This guide will demonstrate how to install Nvidia Drivers on Rocky Linux 9 or 8 utilizing the command-line terminal and the Nvidia CUDA repositories built for Enterprise Linux 9 or 8 for the latest Nvidia and CUDA builds.
Nvidia drivers are pivotal for unleashing the full potential of Nvidia graphics cards, enhancing both the computational power and graphical performance of computers. These drivers bridge the operating system and the hardware, enabling a wide range of applications from gaming to professional rendering and scientific computation. Nvidia’s continuous updates ensure compatibility with the latest software and games, optimizing performance and providing new features and improvements. With the integration of CUDA technology, Nvidia drivers also unlock the power of GPU computing, allowing for accelerated applications in areas such as machine learning, data science, and video processing. The importance of keeping these drivers up-to-date cannot be overstated, as they significantly affect the efficiency and reliability of GPU-intensive tasks.
- Seamless Integration: Ensures flawless communication between the GPU and the operating system.
- Peak Performance: Optimizes graphical and computational tasks for smooth, efficient operation.
- Future-Proof: Regular updates keep the system compatible with the latest applications and games.
- CUDA Support: Enables GPU acceleration for complex computational tasks, vastly improving performance.
- Enhanced Stability: Minimizes crashes and bugs, ensuring reliable system performance.
- Customizable Settings: Allows fine-tuning of graphics settings to match user preferences and system capabilities.
- Energy Efficiency: Optimizes power usage for balance between performance and energy consumption.
- Extended Support: Provides long-term support for a wide range of Nvidia products.
Transitioning to the technical aspects, installing Nvidia drivers on Rocky Linux requires careful attention to detail.
Nvidia Drivers Installation Preparations
Update Rocky Linux Before Nvidia Drivers Installation
The first thing to do before commencing the installation process is to update your system. Doing so will avoid potential conflicts during the installation, often caused by out-of-date packages. To accomplish this task, the command that you need to execute is:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshIdentifying Your Graphics Card
As you progress, it’s important to identify the NVIDIA Graphics card installed in your system. Verifying its compatibility will ensure a smooth installation process. However, you can skip this step if you have a newer model, as they are likely supported.
You can use the following command to determine your graphics card model:
lspci | grep -e VGAThis is what an example output may look like:
03:00.0 VGA compatible controller: NVIDIA Corporation TU117 [GeForce GTX 1650] (rev a1)In case you’re using an older card, it’s prudent to conduct a quick check on NVIDIA’s official website. You might need to install legacy drivers if the latest NVIDIA drivers no longer support your card.
Checking the Secure Boot Status
If you have secure boot enabled, you might encounter issues during the NVIDIA drivers installation. You might need to either disable it or take additional steps to avoid conflicts. Thus, it’s crucial to check the status of the secure boot.
You can use the following command to verify if secure boot is enabled:
mokutil --sb-stateThis command will provide output on your terminal, indicating whether the secure boot is active. Depending on your system configuration, you may need to change your system setup. Be sure to consult your system documentation or the troubleshooting section if you encounter issues related to secure boot.
Add EPEL Repository on Rocky Linux For Nvidia Drivers Installation
Setting Up the EPEL Repository for Nvidia Drivers on Rocky Linux
Our initial task involves the installation of the EPEL repository. It is advisable to incorporate both repositories for the best outcome.
Configuring EPEL for Rocky Linux 9
The first action involves activating the CodeReady Builder (CRB). It can be done using this command:
sudo dnf config-manager --set-enabled crbOnce the CRB is activated, you can install both EPEL versions. Utilize the command below to complete this process:
sudo dnf install \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-9.noarch.rpm \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-next-release-latest-9.noarch.rpmConfiguring EPEL for Rocky Linux 8
To setup the EPEL for Rocky Linux 8, you can use the following command:
sudo dnf install \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-8.noarch.rpm \
https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-next-release-latest-8.noarch.rpmIn the context of these instructions, we are activating and integrating an additional repository of software packages to your Linux distribution. This will broaden the selection of software you can install and ensure compatibility with your specific Rocky Linux version.
Install NVIDIA Drivers on Rocky Linux via DNF Commands
Import Nvidia Drivers RPM
The upcoming process requires the installation of the NVIDIA drivers repository sourced from NVIDIA itself. The reason behind this is the convenience it brings by providing immediate access to newly released updates.
Ensure the repository aligns well with your specific Rocky Linux distribution while importing it into your system.
