APT-Fast is an efficient wrapper for “APT,” the default package manager in Ubuntu, designed to accelerate package downloads by using multiple connections to fetch packages in parallel. By leveraging tools like “aria2” or “axel,” APT-Fast can significantly reduce the time it takes to update, upgrade, and install packages on your system, making it particularly useful for users with slower internet connections or those looking to optimize their package management process.
On Ubuntu, APT-Fast can be installed via the command-line by adding the apt-fast/stable Launchpad PPA. This guide walks through installing APT-Fast from the official PPA, configuring connection counts based on your network speed (5-20 parallel connections), selecting download accelerators (aria2 or axel), and integrating it with automated update workflows for efficient system maintenance. You will also learn when to use APT-Fast versus standard APT and how to troubleshoot common configuration issues.
This guide supports Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and 24.04 LTS installations. The apt-fast/stable Launchpad PPA provides packages for the two most recent LTS releases, while future Ubuntu LTS releases may require checking PPA availability. Commands shown work identically on both supported LTS releases.
Add APT-Fast Launchpad PPA
To begin, access your terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T). Next, input this command to add the Launchpad PPA repository:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable -yThis adds the APT-Fast stable repository to your system. The command automatically refreshes package lists and displays repository information:
Repository: 'Types: deb URIs: https://ppa.launchpadcontent.net/apt-fast/stable/ubuntu/ Suites: noble Components: main ' Description: This PPA contains tested (stable) builds of apt-fast. Project: https://github.com/ilikenwf/apt-fast More info: https://launchpad.net/~apt-fast/+archive/ubuntu/stable Adding repository.
The add-apt-repository command automatically runs apt update to refresh package lists. Verify the PPA was added successfully:
apt-cache policy apt-fastExpected output confirms the package is available from the PPA:
apt-fast:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 1.11.1-1~ubuntu24.04.1
Version table:
1.11.1-1~ubuntu24.04.1 500
500 https://ppa.launchpadcontent.net/apt-fast/stable/ubuntu noble/main amd64 Packages
Install APT-Fast with APT Command
Next, install APT-Fast along with its dependencies (aria2 download accelerator and required libraries):
sudo apt install apt-fastThe installation displays a summary of packages to be installed, then shows configuration prompts for APT-Fast, allowing customization based on your preferences:
The following NEW packages will be installed: apt-fast aria2 libaria2-0 libcares2 libssh2-1t64 0 upgraded, 5 newly installed, 0 to remove and 0 not upgraded. Need to get 1719 kB of archives. After this operation, 6242 kB of additional disk space will be used.
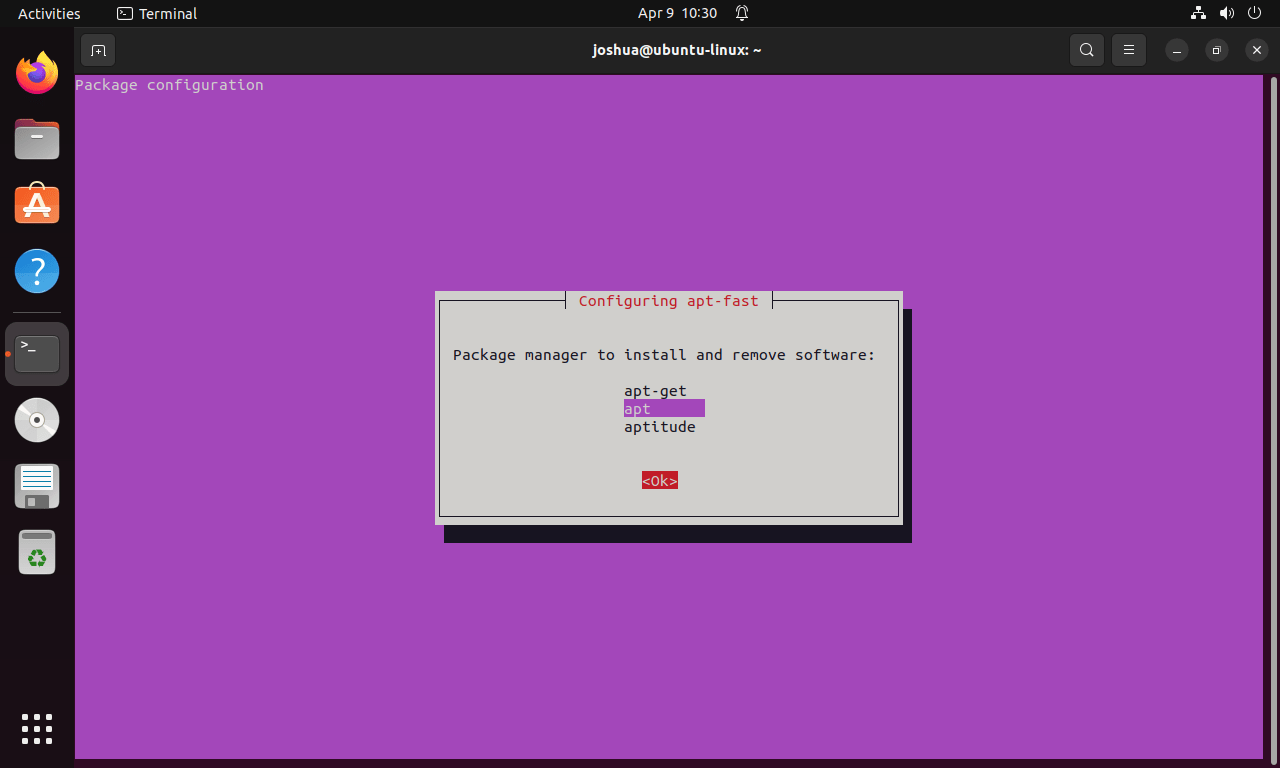
Choosing the Package Manager
During setup, you’ll be prompted to select a package manager. Options include “apt-get,” “apt,” or “aptitude.” For most users, “apt” or “apt-get” are suitable choices. In this guide, select “apt.”
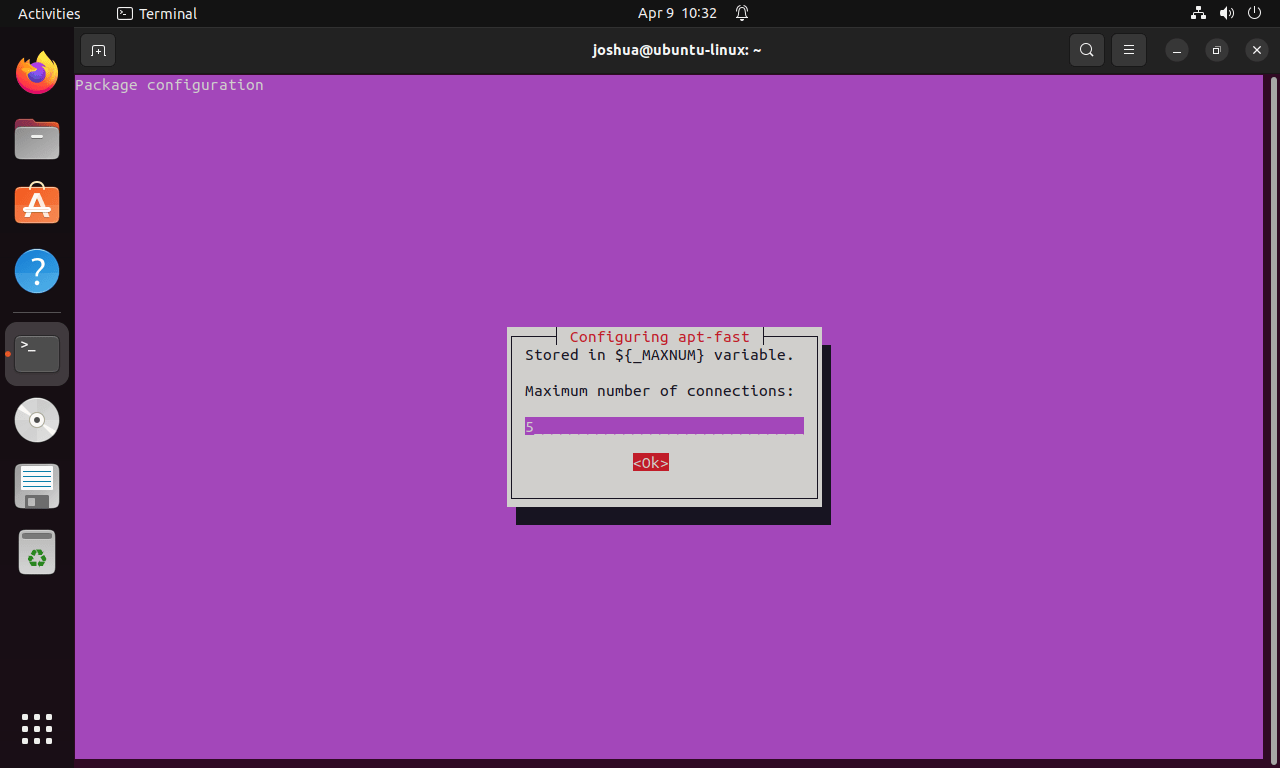
Setting the Maximum Number of Connections
Next, you’ll decide on the maximum number of connections. The default is 5, but you can adjust it to 10 or 20 based on your network’s strength and personal preference.
