Timeshift stands out as a robust open-source utility designed to enhance data protection on Linux systems. This guide will focus on how to install Timeshift on Debian 12 Bookworm or the older stable releases of Debian 11 Bullseye or Debian 10 Buster, ensuring that users across various Debian versions can leverage this powerful tool.
Key Features and Benefits of Timeshift:
- Incremental Snapshots: Timeshift enables the creation of incremental filesystem snapshots, allowing users to capture the state of their system at different points in time. This is particularly useful for reverting to a previous state in case of system issues.
- BTRFS Integration: For those using the BTRFS filesystem, Timeshift offers enhanced functionality, utilizing the built-in snapshot capabilities of BTRFS for efficient and reliable backups.
- User-Friendly Interface: Despite its powerful features, Timeshift boasts a user-friendly interface, making it accessible even to Linux beginners.
- Data Restoration: Timeshift excels in scenarios where system restoration is required, providing a straightforward process to roll back to a previous system state, ensuring minimal downtime and data loss.
- Versatility: Whether you are a Linux novice starting to learn the ropes or an experienced user looking for a reliable backup solution, Timeshift offers a versatile and dependable choice.
In summary, Timeshift provides Debian users with a comprehensive and reliable system backup and restoration tool. Its integration with BTRFS, coupled with its user-friendly interface, makes it a go-to choice for safeguarding your data. As we proceed, this guide will provide detailed instructions on installing Timeshift, helping you secure your Debian system against potential data loss and system issues.
Install Timeshift on Debian 12, 11, or 10 via APT
Step 1: Update Debian System
Before starting, update your system with the following terminal command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeStep 2: Install Timeshift via APT Command on Debian
The Debian default repository already includes the TimeShift application, so installing Timeshift is straightforward. Install the software with this command:
sudo apt install timeshiftLaunch Timeshift on Debian 12, 11, or 10
After installing Timeshift on your Debian system, open the software immediately with the cli command from your command terminal:
timeshiftOr, launch the software using its graphical application icon by navigating to:
Activities > Show Applications > Timeshift
Create Snapshots with Timeshift on Debian 12, 11 or 10
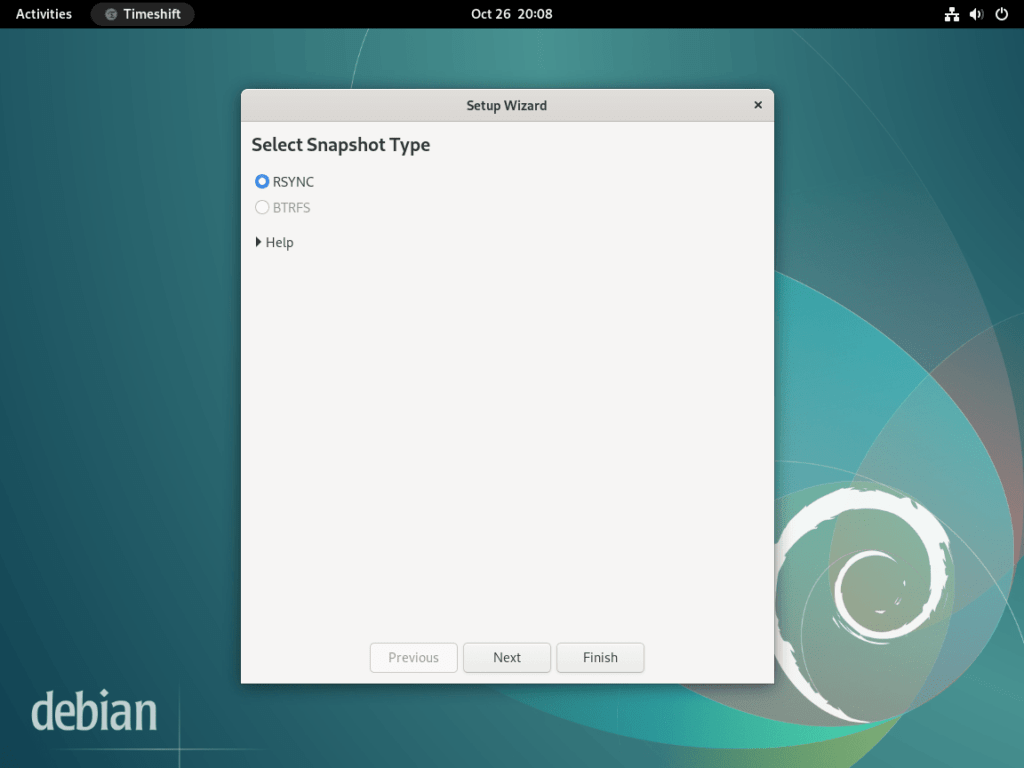
Step 1: Understanding Timeshift Modes
Timeshift is a powerful tool designed to create system snapshots. These snapshots act as checkpoints, which can be reverted to if needed.
