Tor Browser is an excellent tool if you’re using Fedora Linux and are concerned about online privacy. This guide will show you how to install Tor Browser on Fedora Linux using various methods, including the Fedora default repository, manual installation, and Flatpak via Flathub.
Why Use Tor Browser on Fedora Linux?
- Privacy Protection: Tor Browser helps safeguard your privacy by masking your IP address, making it challenging for websites to monitor your online activities.
- Access Restricted Content: If you’re facing regional restrictions on certain websites, Tor Browser can help you bypass these limitations.
- Circumvent Censorship: For users who are under internet censorship, Tor Browser offers a way to access the web freely, without the fear of being monitored.
- Anonymous File Sharing: Tor Browser provides a secure environment for anonymous file sharing if you need to upload or download files without revealing your identity.
Whether you’re a privacy advocate, a journalist, or simply a user who wants to enhance online security, Tor Browser offers a range of features to meet your needs. Stay tuned for the step-by-step guide on installing Tor Browser on your Fedora Linux system.
Install Tor Browser on Fedora Linux via DNF
Step 1: Update Fedora Before Tor Browser Installation
First, update your system to ensure all existing packages are up to date with the following command:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshDo not forget to reboot if you update your Kernel.
Step 2: Install Tor via Fedora’s Default RPM Repository
The first and most preferred option for the average desktop user environment is to install Tor Browser with the Fedora default repository.
Use the following command to install Tor Browser successfully.
sudo dnf install torbrowser-launcherCheck out the two methods below for users who prefer using Flatpaks or installing the application using the extract method.
Install Tor Browser on Fedora Linux via Flatpak and Flathub
If you prioritize ease of use and hassle-free updates for your software, installing the Tor Browser via Flatpak and Flathub is an excellent choice. Flatpak is a software utility for software deployment applications for Linux, and Flathub is a repository for these Flatpak apps. Together, they make updating the Tor Browser straightforward and seamless.
Step 1: Enable Flathub Repository for Tor Browser Installation
The initial action is to enable the Flathub repository within your Flatpak setup. The repository provides an extensive software library and is a critical component for keeping your Tor Browser up to date.
The following command should be entered into your terminal:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoHere’s a breakdown of what this command does:
sudo: Indicates that root privileges are necessary for this operation.flatpak remote-add: The command used to add a new repository in Flatpak.--if-not-exists: This flag ensures that the repository will only be added if it hasn’t been previously.flathub: The name of the repository you are adding.https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepo: The URL where the repository can be found.
Executing this command adds the Flathub repository to your Flatpak configuration, enabling you to install software from Flathub.
Step 2: Install Tor Browser via Flatpak Command
Now that the Flathub repository is enabled, the next step is to install the Tor Browser package.
To install Tor Browser, use the following command:
flatpak install flathub com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcher -yBreaking down this command:
flatpak install: The command to install packages in Flatpak.flathub: Specifies that the package should be installed from the Flathub repository.com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcher: The unique identifier for the Tor Browser package on Flathub.-y: This flag automatically confirms all prompts, making the installation process faster.
After executing this command, the Tor Browser will be installed on your system from the Flathub repository.
If the above command does not work and you receive the “error: Unable to load summary from remote flathub: Can’t fetch summary from disabled remote ‘flathub,” use the following command.
flatpak remote-modify --enable flathubInstall Tor Browser on Fedora Linux via Tor Browser Archive
The third installation option is to install Tor Browser using the latest archive from the downloads page. This method gives you the latest version, but sometimes, you must repeat the process for significant browser changes. For the most part, it should self-update in the browser itself.
Step 1: Download Tor Browser Archive
To obtain the most up-to-date version of the Tor Browser, it’s recommended to download the software directly from the Tor Project’s official website. Doing so ensures you can access the newest features and security updates. Although the browser can self-update, manually installing the latest version is advisable for significant updates.
Most desktop users would just simply download the Tor Browser tar.zx file directly from the website, if you do it should be located in the ~/Downloads directory unless you save downloads elsewhere instead of the default location.
Fetching the Browser Archive via Command Line
You can download the current versions of the Tor Browser, which are made available as .tar.xz files by using the wget command. For example:
https://www.torproject.org/dist/torbrowser/x.x.x/tor-browser-linux64-x.x.x_ALL.tar.xzReplace the {version} placeholder with the specific version number that you intend to download. To ascertain the latest version, consult the Tor Project’s official download webpage.
