many regularly updated, developer-maintained applications.
Why Flatpak Resonates with Debian Users:
- Latest Software Access: Debian users can leverage Flatpak to fetch the newest application versions, bypassing potential limitations of Debian’s native repositories.
- Centralized App Management: Flatpak’s unified management system simplifies software handling on Debian, from installation to updates.
- Enhanced Security Posture: Flatpak’s inherent sandboxing amplifies Debian’s security, segregating applications from the core system components.
In essence, Flatpak presents Debian users with an advanced, secure, and user-friendly avenue for software management. By integrating Flatpak and activating the Flathub repository, Debian users can tap into a rich ecosystem of containerized applications. The subsequent sections will guide you on how to install Flatpak on Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, or Debian 10 Buster, unlocking a vast array of software options.
Install Flatpak on Debian 12, 11, or 10 via APT
Step 1: Update Debian Linux Before Flatpak Installation
Before installing Flatpak on your Debian system, it’s essential to ensure that all existing packages are up-to-date. Updating your system helps to avoid potential conflicts and ensures a smooth installation process.
To update your Debian system, execute the following command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeStep 2: Install Flatpak on Debian via APT Command
Debian includes Flatpak in its standard stable repository by default. This means you don’t need to add repositories to install Flatpak.
To initiate the installation, run the following command:
sudo apt install flatpakThis command will fetch and install the necessary Flatpak packages onto your Debian system.
Step 3: Enable Flathub Repository on Debian
Flathub is a popular and comprehensive repository for Flatpak applications. By enabling Flathub, you gain access to a vast collection of applications from various developers and vendors, which are frequently updated and maintained.
To enable Flathub on your Debian system, execute the following command:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoThis command adds the Flathub repository to your Flatpak configuration, making it available for application installations.
Step 4: Reboot the System
After completing the previous steps, it’s a good practice to reboot your system to ensure that any changes are applied correctly. This step also helps to verify that your system is running without any issues after the installation.
To reboot your system, use the following command:
sudo rebootOnce your system restarts, Flatpak will be installed and configured with the Flathub repository enabled.
Launching Flatpak GUI on Debian 12, 11 or 10
Step 1: Install GNOME Software
To access and manage Flatpak applications via a graphical user interface (GUI), we will need to install GNOME Software. This application provides a user-friendly platform for browsing, installing, and managing Flatpak applications from the Flathub repository.
To install GNOME Software on your Debian system, execute the following command:
sudo apt install gnome-software-plugin-flatpakThis command will install GNOME Software and the necessary plugin for Flatpak support.
If this fails to show, reboot your computer.
Step 2: Launch GNOME Software
Once the installation is complete, you can launch GNOME Software to start browsing and managing Flatpak applications. GNOME Software is in your system’s application menu, usually labeled as “Software” or “GNOME Software.”
Step 3: Browse and Install Flatpak Applications on Debian
With GNOME Software open, you can explore the vast Flatpak applications on Flathub. To find and install an application, follow these steps:
- Use the search bar to look for a specific application or browse through categories to discover new applications.
- Click on the desired application to open its information page, which includes a description, screenshots, and user reviews.
- To install the application, click on the “Install” button. The application will be downloaded and installed as a Flatpak package.
