In-home media solutions, Plex Media Server, emerges as a dynamic and comprehensive platform. For Debian users, integrating Plex offers a seamless media management experience. This guide will elucidate how to install Plex Media Server on Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, or Debian 10 Buster, ensuring you have an all-in-one media hub tailored to your entertainment needs.
Noteworthy Features of Plex Media Server:
- Consolidated Media Library: Plex seamlessly amalgamates movies, TV shows, music, photos, and more, presenting them in a unified library, eliminating the need to hop between various platforms.
- Smart Organization & Search: With its ability to automatically fetch metadata, Plex enriches your content with cover art, descriptions, and ratings, while its robust search functionality ensures you find what you’re looking for in no time.
- Sleek User Interface: Plex boasts a visually captivating interface, enhancing the user experience and making content discovery delightful.
- Plex Pass Perks: The Plex Pass subscription elevates your media experience, offering features like Live TV & DVR, Mobile Sync, Parental Controls, and more.
- Broad Device Support: Plex ensures you can enjoy your media on many devices, from smartphones and tablets to smart TVs and gaming consoles.
- Anywhere Access: With Plex, your media library is always within reach, accessible from any location with internet connectivity.
- Content Sharing: Plex allows you to share your media treasures with friends and family, fostering a shared entertainment experience.
- Expandable with Plugins: The Plex community offers a plethora of plugins, enabling users to further enhance the server’s capabilities and integrate new features.
Having highlighted the myriad advantages of Plex Media Server, the subsequent sections of this guide will delve into the installation process on Debian systems, setting the stage for an unparalleled media journey.
Install Plex Media Server on Debian 12, 11, or 10 via APT
Step 1: Update the Debian System Before Plex Installation
Start by updating your Debian system to ensure a smooth installation process. This ensures all existing packages are up to date:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeStep 2: Install Initial Required Packages For Plex
Plex installation requires some additional packages. Install them by running the following command:
sudo apt install dirmngr ca-certificates software-properties-common apt-transport-https curl -yThese packages will provide the tools for handling the Plex repository, including secure connections and GPG key management.
Step 3: Import Plex APT Repository on Debian
Add the Plex repository to your Debian system to install Plex from the official source. This ensures you install and update the software directly from the official repository using the APT package manager.
First, open your terminal and import the Plex GPG key with the following command:
curl -fsSL https://downloads.plex.tv/plex-keys/PlexSign.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo tee /usr/share/keyrings/plex.gpg > /dev/nullThis command downloads the Plex GPG key, which is used to verify the authenticity of the packages from the repository.
Next, add the Plex repository to your system:
echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/plex.gpg] https://downloads.plex.tv/repo/deb public main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/plexmediaserver.listThis command creates a new file in the sources.list.d directory with the necessary information about the Plex repository.
Step 4: Install Plex Media Server via APT Command on Debian
Before installing Plex, update your package index to include the newly added Plex repository:
sudo apt updateNow you can install Plex Media Server on Debian using the following command:
sudo apt install plexmediaserverDuring the installation, you may see a prompt asking if you want to replace the imported repository list with Plex.
Type “N” to proceed with the installation, as you do not want to replace the imported repository list. This is because the correct signed-by GPG key is already in place.