Alternatively, if you opt to download the browser via the webpage, you’ll need to navigate to your downloads directory:
cd ~/DownloadsStep 2: Unpacking the Tor Browser Archive
After the download is complete, you’ll need to decompress the archive. This can be achieved using the tar command as follows:
tar -xvJf tor-browser-linux64-{version}_ALL.tar.xzAgain, make sure to substitute {version} with the actual version number that you have downloaded.
Step 3: Transferring the Browser Directory
For organizational purposes, it’s advisable to move standalone applications to a specific directory intended for such use. In Fedora, /usr/local/share is a standard directory for storing shared data associated with locally installed standalone applications.
To move the Tor Browser directory to this location, execute the following command:
sudo mv tor-browser /usr/local/share/The sudo prefix indicates that the operation is carried out with administrative rights, which is required to make changes within the /usr/local/share directory.
Step 4: Accessing the New Directory
After the Tor Browser directory has been successfully transferred, navigate to this new location using the cd command:
cd /usr/local/share/tor-browserThis command will lead you to the Tor Browser’s new directory under /usr/local/share.
Step 5: Registering the Browser as a Desktop Application
Once in the proper directory, you can register the Tor Browser as a desktop application. Execute the following command to accomplish this:
./start-tor-browser.desktop --register-appUpon execution, the system will initiate the Tor Browser and register it as a desktop application. You should see an output similar to the one below, confirming the registration:
Tor Browser has been registered as a desktop app for this user in ~/.local/share/applications/
This confirms that the Tor Browser is now successfully registered as a desktop application for the current user.
Launch Tor Browser on Fedora Linux
Now that you have the Tor Browser installed, launching can be done in a few ways.
tor-browserAlternatively, Flatpak users must launch using the command below from a terminal instance.
flatpak run com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcherThe Tor Browser can be found in the applications menu by following the path.