If unsure, stick with the default. However, the configuration section below explains how to modify this setting later.
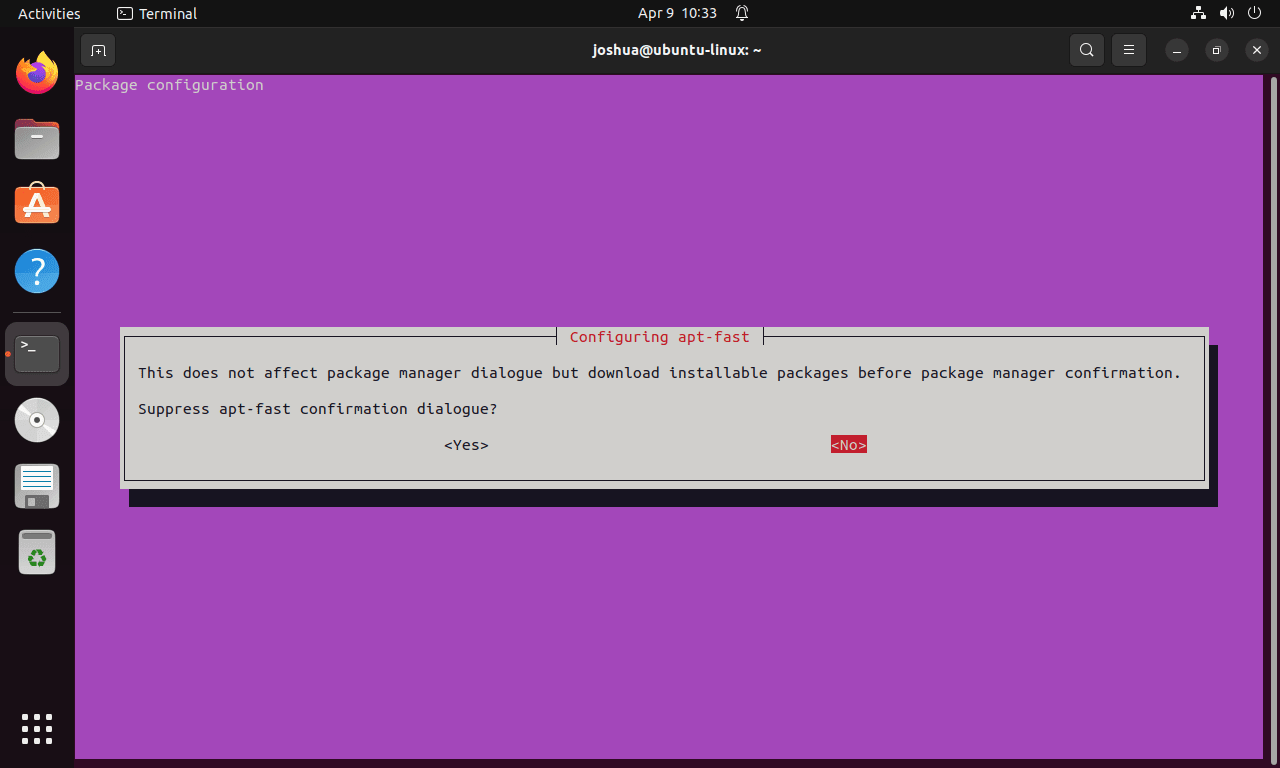
Downloading Packages Before Confirmation
Finally, the last prompt in the APT-Fast installation process concerns the pre-download of installable packages before package manager confirmation. This setting, if enabled, bypasses the usual APT-Fast confirmation dialog.