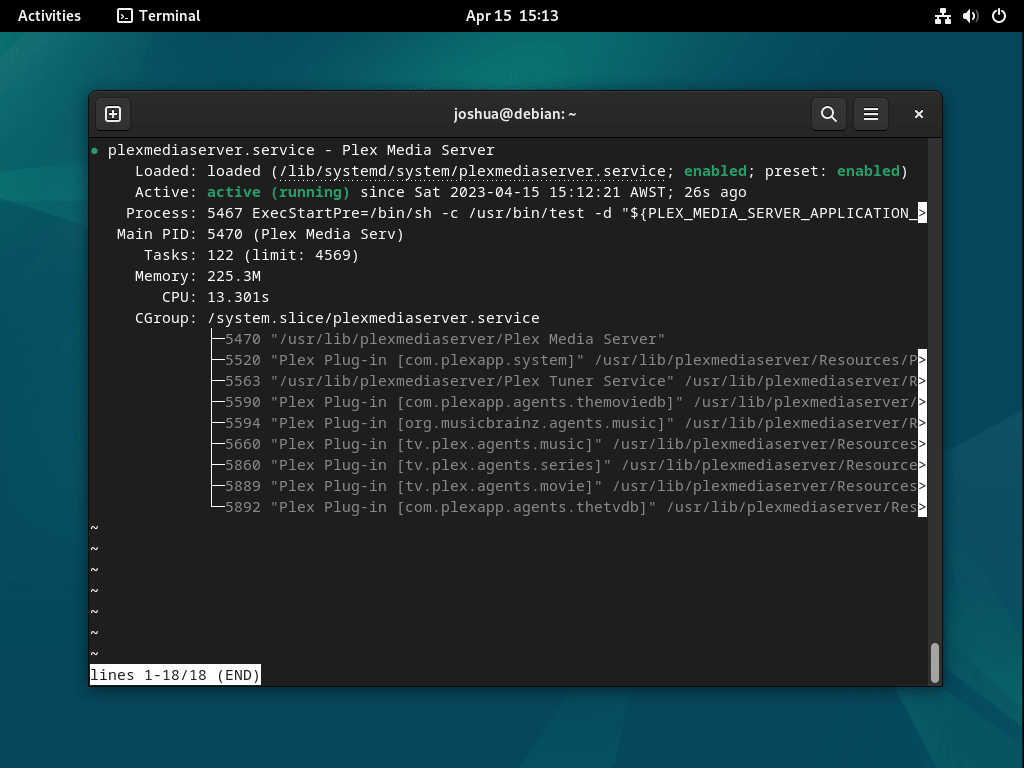
Step 5: Verify Plex Media Server Installation
By default, the Plex Media service should start automatically. To verify this, use the following systemctl command to check the status:
systemctl status plexmediaserverIf the service is not active, use the following command to start Plex Media Server:
sudo systemctl start plexmediaserverTo ensure Plex Media Server starts automatically on system boot, enable the service with this command:
sudo systemctl enable plexmediaserverIf you need to restart the Plex Media Server service for any reason, use the following command:
sudo systemctl restart plexmediaserverConfigure UFW Firewall for Plex Media Server on Debian 12, 11 or 10
Securing your Plex Media Server is crucial, especially when you plan to access it remotely or allow others to access it. UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) is a great way to protect your server.
Step 1: Enable the UFW Firewall
First, check if UFW is installed on your system. If not, install it using the following command:
sudo apt install ufw -yNext, enable UFW with this command:
sudo ufw enableStep 2: Add Plex Media Server Port Rules
Add the default Plex Media Server port (32400) to the UFW rules. You can customize the port later if you wish. If you change the Plex Media Server dashboard port, remember to delete this rule and add a new one.
sudo ufw allow 32400Step 3: Additional UFW Rules for Plex
Plex Media Server uses several additional ports for different services and connections. To allow them through the UFW firewall, use the following commands:
sudo ufw allow 1900/udp
sudo ufw allow 3005/tcp
sudo ufw allow 5353/udp
sudo ufw allow 8324/tcp
sudo ufw allow 32410:32414/udpHere’s a brief explanation of the ports and their purposes:
- 1900/udp: Used to discover Plex Media Server by clients over the network.
- 3005/tcp: Required for Plex Companion, a feature that allows you to control Plex playback from a mobile device.
- 5353/udp: Used for mDNS (Multicast Domain Name System) to help Plex discover devices on the local network.
- 8324/tcp: Required for the Plex DLNA server.
- 32410:32414/udp: Used for media streaming to clients.
Adjust your UFW rules if you customize any of the ports mentioned above. Configuring the UFW firewall for your Plex Media Server can ensure a more secure and protected media hub experience on your Debian system if it faces public connections.
Configure SSH For Plex Media Server on Debian 12, 11, or 10
This section can be skipped and is only useful for those that will be using SSH to login into a remote Debian desktop or server.
If you’ve installed Plex Media Server on a remote headless server or another Debian desktop you don’t always have local access to, you’ll need to set up an SSH tunnel on your local computer for the initial setup. This allows outside connections to access the Plex server.
Step 1: Set up the SSH Tunnel
Replace {server-ip-address} with the actual IP address of your server, for example, 192.168.50.1.
Example:
ssh {server-ip-address} -L 8888:localhost:32400If you’re new to SSH and haven’t installed it yet, you can do so with the following commands:
sudo apt install openssh-server -y
sudo systemctl enable ssh --nowStep 2: Access Plex Media Server via SSH Tunnel
Now you can access the Plex Media Server by opening the following address in your web browser:
http://localhost:8888/webOr use the alternative address if the above one does not work:
https://localhost:8888/web/index.html#!/setupThe HTTP request will be redirected to http://localhost:32400/web on the remote server through the SSH tunnel.