Adding Nvidia Repository RPM for Rocky Linux 9
Use the command below to incorporate the repository into Rocky Linux 9:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel9/$(uname -i)/cuda-rhel9.repoAdding Nvidia Repository RPM for Rocky Linux 8
For Rocky Linux 8, the command changes slightly as follows:
sudo dnf config-manager --add-repo http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel8/$(uname -i)/cuda-rhel8.repoFollowing the repository import, it’s recommended that the necessary dependencies be installed. Some of them might be pre-installed, but running the following command ensures their presence:
sudo dnf install kernel-headers-$(uname -r) kernel-devel-$(uname -r) tar bzip2 make automake gcc gcc-c++ pciutils elfutils-libelf-devel libglvnd-opengl libglvnd-glx libglvnd-devel acpid pkgconfig dkmsOnce done, it’s time to integrate the most recent NVIDIA drivers using:
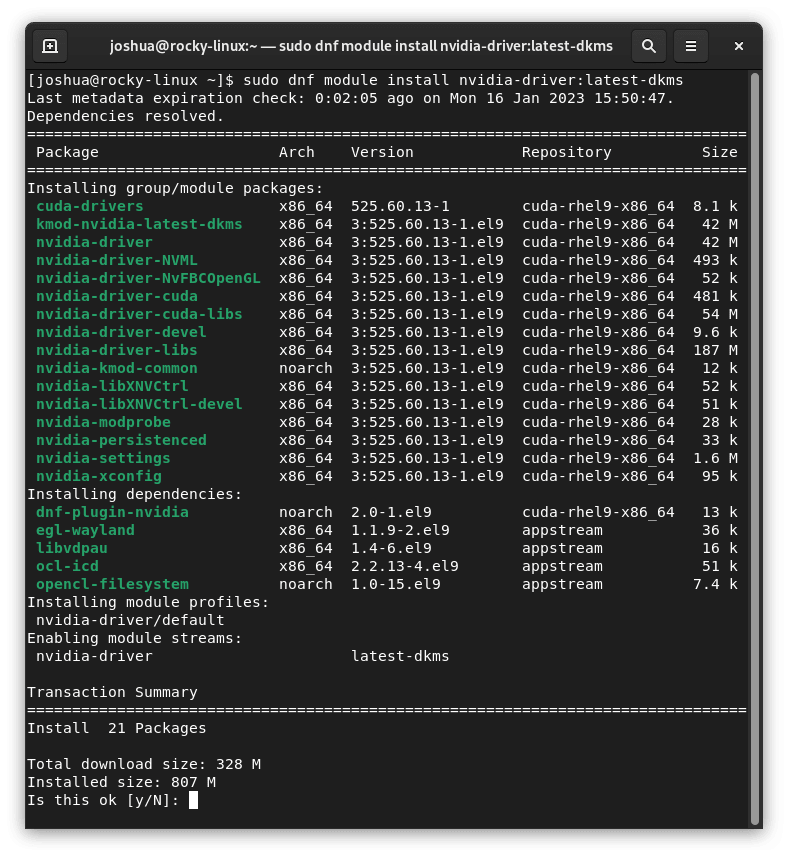
sudo dnf module install nvidia-driver:latest-dkmsYou might encounter a prompt inquiring about importing GPG keys during this step. Should this happen, respond affirmatively with a “Yes.”
To provide you with an idea of what to expect, below is an image showing an example output from my machine:
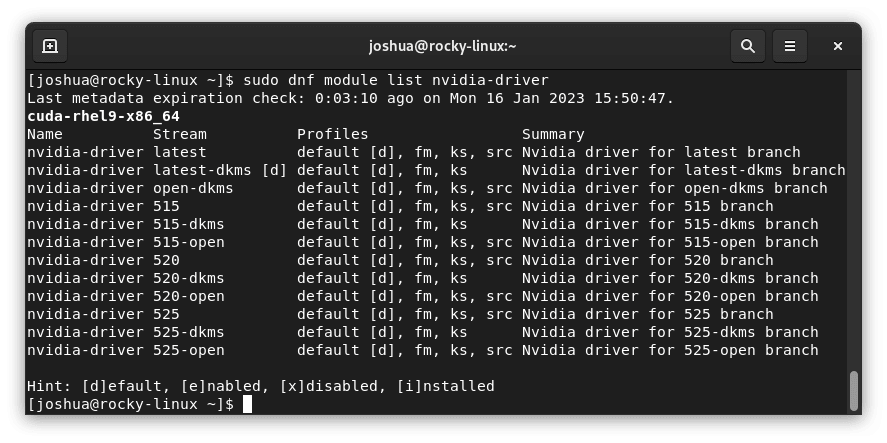
As an alternative, Nvidia RPM modules can be listed using the command:
sudo dnf module list nvidia-driverHere’s another image depicting an example output from this process:
You might consider installing this module instead of the proprietary one if you’re an open-source user. However, feedback indicates that open-source users might encounter bugs depending on the graphics card. If this occurs, switch to the proprietary drivers. Based on user feedback, this switch typically resolves the issue.