Make a selection based on your preference.
Once installation completes, verify APT-Fast is accessible by checking the underlying APT version it wraps:
apt-fast --versionExpected output displays the APT version information, confirming APT-Fast is properly configured:
apt 2.8.x (amd64) Supported modules: *Ver: Standard .deb Pkg: Debian APT solver interface (Priority -1000) *Pkg: Debian dpkg interface (Priority 30)
Understanding APT-Fast
If you are new to APT-Fast, think of it as a turbocharged version of the standard APT package manager. Instead of downloading one package at a time like traditional APT, APT-Fast splits files into multiple chunks and downloads them simultaneously, similar to how download managers accelerate file transfers in web browsers.
Basic APT-Fast Syntax
APT-Fast uses the same command structure as regular APT, making the transition seamless:
sudo apt-fast [apt-command] [package-name]Simply replace apt with apt-fast in your existing commands. The underlying package manager (APT) handles dependency resolution and installation, while APT-Fast accelerates the download phase through parallel connections.
When to Use APT-Fast
- Large system updates: When upgrading hundreds of packages, parallel downloads save significant time.
- Slower connections: Networks with limited bandwidth benefit most from connection pooling.
- Multiple package installations: Installing software bundles like development tools or desktop environments.
- High-latency networks: Parallel connections reduce the impact of latency on download times.
On the other hand, for single small packages or quick updates, the performance difference between APT and APT-Fast is minimal. If you frequently manage PPAs for various software installations, consider reviewing our PPA management guide for best practices.
Quick Reference for Common Operations
| Task | APT-Fast Command | What It Does |
|---|---|---|
| Update package lists | sudo apt-fast update | Refreshes repository metadata with parallel connections |
| Upgrade installed packages | sudo apt-fast upgrade | Updates packages to latest versions using parallel downloads |
| Install new software | sudo apt-fast install [package] | Downloads and installs packages with multiple connections |
| Full system upgrade | sudo apt-fast full-upgrade | Performs complete upgrade with dependency changes |
| Handle complex dependency changes | sudo apt-fast dist-upgrade | Applies in-release upgrades that add or remove packages as needed |
| Remove packages | sudo apt-fast remove [package] | Uninstalls software (downloads not needed) |
Edit APT-Fast Configuration File
To tailor APT-Fast settings, begin by editing its configuration file. Use a command-line text editor, such as Nano, for this purpose:
sudo nano /etc/apt-fast.confThe configuration file contains these key sections:
# Package manager to use (apt-get, apt, or aptitude)
_APTMGR=apt
# Maximum number of connections (5-20 recommended)
_MAXNUM=5
# Maximum connections per server
_MAXCONPERSRV=10
# Split size for parallel downloads
_SPLITCON=8
# Minimum split size (1M = 1 megabyte)
_MINSPLITSZ=1M
# Download piece selection algorithm
_PIECEALGO=default
# Download manager (aria2c or axel)
_DOWNLOADER='aria2c --no-conf -c -j ${_MAXNUM} -x ${_MAXCONPERSRV} -s ${_SPLITCON}'
Adjust Maximum Parallel Connections
Locate the _MAXNUM variable within the configuration file to adjust the number of connections. For instance, setting the maximum connections to 10 is done by:
_MAXNUM=10Select Download Accelerator
Additionally, APT-Fast supports different download accelerators, like Axel and Aria2, which enhance the efficiency of downloading packages. Understanding these options helps you make an informed choice for your system’s configuration.
- Axel: A light and efficient download accelerator, Axel speeds up the process by using multiple connections for a single download. It’s an excellent choice for users looking for a straightforward, minimalistic solution that integrates well with the existing package management system.
- Aria2: Conversely, Aria2 is a more versatile download utility. It supports various protocols, including HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, SFTP, and BitTorrent. Aria2 is known for its flexibility and is suited for users who require a wide range of features and advanced downloading capabilities.
To switch between these download managers in APT-Fast, locate the “_DOWNLOADER” line in the configuration file. For Aria2, adjust the line to:
_DOWNLOADER='aria2c --no-conf -c -j ${_MAXNUM} -x ${_MAXCONPERSRV} -s ${_SPLITCON} --min-split-size=${_MINSPLITSZ} --stream-piece-selector=${_PIECEALGO} -i ${DLLIST} --connect-timeout=600 --timeout=600 -m0 --header "Accept: */*"'Alternatively, if you prefer Axel, modify the line as follows:
_DOWNLOADER='grep -E "^https?://" "${DLLIST}" | cut -f1 | xargs -n 1 -P ${_MAXNUM} axel -a -n ${_MAXCONPERSRV}'Be sure to save your changes after selecting the preferred download manager.