Rsync Mode
When using Timeshift in the Rsync mode, the tool employs both rsync and hard links to generate snapshots efficiently. The brilliance of this mode lies in its ability to share standard files across multiple snapshots. This approach ensures that disk space usage is optimized and the creation of snapshots is expedited.
BTRFS Mode
Contrastingly, in the BTRFS mode, Timeshift taps into the capabilities of the BTRFS file system for snapshot generation. However, a crucial point is that the BTRFS mode is tailored explicitly for systems that align with the Ubuntu-type subvolume layout. If your Debian system doesn’t conform to this layout, it’s prudent to utilize the Rsync mode.
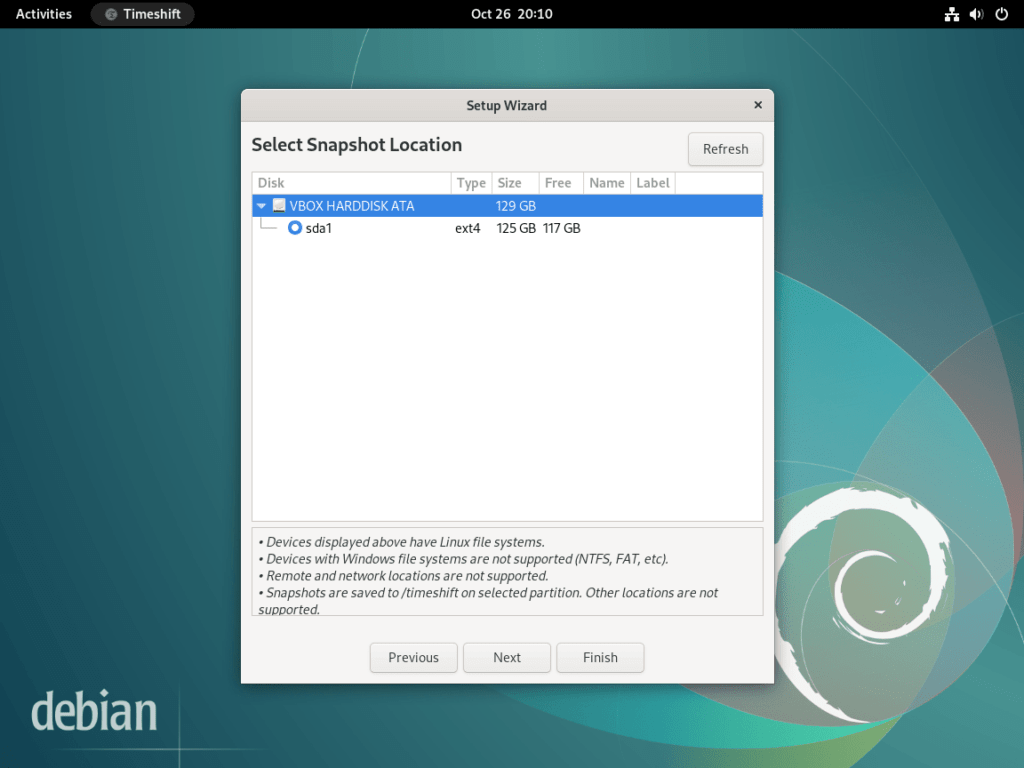
Step 2: Choosing the Right Snapshot Location
Selecting an appropriate location for your snapshots is vital. Ensure that the chosen storage location has adequate space, as snapshots can consume significant disk space over time. Ideally, pick a location that’saccessible and separate from your main system drive to safeguard against potential drive failures.