For instance:
sudo dnf module install nvidia-driver:open-dkmsAfter successful completion, a system restart is necessary. Use the command:
rebootConfirming the NVIDIA Drivers Installation on Rocky Linux
Execution of NVIDIA-SMI Command
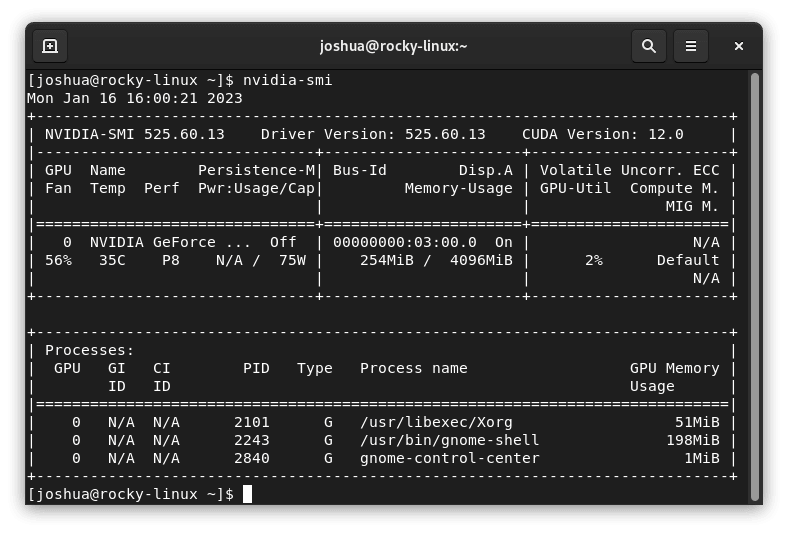
To ascertain the successful installation of the NVIDIA drivers, execute the NVIDIA-SMI command as shown below:
nvidia-smiThis command provides you with an output that serves as evidence of the successful installation. Here is an image to help you anticipate what you should be seeing:
Accessing NVIDIA Settings
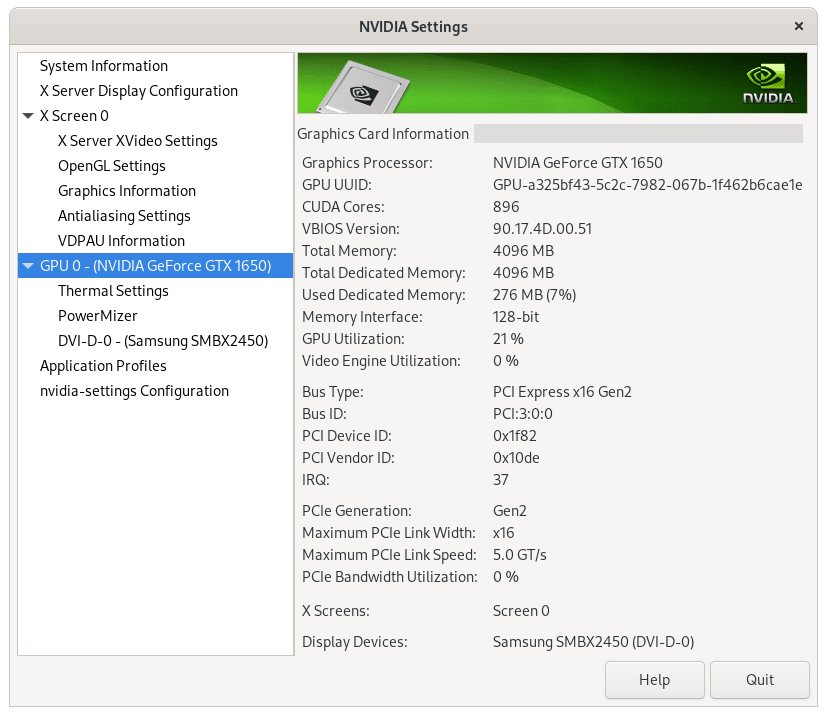
An alternate way to verify the installation is by accessing the NVIDIA settings GUI. This can be accomplished either from the application icon menu or via the command as shown below:
nvidia-settingsLocating the GUI Application Icon
Another route to verification lies in accessing the GUI application icon. This can be done by following the path: Activities > Show Applications > NVIDIA X SERVER within the application menu.