Configure Mirror List
Furthermore, APT-Fast can leverage multiple mirrors to enhance download speeds by distributing requests across geographically diverse servers. Configure these in the /etc/apt-fast.list file. Open it using nano:
sudo nano /etc/apt-fast.listInside this file, you can add or modify the list of mirrors. The configuration file should contain entries in this format:
# Default Ubuntu mirrors deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ noble main restricted universe multiverse deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ noble-updates main restricted universe multiverse deb http://security.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ noble-security main restricted universe multiverse # Add regional mirrors for faster downloads deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ noble main restricted universe multiverse deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ noble-updates main restricted universe multiverse
Replace “noble” with your Ubuntu release codename (“jammy” for 22.04 LTS, “noble” for 24.04 LTS). Add mirrors from your geographic region using the Ubuntu mirror list for optimal download speeds.
Manage Packages with APT-Fast
Update Package Lists and Install Software
APT-Fast enhances the standard APT commands, streamlining package management tasks. Below are key commands to integrate APT-Fast into your workflow.
To update the package list using APT-Fast, run:
sudo apt-fast updateFor package installation, such as htop, the command is:
sudo apt-fast install htopUpgrade Installed Packages
Similarly, to update all installed packages to their latest available versions, execute:
sudo apt-fast upgradeThis command ensures that your system’s packages are up-to-date, maintaining functionality and security.
APT-Fast displays a confirmation prompt showing packages queued for download:
Working... 0% Do you want to download the packages using apt-fast? [Y/n] y [#1 SIZE:2.5MiB/4.1MiB CN:5 DL:8.2MiB ETA:3s] [#2 SIZE:1.8MiB/3.2MiB CN:5 DL:6.5MiB ETA:2s] [#3 SIZE:512KiB/1.5MiB CN:5 DL:4.8MiB ETA:1s]
During parallel downloads, aria2 displays real-time progress for each connection, showing download speed, estimated time, and completion percentage across multiple simultaneous transfers.
Once downloads complete, APT-Fast hands control back to APT for package installation:
Download Results: ================= gid |stat|avg speed |path/URI ======+====+===========+=========== 1 |OK | 8.2MiB/s|/var/cache/apt/archives/package1.deb 2 |OK | 6.5MiB/s|/var/cache/apt/archives/package2.deb 3 |OK | 4.8MiB/s|/var/cache/apt/archives/package3.deb Status Legend: (OK):download completed.
Perform Distribution Upgrade
Use the dist-upgrade flag when a full upgrade within your current Ubuntu release needs to install or remove packages to resolve dependency changes:
sudo apt-fast dist-upgradeThis command can be time-consuming and may remove obsolete packages, so review the summary carefully and back up important data before proceeding.
On Ubuntu, major release upgrades, such as moving from Ubuntu 22.04 LTS (Jammy) to Ubuntu 24.04 LTS (Noble), should still use
sudo do-release-upgrade. The dedicated upgrade utility disables PPAs, updates third-party sources, and mitigates issues that APT-Fast alone cannot handle.
First-Time User Tips
Choosing the Right Connection Count
The number of parallel connections significantly impacts download performance. Here are recommendations based on connection type:
- Slow connections (under 10 Mbps): Use 5-10 connections to maximize throughput without overwhelming bandwidth.
- Medium connections (10-50 Mbps): Use 10-16 connections for optimal balance between speed and stability.
- Fast connections (over 50 Mbps): Use 16-20 connections to fully utilize available bandwidth.
- Server/datacenter connections: Use 20+ connections for maximum throughput on high-speed links.
While higher connection counts increase memory usage slightly, they provide diminishing returns beyond 20 connections for most users.
Testing Download Speed Improvements
To measure APT-Fast’s performance gains, compare download times for the same operation:
# Test standard APT speed
time sudo apt install --download-only libreoffice
# Test APT-Fast speed
time sudo apt-fast install --download-only libreofficeThe --download-only flag downloads packages without installing them, allowing fair comparison. In many situations, APT-Fast delivers noticeably faster downloads, often several times quicker than standard APT depending on connection quality and mirror availability.
