This guide will demonstrate how to install Darkstat on Ubuntu 24.04, 22.04, or 20.04 LTS releases utilizing the command-line terminal, along with basic tips on start-up configuration to help you get started.
Darkstat captures network traffic, calculates statistics about usage, and serves reports over HTTP. Its lightweight footprint offers a simple yet powerful way to monitor network traffic without imposing a significant load on your system. Ideal for system administrators and network enthusiasts, Darkstat provides an insightful look into your network’s operations, enabling you to identify trends, pinpoint issues, and understand traffic patterns at a glance.
Why Choose Darkstat?
- Effortless Installation: A straightforward setup process that integrates seamlessly with Ubuntu’s package management system.
- Real-Time Insights: Offers live network monitoring, delivering immediate feedback on your network’s status.
- Historical Data Analysis: Stores traffic data to analyze past network activities and trends.
- User-Friendly Interface: Accessible via any web browser, its interface simplifies network monitoring for experts and novices alike.
Transitioning into the technical how-to, this guide ensures you have the tools and knowledge to deploy Darkstat on your Ubuntu system effectively.
Install Darkstat on Ubuntu via APT
Install Darkstat via APT Command
To install Darkstat, a network traffic analyzer, utilize the apt package manager available in Ubuntu’s official repositories. Execute the command below in your terminal:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install darkstatFirstly, sudo apt update refreshes your system’s package list, ensuring you have the latest versions of packages and their dependencies. Following this, sudo apt install darkstat installs the Darkstat package along with any required dependencies.
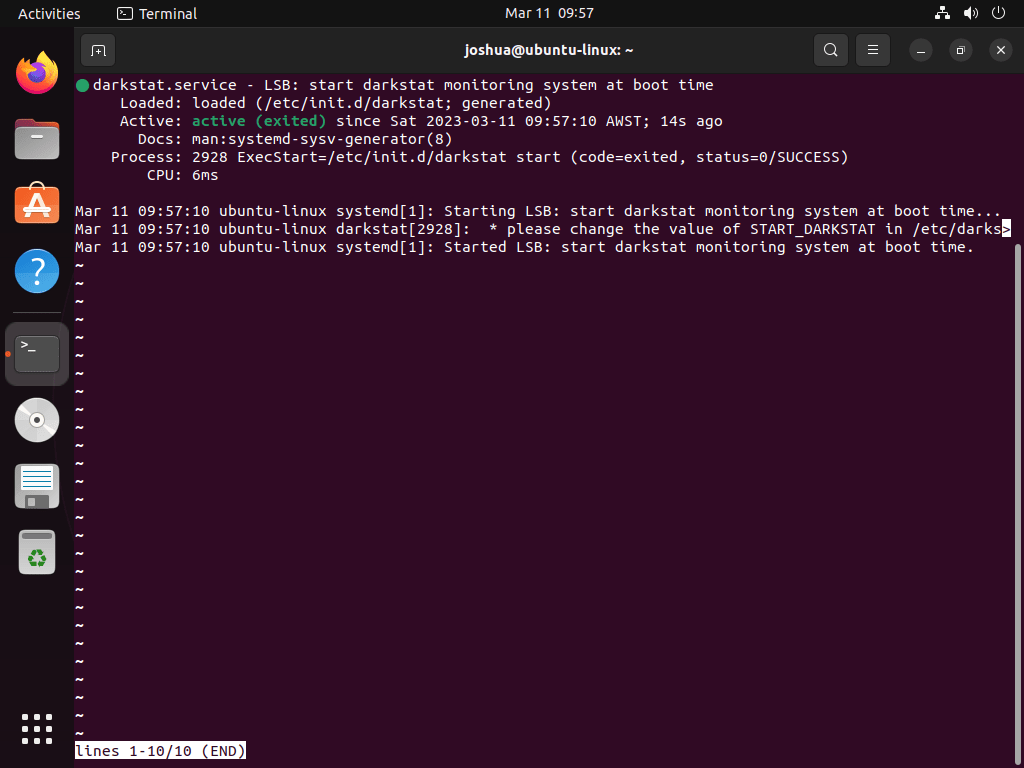
Verify Darkstat Service Status
Once Darkstat installation completes, confirm its operational status with the following command:
systemctl status darkstatThis command queries and displays the Darkstat service status. A successful query will show Darkstat as active and running, indicating a successful installation and startup.
