HPLIP (HP Linux Imaging and Printing) is HP’s official driver suite for Linux, providing print, scan, and fax support for over 3,400 HP devices including DeskJet, OfficeJet, LaserJet, and multifunction printers. This guide walks you through installing HPLIP on Fedora Linux, configuring your HP printer or scanner using the setup wizard, and verifying the installation works correctly.
Before proceeding, you can verify your HP device is supported by checking the official HPLIP supported devices list. Most modern HP printers released within the last decade have full driver support.
Update Fedora Packages Before HPLIP Installation
First, update your Fedora system to ensure you have the latest package versions and security patches. Open a terminal by searching for “Terminal” in Activities, then run the following command:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshSpecifically, the --refresh flag forces DNF to refresh repository metadata before upgrading, ensuring you receive the latest available package versions.
Install HPLIP via DNF Command
Next, install HPLIP from Fedora’s default repositories using DNF. Run the following command to install both the core driver package and the graphical configuration tools:
sudo dnf install hplip hplip-guiSpecifically, the hplip package provides the core drivers and command-line utilities for HP printers and scanners. Meanwhile, the hplip-gui package adds graphical tools for device management and configuration. If you prefer a CLI-only setup, you can omit hplip-gui.
Once the installation completes, verify the packages are installed correctly:
rpm -q hplip hplip-guiExpected output confirming successful installation:
hplip-3.25.6-1.fc43.x86_64 hplip-gui-3.25.6-1.fc43.x86_64
Configure HP Printer with HPLIP Setup Wizard
Launch the HPLIP Setup Wizard
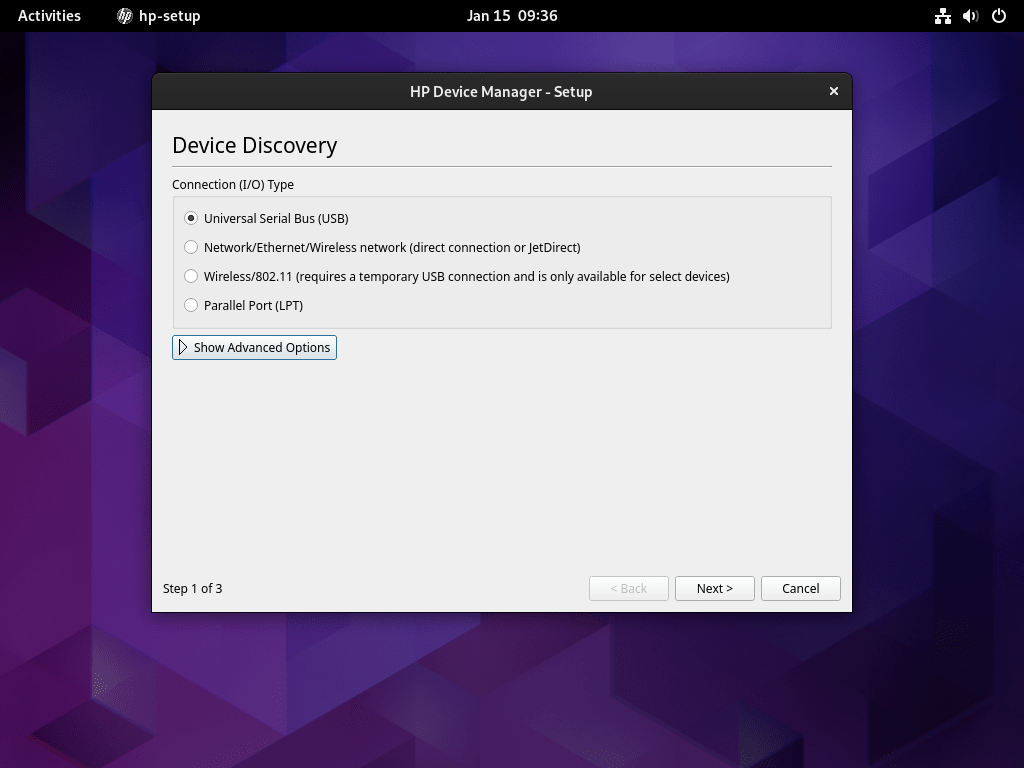
With HPLIP installed, you can now configure your HP printer or scanner using the setup wizard. The wizard automatically detects connected devices and guides you through driver installation and configuration.
To begin, launch the setup wizard from your terminal:
hp-setupRunning
hp-setupwithoutsudois recommended. The wizard will prompt for elevated permissions when needed and displays a warning if run as root.
Once launched, the graphical wizard scans for connected HP devices. Then, follow the on-screen prompts to complete printer configuration.
Configure USB-Connected HP Devices
If your HP printer or scanner connects via USB, you can specify the USB bus directly to speed up device detection:
hp-setup -b usbSpecifically, the -b usb flag tells the setup wizard to scan only USB-connected devices, bypassing network discovery.