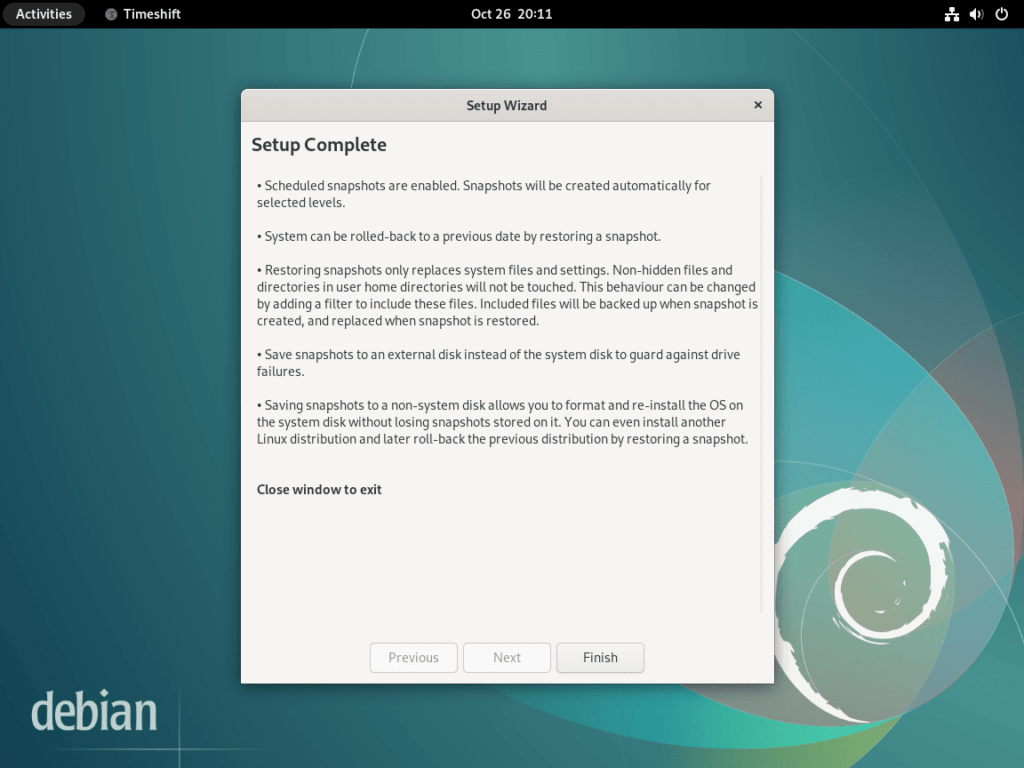
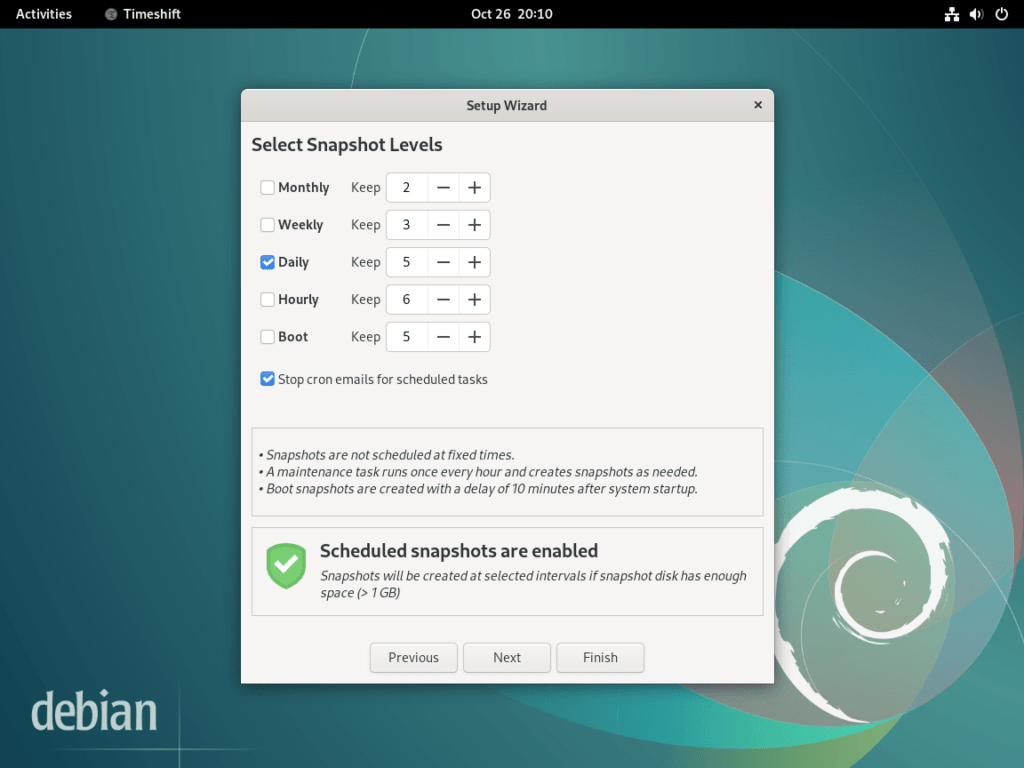
Step 3: The Importance of Scheduling Snapshots
To maximize the utility of Timeshift, it’s advisable to set up regular snapshot schedules. Scheduled snapshots serve as a safeguard, allowing users to revert to a stable state if a recent change causes system instability.