Configure Darkstat on Ubuntu
Identify the Network Interface
To tailor Darkstat’s monitoring, select the network interface it will observe. This interface could be an Ethernet connection, a Wi-Fi link, or a virtual network interface established by VPN services.
Discover the desired network interface’s name by executing:
ip linkThis command lists all network interfaces available on your system. Identify the one you intend to monitor, noting its name. For the purpose of this guide, we’ll assume the interface name is eth0.
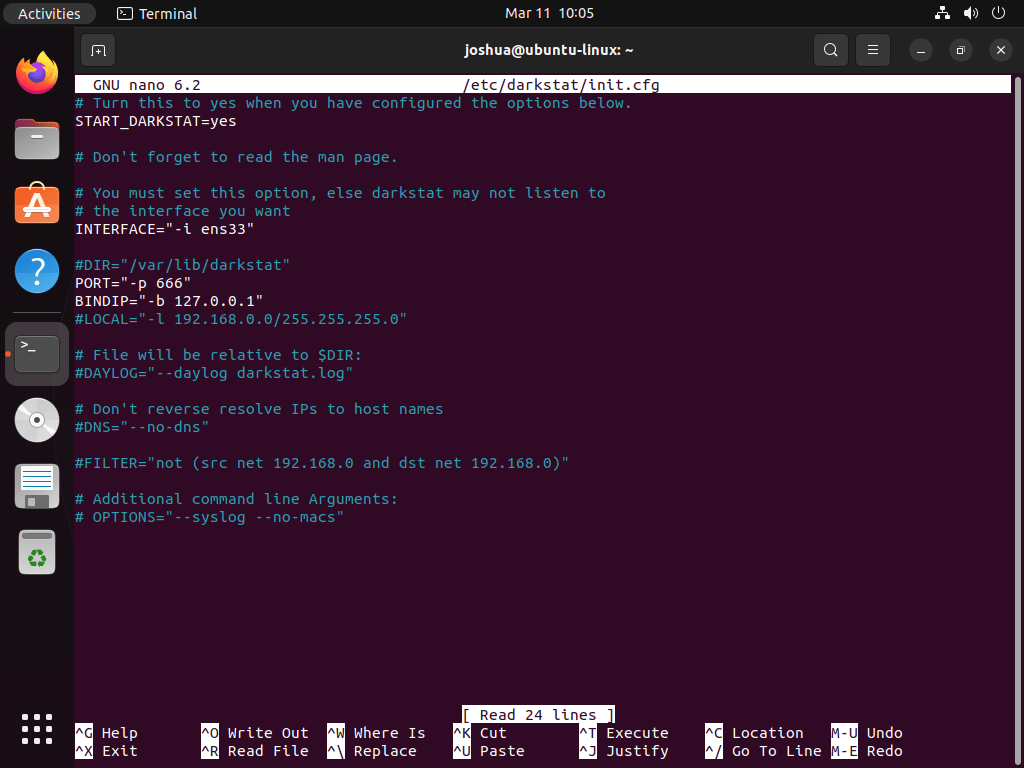
Edit Darkstat Configuration
Access Darkstat’s configuration file to customize its settings:
sudo nano /etc/darkstat/init.cfgIn the configuration file, activate Darkstat to launch at system startup by modifying the line:
#RUN_DARKSTAT=noto:
RUN_DARKSTAT=yesSpecify the network interface for Darkstat to monitor by adjusting:
#INTERFACE=""to include your chosen interface name, here exemplified as eth0:
INTERFACE="eth0"Optionally, alter the PORT setting to choose a different port for Darkstat’s web interface. The default port is 667, but you may set it to any preferred value. After making your adjustments, save and exit the editor by pressing CTRL+X, then Y to confirm.