Activities > Show Applications > Tor Browser.
Quick Close-Up Tor Browser Settings on Fedora Linux
First Encounter with the Tor Browser Interface
Embarking on your Tor Browser experience marks a pivotal step towards fortified web privacy and security. This guide aims to steer you through initiating the Tor Browser, acquainting you with the diverse options and configurations at your disposal. By the conclusion of this segment, you will be well-prepared for a secure and private online exploration.
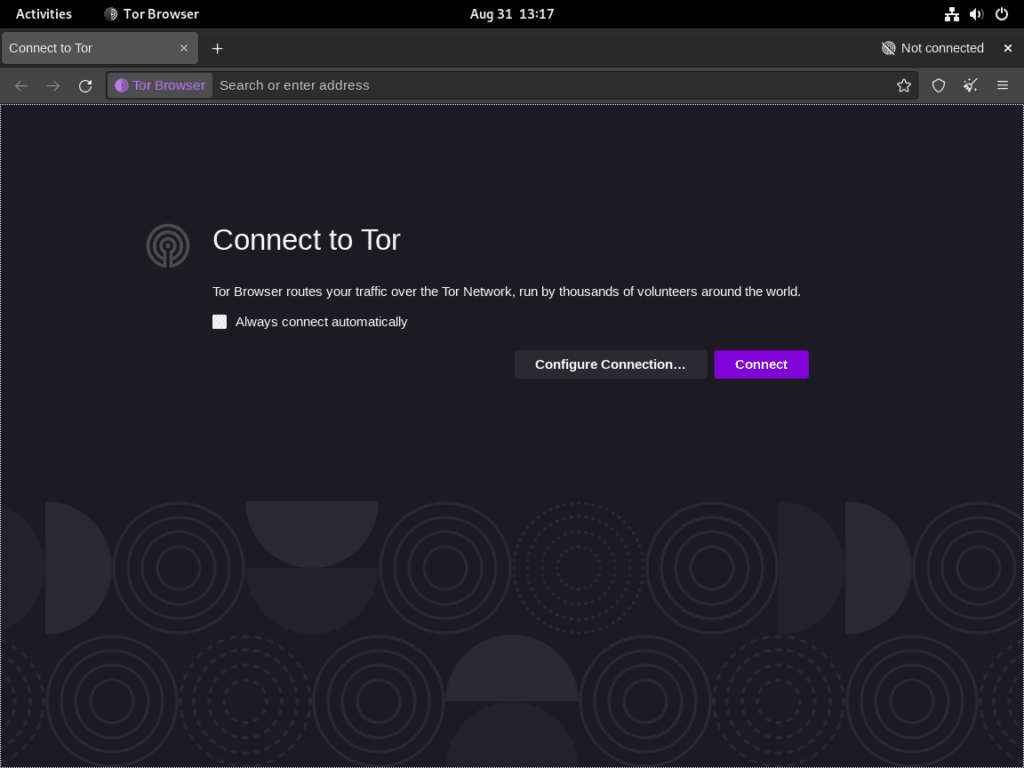
Upon your initial launch, you will be greeted with a dialog window that presents two primary options: “Connect” and “Configure Connection…”
Selecting an Appropriate Connection Strategy
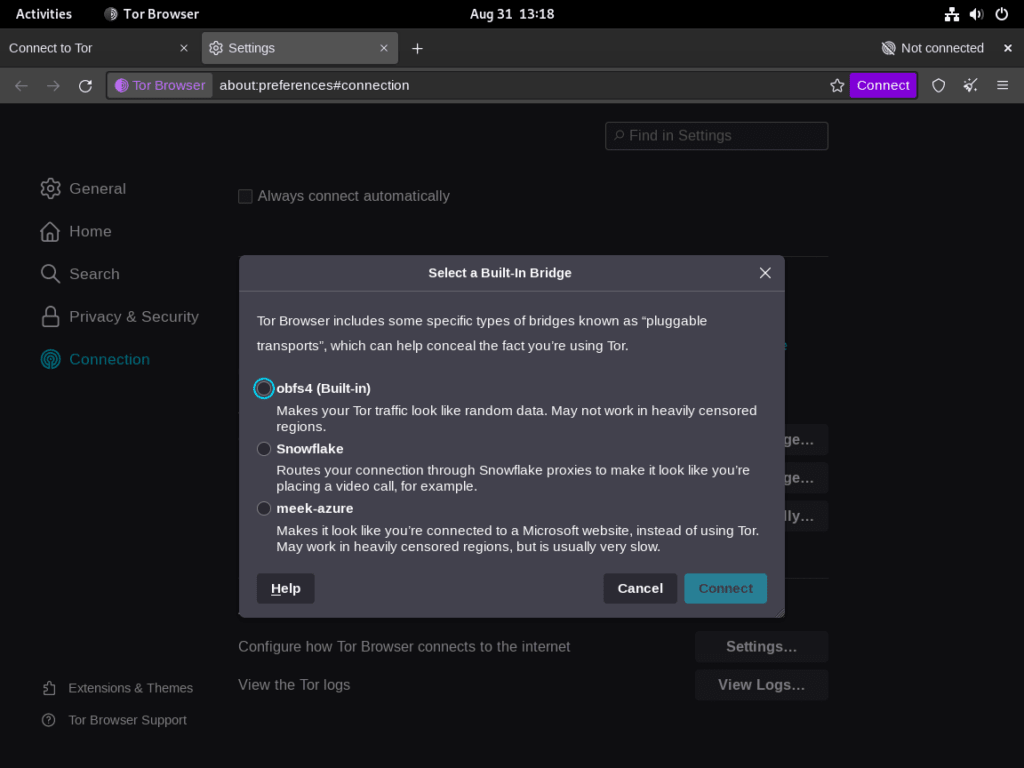
For the average user, clicking “Connect” suffices for general browsing requirements. However, those in jurisdictions with rigorous internet censorship or individuals requiring specialized privacy configurations may opt for “Tor Network Settings” to unlock a broader array of setup alternatives. This setting enables the adjustment of proxy configurations and offers the capacity to establish Tor bridges. These bridges are advantageous for individuals who face challenges accessing specific online resources or require an enhanced connection quality.
Arriving at the Tor Browser’s Home Page
After completing the connection procedure, you’ll be routed to the Tor Browser’s default homepage. By design, the Tor Browser utilizes DuckDuckGo as its primary search engine, a decision motivated by DuckDuckGo’s strong commitment to user privacy.
This concludes your initial setup, positioning you for a secure and private browsing experience on the Tor Browser.
Additional Commands & Tips for Tor Browser on Fedora
Tips on Getting Started on Using Tor Browser on Fedora
Embarking on your journey with the Tor Browser on Fedora elevates your privacy and strengthens your online security. To truly harness the power of this tool, it’s pivotal to comprehend its essential features and learn how to fine-tune them for optimal use. This guide offers specialized tips and recommendations, particularly suited for Fedora installations, to enrich your Tor Browser experience and bolster your digital privacy.