Configure Network-Connected HP Printers
For HP printers connected to your network, specify the printer’s IP address directly. Replace the example IP with your printer’s actual address:
hp-setup 192.168.1.100To locate your printer’s address, check its control panel network settings menu. Alternatively, review your router’s connected devices list.
If your network printer isn’t discovered, ensure firewalld allows IPP traffic. Fedora’s default firewall typically permits outbound connections, but restrictive configurations may require opening port 631 for printer discovery.
Access HPLIP from Applications Menu
After initial configuration, you can access the HPLIP toolbox anytime through Fedora’s application menu. Search for “HPLIP” in Activities, or navigate to:
Activities > Show Applications > HPLIP Toolbox
From here, the HPLIP Toolbox provides access to printer status, supply levels, device settings, and scanning functions.

Print a Test Page to Verify Configuration
After configuring your printer, verify everything works by printing a test page. HPLIP includes a dedicated test page utility that prints device information and margin tests.
To verify your setup, run the test page utility and specify your printer name:
hp-testpage -p printer-nameReplace printer-name with your actual printer name as shown in CUPS. To list available printers, run lpstat -p.
Alternatively, use the graphical interface for interactive printer selection:
hp-testpageOnce printed successfully, this confirms your printer drivers are correctly installed and the printer is communicating with your system.
Print Documents from Command Line
Beyond test pages, you can print any document using the lp command. For example, to print a PDF file:
lp -d printer-name /path/to/document.pdfReplace printer-name with your printer’s CUPS name and /path/to/document.pdf with your file’s actual path. This confirms your printer handles standard documents correctly.
Scan Documents with HP Multifunction Printers
In addition to printing, HPLIP provides the hp-scan utility for scanning documents and images if your HP device includes a scanner. This works with HP all-in-one printers and standalone scanners supported by the HPLIP driver suite.
Scan Using the Graphical Interface
Launch the graphical scanning interface to select your device and configure scan settings:
hp-scanFrom this interface, you can preview the scan area, select resolution, choose color or grayscale output, and specify the destination file format.
Scan from Command Line
For automated scanning or headless systems, use the interactive command-line mode. Specify your device with the -d flag:
hp-scan -i -d hp:/usb/HP_LaserJet_Pro_MFP?serial=XXXXXXXXReplace the device URI with your actual scanner identifier. You can find available HPLIP devices by running hp-probe -b usb for USB scanners or hp-probe -b net for network devices.
Like other HPLIP utilities,
hp-scanshould be run withoutsudo. The utility will request elevated permissions only when necessary.
Troubleshoot Common HPLIP Issues
Printer Not Detected
If hp-setup does not detect your printer, first verify the device is powered on and connected. For USB printers, check the connection with:
lsusb | grep -i hpAs a result, this lists USB devices containing “HP” in their description. If your printer appears, the connection is working and the issue is likely driver-related.
For network printers, verify connectivity by pinging the printer’s IP address:
ping -c 4 192.168.1.100Check CUPS Printer Service Status
Because HPLIP relies on CUPS (Common Unix Printing System) for print job management, you should verify CUPS is running:
systemctl status cupsExpected output when CUPS is running:
● cups.service - CUPS Scheduler
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/cups.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running)
If CUPS is not active, start and enable it:
sudo systemctl enable --now cupsView Installed Printers
List all printers registered with CUPS to verify your HP device is configured:
lpstat -p -dAs a result, this shows all available printers and the default printer. If your HP printer is missing, re-run hp-setup to add it.
Manage HPLIP Installation
Update HPLIP
HPLIP updates are delivered through Fedora’s standard package updates. To update HPLIP along with other system packages, run:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshConsequently, this ensures you receive the latest driver updates and bug fixes. For information on configuring automatic updates, see our guide on DNF Automatic on Fedora.
Remove HPLIP
If you no longer use HP devices or need to troubleshoot by reinstalling, remove HPLIP with:
sudo dnf remove hplip hplip-guiAfter removal, clean up orphaned dependencies that were installed alongside HPLIP:
sudo dnf autoremoveAs a result, removing HPLIP disables HP-specific printer and scanner functionality. Generic CUPS printing may still work for some devices, but HP-specific features like supply level monitoring and fax support will be unavailable.
Conclusion
At this point, you have successfully installed and configured HPLIP on Fedora Linux, giving your system full support for HP printers, scanners, and multifunction devices. Furthermore, the HPLIP Toolbox provides ongoing access to device status monitoring, supply levels, and advanced configuration options. Finally, keep HPLIP updated through regular system upgrades to maintain compatibility with the latest HP hardware and receive driver improvements.



Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags currently allowed:
<code>command</code>command<strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><a href="URL">link</a><blockquote>quote</blockquote>