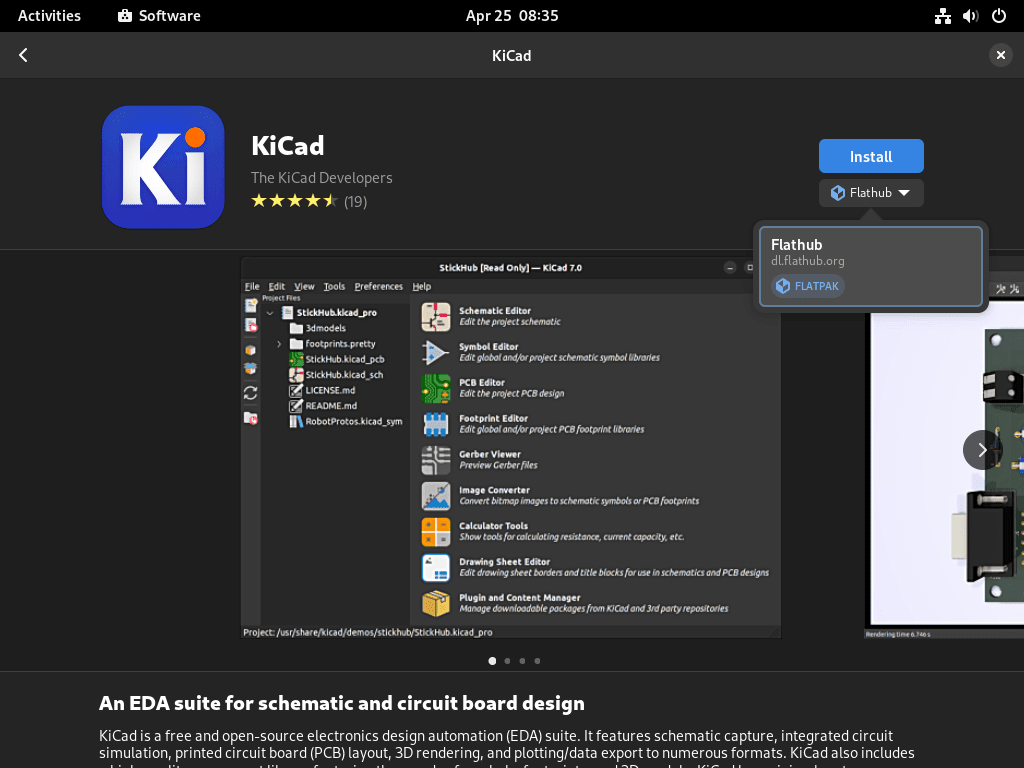
Step 4: Launch and Manage Installed Flatpak Applications
After installing an application through GNOME Software, you can launch it directly from the application’s information page or your system’s application menu. Additionally, you can use GNOME Software to manage your installed Flatpak applications. This includes updating, removing, and viewing information about each application.
Flatpak Common Commands Examples on Debian 12, 11, or 10
This section will explore some commonly used Flatpak commands with examples. Using the command line, these commands will help you manage Flatpak applications on your Debian system.
Step 1: Search for Flatpak Applications
To search for a specific Flatpak application in the Flathub repository, use the following command:
flatpak search [application_name]Replace [application_name] with the name of the application you are looking for. For example, to search for GIMP, execute:
flatpak search gimpThis command will display a list of matching applications, along with their application IDs and descriptions.
Step 2: Install Flatpak Applications
To install a Flatpak application from Flathub, use the following command:
flatpak install flathub [application_id]This command will download and install the selected application as a Flatpak package.
Step 3: List Installed Flatpak Applications
To view a list of all installed Flatpak applications on your system, use the following command:
flatpak listThis command will display a list of installed applications and their application IDs, versions, and branches.
Step 4: Update Flatpak Applications
To update all installed Flatpak applications on your system, execute the following command:
flatpak updateThis command will check for updates and apply them to your installed Flatpak applications.
Step 5: Remove Flatpak Applications
To remove a Flatpak application from your system, use the following command:
flatpak uninstall [application_id]Replace [application_id] with the application ID of the application you want to remove. For example, to remove GIMP, execute:
flatpak uninstall org.gimp.GIMPThis command will uninstall the selected application and remove its associated data.
Conclusion
In this guide, we have successfully demonstrated how to install Flatpak and enable the Flathub repository on Debian Linux. Following these steps, you can easily access, install, and manage a wide range of containerized applications on your Debian system. We also covered the basics of using GNOME Software to manage Flatpak applications through a graphical user interface and some common Flatpak command-line examples for more advanced users.
With Flatpak and Flathub enabled on your Debian system, you can enjoy the benefits of containerized applications, such as easy updates, sandboxed environments, and a vast selection of applications from various developers and vendors.