Step 3: Access Plex Media Server Remotely
Once you’ve completed the initial setup, you can access your Plex Media Server using your remote server’s IP address:
http://{server-ip-address}:32400Section 5: Configuring Plex Media Server in WebUI on Debian
Now that Plex is installed on your system, you must configure and complete the setup through the WebUI. The WebUI enables you to manage your media library and customize your server settings. Follow the steps below to access and configure the Plex Media Server in WebUI:
Step 1: Access the WebUI
To access the WebUI, open your preferred internet browser and navigate to one of the following addresses:
http://127.0.0.1:32400/webor
http://localhost:32400/webIf these two do not work, try using the following address:
http://localhost:32400/web/index.html#!/setupNow, you can log in using an existing social media account listed above or with your email to register a new account if you are new to Plex. Once logged in, you will begin the initial configuration setup.
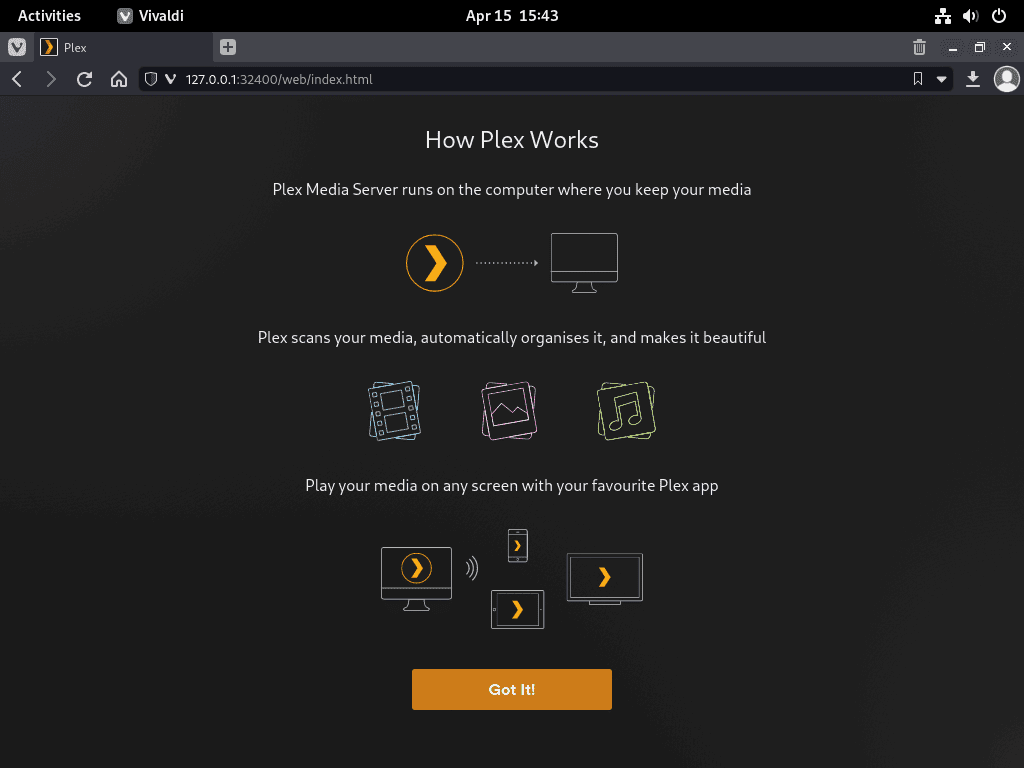
Step 2: Understanding Plex
The first configuration page briefly explains what Plex is and how it works.
Depending on your internet browser, Firefox users may see a message prompting them to enable DRM. This choice is necessary; without it, Plex WebUI may not work correctly.
Click GOT IT! to proceed.
Step 3: Optional Plex Pass
Next, you will be prompted to upgrade to Plex Pass, which is optional. Plex Pass offers benefits like HDR options and access to beta builds.
If you want to skip this, click the X in the top right-hand corner. You can always set this up later.
Step 4: Server Setup
Configure your server name, which can be anything you desire. You also have the option to disable Allow me to access my media outside my home. By default, access to outside media is enabled; untick the feature if you don’t plan to do so.
Once configured, click the NEXT button.
Step 5: Media Library
The Media Library page gives you the option to pre-add your media directories.
If you have a media drive or folder ready, click the ADD LIBRARY button.

Now select the type of media you want your folders to be organized into, such as TV shows, movies, music, etc. Click the NEXT button to proceed to add folders.
Click the BROWSE FOR MEDIA FOLDER button and select the media directory. Once the folder is added, the Advanced options will appear, where you can further customize Plex to your liking.