Prioritizing Safety
While the Tor Browser is a formidable digital privacy asset, it is not infallible. Caution is advised when downloading files or opening documents acquired through Tor, as doing so with other applications could inadvertently disclose your actual IP address, jeopardizing your anonymity.
Keeping Current
It’s advisable to routinely upgrade your Tor Browser to the most recent version. This practice ensures you’re equipped with the latest features and security enhancements.
Prudent Bookmarking
Although the Tor Browser allows for bookmarks, it’s wise to be selective. Bookmarking sites tied to your interests or identity could unintentionally expose you.
The Importance of HTTPS
While the Tor network encrypts your internal traffic, relying solely on HTTPS-enabled websites guarantees end-to-end encryption.
Personalizing Your Tor Browser Experience
Tweaking specific settings can make your Tor Browser usage not only more secure but also more user-friendly.
Security Level Adjustments
Navigate to the “shield” icon in the browser’s upper-right corner, and choose “Advanced Security Settings.” Here, you can make adjustments as you see fit. Remember that heightened security configurations may interfere with some website functionalities.
Visual Customization
You can also alter the Tor Browser’s aesthetics. Click on the hamburger menu icon (three horizontal lines) at the top-right corner, choose “Customize,” and drag desired elements to the toolbar.
Leveraging Additional Tor Features
The Tor Browser offers a variety of advanced settings and features that can further refine your browsing experience and enhance your online privacy.
Utilizing Tor Bridges
If you’re situated in an area where Tor is restricted, Tor Bridges can help you circumvent these limitations. To set up a bridge, go to the “Tor Network Settings” and select the “Use a bridge” option.
Abstaining from Torrenting
Tor is not engineered to support high-bandwidth activities like torrenting, which could decelerate the network for others and risk exposing your IP address.
Exercising Discretion with Personal Data
Even when using Tor, it’s advisable to refrain from disclosing sensitive personal data, such as your real name, location, or contact information.
Armed with these insights, you are better positioned to navigate the complexities of the Tor Browser on your Fedora system proficiently.
Keeping Your Tor Browser Updated on Fedora
Once you’ve embarked on your journey towards digital anonymity with the Tor Browser, it’s critical to understand how to maintain it effectively. This involves staying current with updates often laden with vital security patches and feature enhancements. Although the Tor Browser typically updates automatically, it’s prudent to check for new versions routinely. If you initiated the manual installation, you might need to revisit the original installation steps for specific updates. However, most updates are seamlessly managed within the client, negating the need for manual adjustments unless explicitly indicated.
Updating Tor Browser via Flatpak on Fedora
If your installation leveraged Flatpak, the update procedure will differ. Execute the following command in your terminal:
flatpak updateThis command signals your system to scan for updates pertinent to all Flatpak applications, applying them as necessary.
Uninstalling the Tor Browser on Fedora
While the Tor Browser is an invaluable instrument for secure and anonymous browsing, situations might arise where you wish to uninstall it. The uninstallation method is contingent upon your initial installation approach.
Manual Uninstallation Steps of Tor Browser on Fedora
For users who chose the manual installation route, the uninstallation process involves unregistering the application icon and eradicating its directory. Here’s how to go about it:
First, direct yourself to the applications directory:
cd ~/.local/share/applications/
Subsequently, erase the Tor Browser desktop file:
rm tor-browser.desktopLastly, purge the Tor Browser directory:
rm -rf /usr/local/share/tor-browser/
Flatpak Uninstallation of Tor Browser on Fedora
If you installed the Tor Browser via Flatpak, the uninstall command is as follows:
flatpak remove --delete-data com.github.micahflee.torbrowser-launcher
The --delete-data flag ensures the complete removal of any residual data linked to the Tor Browser.
DNF Uninstallation of Tor Browser on Fedora
sudo dnf remove torbrowser-launcherConclusion
In conclusion, we’ve explored the importance of online privacy and security, particularly for Fedora Linux users, and how Tor Browser can be a valuable tool. We’ve delved into the key features that make Tor Browser a compelling choice, from privacy protection and anonymous file sharing to circumventing censorship and accessing restricted content. The guide aims to provide multiple methods for installing Tor Browser on Fedora Linux, ensuring you can choose the one that best suits your needs. By following this guide, you’re taking a proactive step towards enhancing your online privacy and security.