Restart Darkstat Service
Apply the configuration changes and restart Darkstat to activate monitoring:
sudo systemctl restart darkstatThis restart makes Darkstat monitor the specified interface and start automatically on boot, using the updated settings.
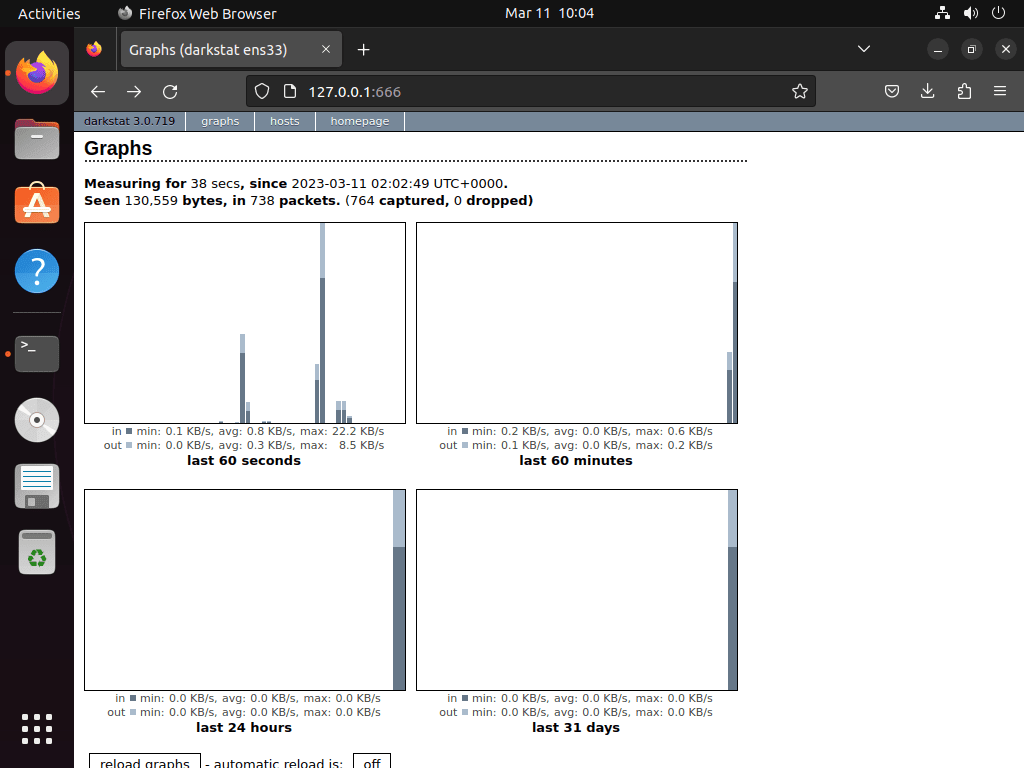
Accessing the Darkstat Dashboard on Ubuntu
With Darkstat configured, its web interface serves as a powerful tool for monitoring your network traffic. To access it, open any web browser on your Ubuntu machine and navigate to your system’s IP address on port 667. For instance, if your system’s IP address is 192.168.1.100, you would enter:
http://192.168.1.100:667Upon doing so, Darkstat’s web interface will present itself, showcasing detailed insights into your system’s network traffic. This interface includes several tabs and options that allow for comprehensive traffic analysis and monitoring.
Conclusion
In this guide, we walked through the steps to install and configure Darkstat on Ubuntu, from setting it up with APT to monitoring your network through its web interface. We aimed to keep things simple and straightforward, ensuring that even beginners could follow along. Now that you have Darkstat up and running, you can enjoy real-time insights into your network’s traffic, helping you make informed decisions about its management. Remember, regular check-ins are key to effective network monitoring, so use Darkstat’s dashboard to avoid any issues. Happy monitoring, and here’s to a smoother, more manageable network!