To give you a better understanding of what a successful NVIDIA drivers installation looks like, refer to the following image:
Problem Resolution: Troubleshooting Instructions
These solutions may work, but given the many different system setups, hardware, and potential issues, you may need to do further research.
Addressing Secure Boot Issues with Nvidia Driver Installation
If you’ve installed the NVIDIA drivers and are encountering problems due to Secure Boot, it may be possible to resolve these without disabling Secure Boot. Please follow these steps:
Disabling Nouveau Drivers
Nouveau drivers can cause conflicts with NVIDIA drivers. To prevent these issues, use the following commands to blacklist the Nouveau drivers:
echo "blacklist nouveau" | sudo tee /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist-nouveau.conf
echo 'omit_drivers+=" nouveau "' | sudo tee /etc/dracut.conf.d/blacklist-nouveau.confOnce you’ve made these modifications, regenerate all Dracut initramfs images and update the module dependency list with these commands:
sudo dracut --regenerate-all --force
sudo depmod -aActivating Secure Boot
Should Secure Boot be enabled on your system, importing the Machine Owner Key (MOK) public key will be necessary. This key signs the NVIDIA kernel module. To do this, use the mokutil command:
sudo mokutil --import /var/lib/dkms/mok.pubThe mokutil command will prompt you to create a password, which you’ll use during the system reboot.
Following this, reboot your system:
sudo rebootDuring the reboot, your system may ask for key enrollment. Confirm this request and enter the password you created with the mokutil command.
Checking the Driver Installation
To confirm that the NVIDIA drivers have been successfully installed, run the nvidia-smi command:
nvidia-smiPost-Windows Update Troubleshooting
A firmware update may reset the TPM chip in a dual boot scenario with Windows. You must re-import the Machine Owner Key (MOK) if this occurs. To resolve this, repeat the mokutil command:
sudo mokutil --import /var/lib/dkms/mok.pubThese instructions provide a step-by-step guide through the troubleshooting process to resolve any potential issues you may encounter while installing the NVIDIA drivers.
Conclusion
Installing NVIDIA drivers on Rocky Linux 9 or 8 can be challenging, especially when considering variables like Secure Boot and the Nouveau drivers. However, we’ve aimed to simplify this process for you in this comprehensive guide, detailing each step in an understandable and actionable manner. Whether dealing with conflicts from the Nouveau drivers or managing Secure Boot, the steps provided should enable you to install the NVIDIA drivers successfully.
Our final recommendation is to keep your drivers updated to the latest version to ensure optimal performance and security. Regular updates can prevent many issues before they occur, so it’s worth checking for new versions periodically.


When executing the following:
sudo dnf install kernel-headers-$(uname -r) kernel-devel-$(uname -r) tar bzip2 make automake gcc gcc-c++ pciutils elfutils-libelf-devel libglvnd-opengl libglvnd-glx libglvnd-devel acpid pkgconfig dkms
The following error is thrown:
========================
[azureuser@Rocky9Nvidia ~]$ sudo dnf install kernel-headers-$(uname -r) kernel-devel-$(uname -r) tar bzip2 make automake gcc gcc-c++ pciutils elfutils-libelf-devel libglvnd-opengl libglvnd-glx libglvnd-devel acpid pkgconfig dkms
created by dnf config-manager from http://developer.download.nvidia.com/comput 793 B/s | 433 B 00:00
Errors during downloading metadata for repository ‘developer.download.nvidia.com_compute_cuda_repos_rhel9_x86_64_cuda-rhel9.rep’:
Status code: 404 for http://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel9/x86_64/cuda-rhel9.rep/repodata/repomd.xml (IP: 152.195.19.142)
Error: Failed to download metadata for repo ‘developer.download.nvidia.com_compute_cuda_repos_rhel9_x86_64_cuda-rhel9.rep’: Cannot download repomd.xml: Cannot download repodata/repomd.xml: All mirrors were tried
=====================
The correct location for the missing file is: https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/rhel9/x86_64/repodata/repomd.xml
Is there a way to provide the correct path?