When you’re done, click ADD LIBRARY to continue to the Finish tab.
Step 6: Finishing up
Next, hit the NEXT button to finish the initial setup, with or without adding a Media Library. The next screen informs you that you’re all set.
Click the DONE button to proceed to the Plex Dashboard.
Configure Files & Folders Permissions on Debian 12, 11 or 10
You may have noticed that your media did not appear during the initial setup. You may have problems adding content that will not be picked up, with Plex refusing to find the content on your existing internal and external secondary hard drives. This is partly due to Plex creating a dedicated user account named plex, which needs read and execute permission on your media directories.
Debian permissions can be set using chown or setfacl; both are effective. Below are some examples of how to apply these commands to ensure proper access.
Step 1: Set permissions using setfacl
To set permissions using setfacl, execute the following commands, replacing /media/yourfolder/ with the path to your media directory:
sudo setfacl -R -m u:plex:rx /media/yourfolder/
sudo setfacl -R -m u:plex:rx /media/yourfolder/tv
sudo setfacl -R -m u:plex:rx /media/yourfolder/moviesStep 2: Set permissions using chown
To set permissions using chown, execute the following commands, replacing /media/yourfolder/ with the path to your media directory:
sudo chown -R plex:plex /media/yourfolder/Or set permissions for individual files in the hard drive if other folders are present that you do not want Plex to access:
sudo chown -R plex:plex /media/yourfolder/tv
sudo chown -R plex:plex /media/yourfolder/moviesStep 3: Install ACL package (if necessary)
If the commands above are not working, you may need to reinstall the ACL package if it is missing from your system:
sudo apt install acl -ySetup Nginx Reverse Proxy for Plex Media Server on Debian 12, 11, or 10
This section can be skipped if you do not plan to use Plex through a reverse proxy setup.
Setting up a reverse proxy allows you to access Plex Media Server from a remote computer or network. In this example, we will set up an Nginx proxy server.
Step 1: Install Nginx
First, install Nginx with the following command:
sudo apt install nginx -yBy default, Nginx should be enabled. If it is not activated, use the following command:
sudo systemctl start nginxNow check to make sure Nginx is activated and has no errors:
sudo systemctl enable nginxNow check to make sure Nginx is activated and has no errors:
systemctl status nginxStep 2: Create a Plex Nginx Server Block
Create a new server block as follows:
sudo nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/plex.confYou will need an active domain name and need to create a sub-domain. Once done, add the following to the server block file:
server {
listen 80;
server_name plex.example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:32400;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
#upgrade to WebSocket protocol when requested
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "Upgrade";
}
}Save the file (CTRL+O), then exit (CTRL+X).
Step 3: Test Nginx Configuration
Perform a dry run to ensure there are no errors in the Nginx configuration or your server block:
sudo nginx -tIf everything is working correctly, the example output should be:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Reload Nginx for the change to take effect:
sudo systemctl reload nginxIf you have set up your domain and DNS records to point to your server IP, you can now access your Plex Media Server at plex.example.com.
Step 4: Secure Nginx Reverse Proxy with Let’s Encrypt SSL Free Certificate
It is recommended to run your Nginx on HTTPS using an SSL certificate. You can use Let’s Encrypt, a free, automated, open certificate authority run by the nonprofit Internet Security Research Group (ISRG).
First, install the certbot package as follows:
sudo apt install python3-certbot-nginx -yOnce installed, run the following command to start creating your certificate:
sudo certbot --nginx --agree-tos --redirect --hsts --staple-ocsp --email you@example.com -d www.example.comThis setup includes force HTTPS 301 redirects, a Strict-Transport-Security header, and OCSP Stapling. Make sure to adjust the email and domain name to your requirements.
Now your URL will be https://plex.example.com instead of http://plex.example.com. If you use the old HTTP URL, it will automatically redirect to HTTPS.
Step 5: Set Up Nginx Automatic SSL Certificate Renewal
Optionally, you can set a cron job to renew the certificates automatically. Certbot offers a script that does this automatically. First, test to make sure everything is working by performing a dry run:
sudo certbot renew --dry-runIf everything is working, open your crontab window using the following terminal command:
sudo crontab -eNext, specify the time when the certificate should auto-renew. This should be checked daily at a minimum, and if the certificate needs to be renewed, the script will update the certificate.
Add the following line to your crontab:
00 00 */1 * * /usr/sbin/certbot-auto renewThis command will check for certificate renewal daily at midnight. If a certificate is due for renewal, it will automatically update it. This ensures that your SSL certificate stays up to date and your reverse proxy remains secure.