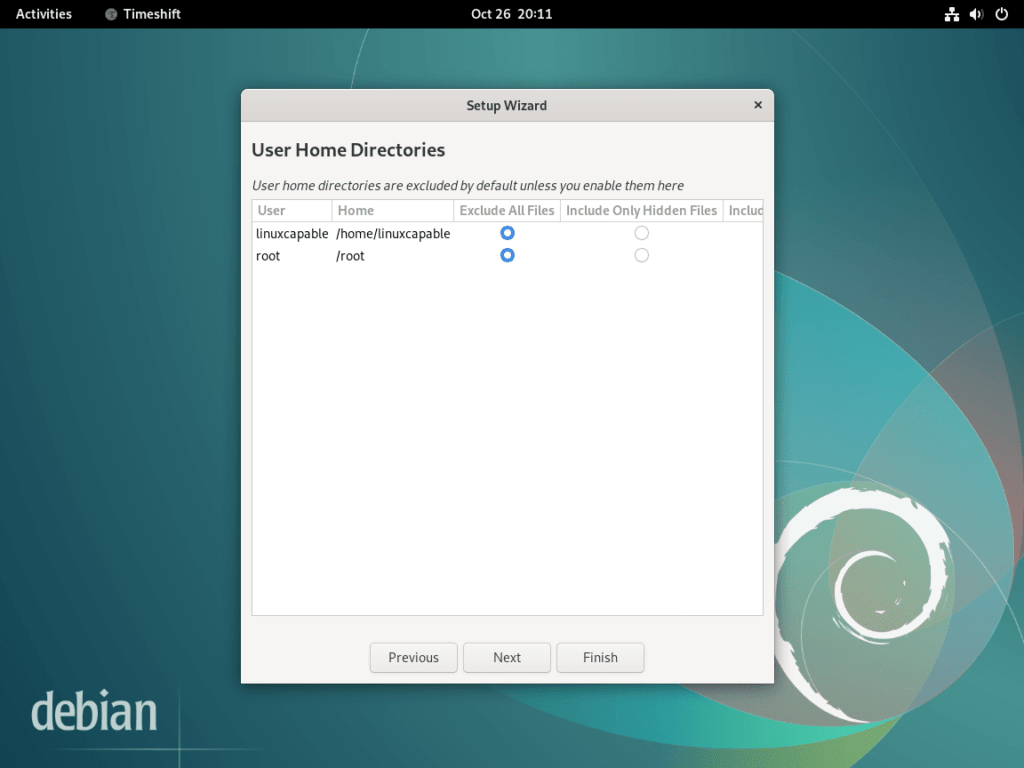
Step 4: Configuring User Home Directories
Timeshift offers flexibility in determining which user home directories should be included in the snapshot. Depending on your needs, you can include all user data or exclude specific directories to streamline the snapshot size.
