BleachBit helps you reclaim disk space and protect your privacy by removing cache files, cookies, browser history, logs, and temporary files that accumulate over time. Whether you need to free up storage on a space-constrained system, securely shred sensitive files to prevent recovery, or speed up Firefox by vacuuming its database, BleachBit provides a straightforward solution. By the end of this guide, you will have BleachBit installed and ready to clean over a thousand applications on your Ubuntu system.
Choose Your BleachBit Installation Method
Ubuntu offers two installation paths for BleachBit, each with distinct advantages depending on your needs. The following table summarizes the key differences to help you decide.
| Method | Channel | Version | Updates | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| APT Package Manager | Ubuntu Repos | Distribution default | Automatic via apt upgrade | Most users who prefer distro-tested packages |
| Flatpak | Flathub | Latest stable | Automatic via flatpak update | Users who want the newest features with sandboxing |
We recommend the APT method for most users because it integrates seamlessly with Ubuntu’s package management, receives automatic security updates, and requires no additional setup. However, choose Flatpak if you need the latest BleachBit features before they reach Ubuntu’s repositories.
This guide supports Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and 24.04 LTS. Both installation methods work identically across all supported LTS releases. The APT method installs version 4.4.2 on Ubuntu 22.04 and version 4.6.0 on Ubuntu 24.04, while Flatpak provides version 5.0.0 regardless of your Ubuntu release.
Method 1: Install BleachBit via APT
The APT method installs BleachBit from Ubuntu’s official repositories, ensuring compatibility and automatic security updates.
Update Ubuntu
Before installing new software, first refresh your package index to ensure you receive the latest available version. This command also upgrades any outdated packages on your system.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeInstall BleachBit
After refreshing the package index, install BleachBit with the following command. The -y flag automatically confirms the installation prompt, which is useful for scripted deployments but means you will not see the package list before installation proceeds.
sudo apt install bleachbit -yVerify Installation
After the installation completes, confirm that BleachBit is accessible by checking the version. This verification step ensures the binary installed correctly and is available in your PATH.
bleachbit --versionExpected output on Ubuntu 24.04:
BleachBit version 4.6.0 Copyright (C) 2008-2021 Andrew Ziem. All rights reserved. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>. This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
On Ubuntu 22.04, you will see version 4.4.2 instead. Either output confirms a successful installation.
Method 2: Install BleachBit via Flatpak
Alternatively, Flatpak provides the latest BleachBit release directly from Flathub, independent of Ubuntu’s release cycle. This method also sandboxes the application for additional security, isolating it from your system files.
Flatpak is not pre-installed on Ubuntu. If you have not set it up yet, first install it with
sudo apt install flatpakand restart your session before continuing. For detailed setup including the Flathub repository, follow our Flatpak installation guide for Ubuntu, which typically takes under five minutes.
Enable Flathub Repository
Flathub is the primary source for Flatpak applications. Before installing BleachBit, add the Flathub repository to your system if you have not already done so. The --if-not-exists flag prevents errors if the repository is already configured.
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoInstall BleachBit from Flathub
With Flathub enabled, you can now install BleachBit. Because the remote-add command used sudo, subsequent Flatpak commands must also use sudo to access the system-wide repository.
sudo flatpak install flathub org.bleachbit.BleachBit -yVerify Flatpak Installation
After installation completes, confirm that BleachBit installed correctly by checking the application details. The output shows the installed version and confirms the application is ready to use.
flatpak info org.bleachbit.BleachBitExpected output:
BleachBit - Cleans files to free disk space and to maintain privacy
ID: org.bleachbit.BleachBit
Ref: app/org.bleachbit.BleachBit/x86_64/stable
Arch: x86_64
Branch: stable
Origin: flathub
Version: 5.0.0
Launch BleachBit
Once installed, you can launch BleachBit from the terminal or through your desktop environment’s application menu. The method depends on how you installed the application.
Launch from Terminal
For APT installations, start BleachBit directly with the following command:
bleachbitIf you installed via Flatpak, use the Flatpak run command instead:
flatpak run org.bleachbit.BleachBitLaunch from Applications Menu
Alternatively, open your application menu or Activities overview, search for “BleachBit,” and click the application icon to launch it.
Manage BleachBit
This section covers updating and removing BleachBit from your Ubuntu system. The commands differ depending on your installation method.
Update BleachBit
For APT installations, BleachBit updates automatically when you upgrade your system packages. Running the following command checks for and applies all available updates:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeFor Flatpak installations, update all Flatpak applications including BleachBit with the following command:
sudo flatpak updateRemove BleachBit
If you no longer need BleachBit, follow the appropriate removal steps based on your installation method.