Getting Started with Plex Media Server on Debian 12, 11, or 10
This section will cover some tips and tricks to enhance your experience with Plex Media Server on Debian Linux.
General Plex Media Server Tips with Debian
- Organize your media: Use a consistent naming and folder structure for your media files. This makes it easier for Plex to recognize and categorize your content. Check the Plex Naming Guide for more information.
- Optimize database performance: Regularly optimize the Plex database to improve performance and reduce the chance of issues. To do this, go to
Settings>Server>Scheduled Tasksand enableOptimize DatabaseandClean Bundles.
Plex Media Server Customizations with Debian
- Customize your Dashboard: Tailor the Plex Dashboard to your preferences by pinning or unpinning libraries, adding or removing sections, and reordering items. To customize your Dashboard, click on the
Customizebutton in the top-right corner. - Enable or disable automatic media analysis: Plex automatically analyzes your media files for quality, duration, and other information. If you prefer to control this process manually, go to
Settings>Server>Libraryand toggleAnalyze media files. - Adjust video quality settings: To optimize video playback quality and performance, go to
Settings>Qualityand adjust the streaming quality settings based on your network conditions and device capabilities.
Other Plex Media Server Tips with Debian
- Use keyboard shortcuts: Learn and use Plex keyboard shortcuts to quickly navigate and control playback. Some common shortcuts include:
- Spacebar: Play/PauseF: Full-screen toggleS: Stop playbackM: Mute/Unmute
- Enable subtitles: Plex supports subtitles in various formats, such as SRT, SSA, and ASS. To enable subtitles, click the speech bubble icon during playback and select the desired subtitle track.
- Control Plex with your smartphone: Download the Plex mobile app to control playback and manage your server from your smartphone. The Plex mobile app is available for both Android and iOS.
Following these tips, you’ll be able to get the most out of your Plex Media Server on Debian Linux.
Additional Commands For Plex Media Server on Debian 12, 11, or 10
Update Plex Media Server on Debian
Keep your Plex Media Server current to ensure you have the latest features, bug fixes, and security patches.
To check for updates, run the following command:
sudo apt updateIf an update is available, use the upgrade command to update Plex Media Server:
sudo apt upgrade plexmediaserverOr update all packages at once along with Plex Media Server:
sudo apt upgradeRemoving Plex Media Server From Debian
If you no longer wish to use Plex and want to remove it from your Debian system, follow these steps.
Step 1: Uninstall Plex Media Server
Execute the following command to remove Plex Media Server from your system:
sudo apt remove plexmediaserverStep 2: Disable Nginx reverse proxy (if applicable)
If you installed the Nginx reverse proxy, don’t forget to disable it and, if needed, delete the configuration file associated with your domain.
To disable the Nginx reverse proxy, run the following command:
sudo systemctl disable nginx --nowTo remove the configuration file, use the following:
sudo rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/plexmediaserver.listFinally, reload Nginx to apply the changes:
sudo rm usr/share/keyrings/plex.gpgConclusion
In conclusion, installing Plex Media Server on Debian Linux is a straightforward process that enables you to create a powerful and flexible media server for your home or organization. Following the steps outlined in this guide, you can have a fully functioning Plex Media Server up and running quickly. Remember to keep your server updated and maintained to ensure optimal performance and security.






Thanks for the guide, very straightforward, I got my Plex server container up in 3 minutes or so.
Following issues with DLNA, I noticed shortly after that the firewall ports mentioned in this article don’t match (anymore?) with those in the official documentation: https://support.plex.tv/articles/201543147-what-network-ports-do-i-need-to-allow-through-my-firewall
In particular:
1. Port 3005/tcp, here stated as “Required for Plex Companion” is actually not (anymore?) necessary, see also 8324/tcp below
2. Port 32469/tcp, is mentioned in official documentation to be necessary to access to the Plex DLNA Server
3. Port 8324/tcp, here stated as “Required for the Plex DLNA server” is mentioned in official documentation to be used for “Controlling Plex for Roku via Plex Companion”
Greetings
Lots of articles out there on how to install Plex on Raspberry Pi with Debian. This was the article which got me past issues I was having. Very well done and thank you.
Hi James,
Thanks for feedback, I appreciate it.
Personally, I have moved my personal media server to Jellyfin Media Server recently after using Plex for a very long time, and really enjoying it. It also supports AMD64, ARMHF, and ARM64 architectures.
If Plex gives issues in the future or you start getting unhappy with it, I would personally recommend to try Jellyfin out.