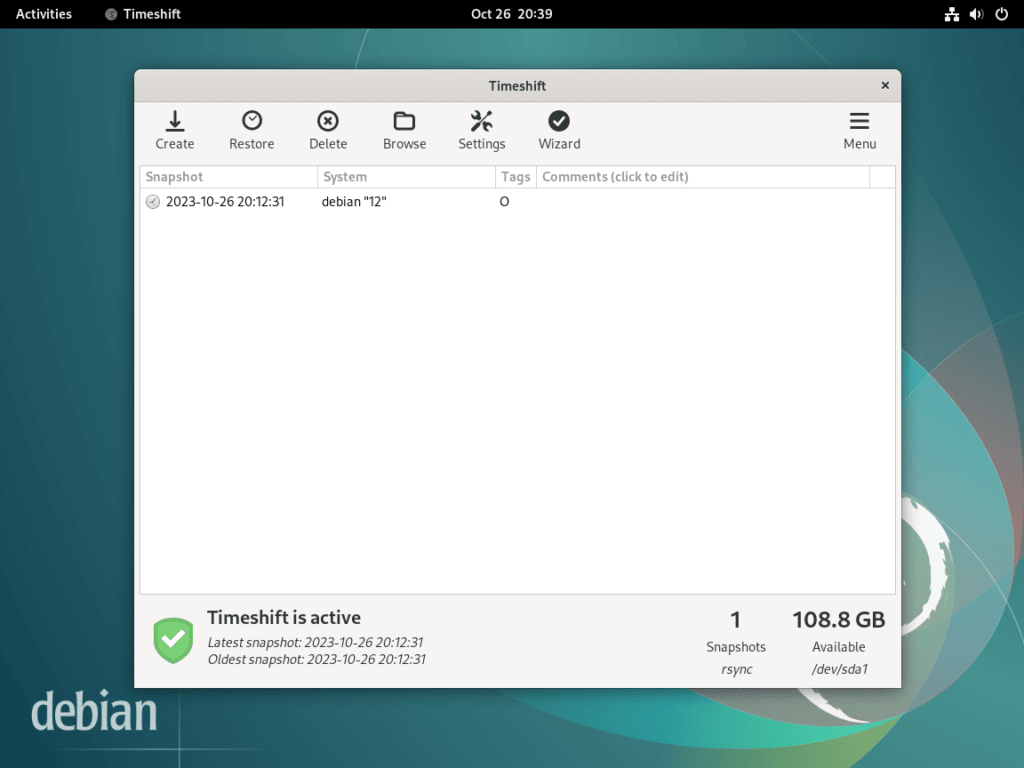
Step 5: Finalizing the GUI Setup
After configuring the settings above, the final step involves reviewing all configurations in the Timeshift graphical user interface (GUI). Ensure that all settings align with your requirements before confirming. Once set, Timeshift will take care of the rest, generating snapshots based on your preferences.
Additional Commands For Timeshift on Debian 12, 11 or 10
Remove (Uninstall) TimeShift From Debian
Users without needing or requiring the backup software can easily remove this using the following command.
sudo apt remove timeshiftThe command will remove all data and dependencies, resulting in complete removal.
Conclusion
In wrapping up this guide, we’ve covered the essential steps to install and set up Timeshift on Debian Linux, spanning Debian 12 Bookworm, Debian 11 Bullseye, and Debian 10 Buster. The process, from terminal commands to the graphical installer’s initial setup wizard, is designed to be straightforward, ensuring users at all levels can secure their system with Timeshift’s snapshot capabilities. Whether utilizing BTRFS or RSYNC, Timeshift provides a reliable method for system restoration, making it a crucial tool for data protection on Debian systems.