Navigating system processes and monitoring resources is crucial for any system administrator. While traditional tools like ‘top’ have been the go-to for many, htop emerges as a superior, user-friendly alternative. This guide will elucidate how to install Htop on Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, or Debian 10 Buster, ensuring you have an efficient system monitoring tool at your fingertips.
Noteworthy Features of htop:
- Real-Time System Snapshot: Unlike ‘top,’ htop presents a comprehensive view of the system’s status, including CPU usage, memory consumption, and more, all on a single screen.
- Simplified Process Management: htop allows for direct process management. Users can navigate and manage processes in real-time without referencing specific process IDs.
- Visual Appeal: With its color-coded interface, htop makes data interpretation straightforward. The colors, which differentiate between used and free resources, can also be customized.
- Interactive Interface: htop’s interface is visually appealing and interactive. Users can scroll vertically to view processes and horizontally to see complete command lines.
- Customization Galore: From setting up a process tree view by default to adjusting display settings, htop provides many customization options.
- Safer Process Termination: htop allows users to terminate processes without entering their process number, minimizing the risk of ending the wrong one.
With htop, system monitoring becomes a more streamlined and intuitive process. Its features cater to both novices and experienced users, making it a valuable tool for anyone keen on efficient system management.
The subsequent sections of this guide will delve into the installation process of htop on Debian systems. By the end, you’ll be well-equipped to harness the full capabilities of this dynamic system monitoring tool.
Install Htop on Debian 12, 11, or 10 via APT
Step 1: Refresh Debian Packages Before Htop Installation
Before you install htop, update your system packages. Use the following command to update the package list and upgrade the system packages:
Here’s what the command does:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThe sudo apt update command scans your repository to check for any new, removed, or updated software packages.
Step 2: Install Htop via APT Command on Debian
With your current system, you can move forward with installing htop. This tool is readily available in the Debian repository and can be fetched and installed using the apt package manager.
Here’s the command that does the job:
sudo apt install htopThis command tells your system to download and install the htop package on your machine. The sudo prefix ensures you have the necessary administrative privileges for the installation process.
Step 3: Verify Htop Installation on Debian
After installing htop, always check its version to confirm successful installation.
Use this command to check the htop version:
htop --versionRunning this command will display the htop version installed on your Debian system, confirming a successful installation.
Basic Htop Commands with Debian 12, 11 or 10
This section will guide you through the essential htop commands, providing examples and detailed explanations to enhance your understanding and usage of this versatile tool.
Initiating Htop on Debian
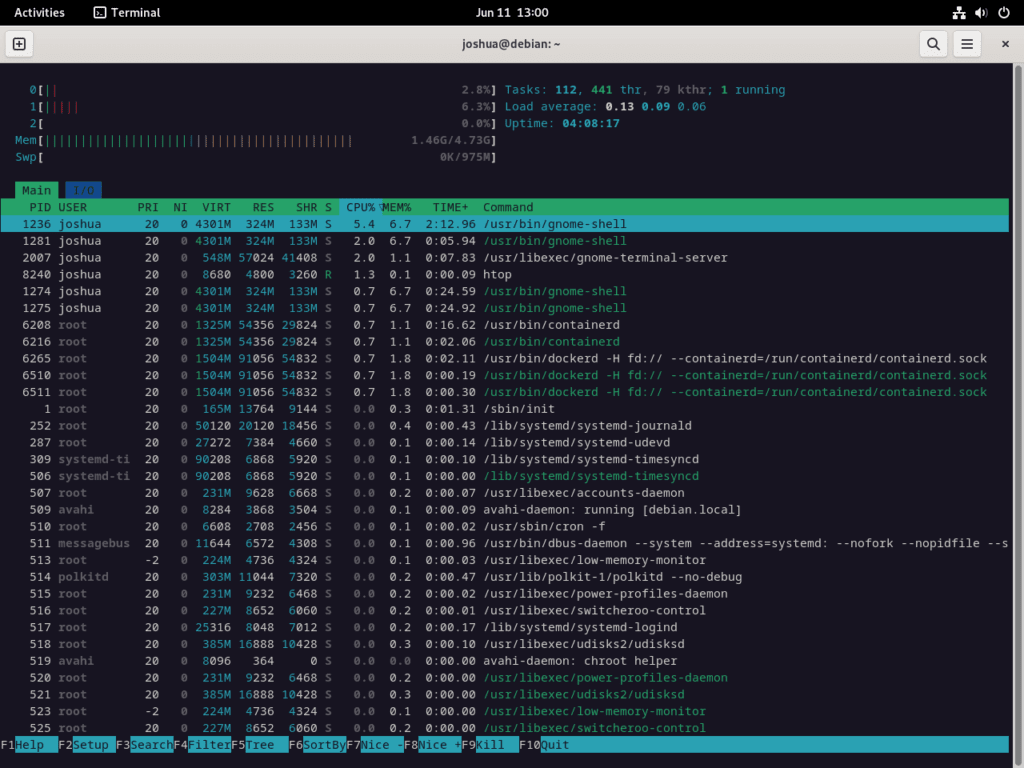
htopUpon execution, htop provides a live, interactive glimpse of your system’s resources – like CPU and memory usage – and the active processes. It paints a vivid picture of the system’s workings, making it a pleasure to interact with.
Process Navigation and Sorting in Htop on Debian
Htop offers a user-friendly interface for navigating through and sorting processes. Basic navigation is achieved via:
- Up/Down Arrow Keys: Traverse the list of processes.
- Left/Right Arrow Keys: Toggle between metrics, including CPU usage, memory usage, and process priority.
Sorting processes based on specific metrics can be done by using the function keys:
- F6: Allows for user-defined criteria (such as CPU usage, memory usage, process ID) for sorting processes.
- F5: Enables a tree view of the processes, illustrating the parent-child relationships between processes.
Direct Process Management through Htop on Debian
Htop provides direct process management right from its interface. Key commands include:
- F9: Send signals to the selected process (for instance, SIGTERM to terminate the process, SIGHUP to restart the process).
- F7/F8: Adjust the selected process’s priority (also referred to as the “nice” value). Here, lower values denote higher priority, whereas higher values represent lower priority.
Process Search and Filter in Htop on Debian
Htop comes equipped with search and filter functionalities, enabling you to locate specific processes swiftly:
- F3: Allows you to search for a process by name. After entering the process name, press Enter to highlight the corresponding process in the list.
- F4: Filters the process list based on user-defined criteria (like process name, user). Enter your filtering criteria and press Enter to display only the corresponding processes.
Personalize Your Htop Display on Debian
You can customize the htop to suit your preferences better:
- F2: Leads you to the htop setup menu. Here, you can adjust the display, colors, and layout.
Exiting Htop on Debian
To exit htop, either press the F10 key or the Q key. This brings your htop session to a graceful end, allowing you to return to your terminal prompt.
Conclusion
We guided you through how to install and use htop on Debian. We covered everything from setting up and updating packages to mastering Htop’s command-line interface. Now, htop is installed on your Debian system. You can use its features for system monitoring, managing processes, and searching. With this knowledge, you can fully utilize htop.