When to Use Regular APT Instead
While APT-Fast excels at large downloads, standard APT remains preferable for:
- Single small packages: Overhead from parallel connections negates benefits for packages under 5 MB.
- System scripts: Automated scripts should use regular APT for reliability and simpler error handling.
- Troubleshooting: When diagnosing package issues, standard APT provides clearer, more detailed output.
- Unstable connections: Networks with frequent interruptions may experience more failures with parallel downloads.
Troubleshooting Common APT-Fast Issues
PPA Connection Failures
If adding the PPA fails with connection errors, verify your internet connection and try updating certificates:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install ca-certificates
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable -yAlternatively, check if your firewall or proxy blocks Launchpad connections. In particular, corporate networks often require proxy configuration in /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/.
Download Manager Not Found
If APT-Fast reports “aria2c: command not found” or similar errors, install the required download manager:
# Install aria2 (recommended)
sudo apt install aria2
# Or install axel (alternative)
sudo apt install axelFollowing installation, verify the configuration file points to the correct download manager in /etc/apt-fast.conf.
Configuration Dialog Not Appearing
If the installation completes without showing configuration prompts, manually reconfigure APT-Fast:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure apt-fastThis reopens the configuration dialogs for package manager selection, connection count, and download behavior.
Mirror Connectivity Problems
When downloads fail or timeout frequently, test mirror availability:
# Test default Ubuntu mirror
curl -I http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/
# Test specific mirror
curl -I http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/Successful mirror responses show HTTP 200 status and server headers:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Tue, 10 Dec 2025 12:00:00 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.x Last-Modified: Mon, 09 Dec 2025 18:30:00 GMT
If mirrors respond slowly or timeout, select geographically closer mirrors in /etc/apt-fast.list using the Ubuntu mirror list. Subsequently, replace unresponsive mirrors with active alternatives from your region.
Package Verification Errors
If APT-Fast downloads packages but APT reports hash mismatches:
# Clear package cache
sudo apt clean
# Rebuild package lists
sudo apt update
# Retry installation
sudo apt-fast install [package-name]Typically, hash mismatches occur when mirror synchronization lags or interrupted downloads leave corrupted files in /var/cache/apt/archives/.
Remove APT-Fast
If you eventually need to uninstall APT-Fast and revert to standard APT package management, follow these steps.
Uninstall APT-Fast Package
Remove the APT-Fast package and its configuration files:
sudo apt purge apt-fastThe purge command removes both the package and configuration files in /etc/apt-fast.conf and /etc/apt-fast.list.
Remove APT-Fast PPA
Remove the PPA repository to prevent future update checks:
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:apt-fast/stable -y
sudo apt updateConsequently, this removes the repository from /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ and updates package lists. Verify the PPA was removed successfully:
apt-cache policy apt-fastExpected output shows no repository URL, confirming the PPA is no longer configured:
apt-fast:
Installed: 1.11.1-1~ubuntu24.04.1
Candidate: 1.11.1-1~ubuntu24.04.1
Version table:
*** 1.11.1-1~ubuntu24.04.1 100
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
Remove Download Manager (Optional)
If you no longer need aria2 or axel for other purposes, remove them:
# Remove aria2
sudo apt remove aria2
# Or remove axel
sudo apt remove axelFollowing removal, continue using standard apt commands for all package operations. Your system reverts to single-connection downloads with identical functionality to before APT-Fast installation.
Conclusion
APT-Fast accelerates package downloads by leveraging parallel connections through aria2 or axel, significantly reducing update and upgrade times. You have configured connection counts based on network speed, selected the appropriate download accelerator, and integrated APT-Fast into your package management workflow. To maximize performance, benchmark download speeds against standard APT using the --download-only flag on large package sets, configure geographically closer mirrors from the Ubuntu mirror list for reduced latency, and consider integrating APT-Fast with unattended-upgrades for automated system maintenance. Remember to use standard APT for troubleshooting and system scripts where reliability outweighs speed benefits.


Formatting tips for your comment
You can use basic HTML to format your comment. Useful tags:
<code>command</code>command<pre>block of code</pre><strong>bold</strong><em>italic</em><a href="URL">link</a><blockquote>quote</blockquote>