APT Installation:
First, remove BleachBit and its configuration files. Then, clean up any orphaned dependencies that APT installed alongside the application:
sudo apt remove --purge bleachbit -y
sudo apt autoremove -yFlatpak Installation:
Remove BleachBit and then clean up any unused runtimes that are no longer needed by other applications:
sudo flatpak uninstall org.bleachbit.BleachBit -y
sudo flatpak uninstall --unused -yRemove User Configuration (Optional):
The following command permanently deletes your BleachBit settings and custom configurations. Only run this if you want a complete removal with no traces remaining.
rm -rf ~/.config/bleachbit ~/.var/app/org.bleachbit.BleachBitTroubleshooting
BleachBit Does Not Detect Firefox Snap Cache
If you use Firefox as a Snap package (the default on Ubuntu 22.04 and later), BleachBit may not automatically detect its cache location. This happens because Snap applications store data in ~/snap/firefox/ rather than the traditional ~/.mozilla/ directory.
To verify whether Firefox runs as a Snap, run:
snap list firefoxIf Firefox appears in the list, its cache resides at:
~/snap/firefox/common/.cache/
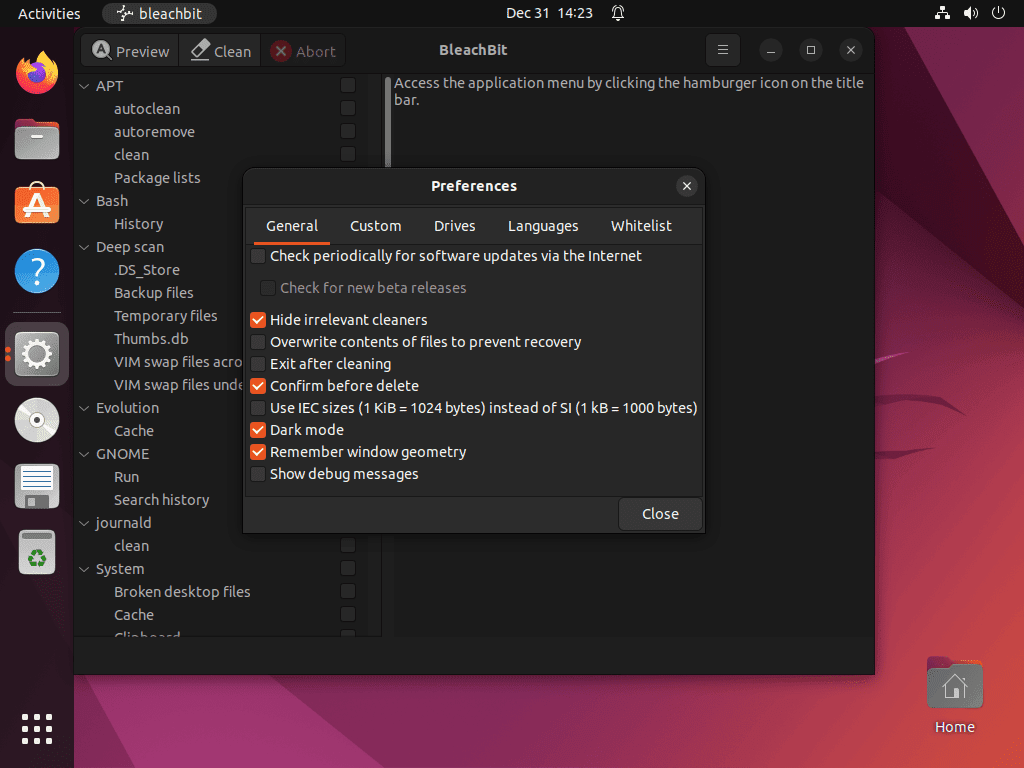
To clean Firefox Snap cache, use BleachBit’s “Deep Scan” feature in Preferences, or manually add the Snap directory as a custom location.
Clean System Files with Root Mode
BleachBit offers two modes: regular user mode and root mode. Running as root allows cleaning system-wide files that regular users cannot access, such as APT cache, system logs, and temporary files in /tmp.
To launch BleachBit with root privileges, use:
sudo bleachbitOn systems using Wayland (Ubuntu 22.04 and later default to Wayland), running graphical applications with sudo may display a blank window. If this occurs, use pkexec instead:
pkexec bleachbitA polkit authentication dialog will appear prompting for your password. After authentication, BleachBit opens with root privileges and displays additional system cleaning options.
Version Command Shows Warnings in Headless Environments
When running bleachbit --version in a headless environment such as Docker containers or SSH sessions without X forwarding, you may see GTK or Wayland-related warnings like:
(bleachbit:1234): Gdk-CRITICAL **: gdk_screen_get_root_window: assertion 'GDK_IS_SCREEN (screen)' failed
These warnings occur because BleachBit attempts to initialize a graphical display that does not exist in headless environments. The warnings do not affect BleachBit’s core functionality and can be safely ignored. The version information still displays correctly despite the warning messages.
Conclusion
You now have BleachBit installed and ready to clean your Ubuntu system. Both the APT and Flatpak methods provide a reliable way to free disk space and maintain privacy by removing temporary files, browser cache, and application logs. For a complementary system cleaning tool with a graphical interface, consider Ubuntu Cleaner as an alternative or additional option.

