The upgrade from Fedora 38 to Fedora 39 introduces enhancements and new features to improve the user experience. Here’s a peek into the key changes that come with Fedora 39:
Technical Advancements:
- A noticeable shift is the migration from NetworkManager ifcfg profiles to keyfile, simplifying network configuration management.
- The update to Golang 1.21 and GNU Toolchain will surely excite developers with the promise of improved performance and new features.
- The inclusion of LLVM 17 and Python 3.12 underpins Fedora’s commitment to staying updated with the latest in programming language compilers and interpreters.
- The adoption of RPM 4.19, LLVM 17, Golang 1.21, Python 3.12, and Perl 5.38 reflects Fedora 39’s stride in keeping up with the latest programming and package management advancements.
- Vagrant 2.3 integration is another noteworthy addition for developers, facilitating better environment management.
Software Upgrades:
- The upgrade to LibreOffice 7.6 continues to enhance productivity capabilities, providing users with a more robust and feature-rich office suite.
- FontAwesome 6 inclusion is a subtle but effective upgrade for a richer iconography experience.
User Interface and Experience:
- The introduction of Color Bash Prompt and Noto fonts for Indic scripts are minor but impactful changes to the user interface.
- Improved Default Font Handling enhances the text readability and overall aesthetic appeal of the system.
System Improvements:
- The ability to remove tzdata is a critical step towards enabling minimal system installations.
- The decision to make Toolbox a release-blocking deliverable illustrates a shift towards ensuring robust container management.
These changes and others are part of Fedora’s continuous effort to provide a polished, user-friendly, and up-to-date operating system.
Pre-Upgrade Checklist For Upgrading to Fedora 39
Before starting the upgrade process, performing a few preliminary steps is essential to ensure a smooth transition. In this section, we’ll walk you through the pre-upgrade checklist.
Step 1: Update Fedora 38 (Required)
Updating your Fedora 38 system is a crucial first step to ensure all packages are current and compatible with the new version. To update your system, open a terminal and enter the following command:
sudo dnf upgrade --refreshThis process may take some time, so be patient. Ensure your system is current before proceeding to the next step.
Step 2: Remove Old Obsolete Fedora 38 Packages (Recommended)
Cleaning up your existing Fedora system by removing old, obsolete packages can help prevent potential conflicts during the upgrade process. To remove old packages, enter the following command in the terminal:
sudo dnf autoremoveThis command will identify and remove any packages no longer needed on your system, freeing up space and ensuring a cleaner upgrade.
Step 3: Increase DNF Speed / Add DNF Mirrors (Optional)
Upgrading to Fedora 39 involves downloading numerous packages, which can be time-consuming. To speed up the process, consider optimizing the DNF package manager by adding DNF mirrors and servers hosting Fedora packages. This lets you download packages from a server closer to your location, resulting in faster download speeds.
If you’re interested in configuring DNF for faster performance, refer to the guide on Increasing DNF Speed on Fedora Linux. This resource will walk you through optimizing your DNF package manager for improved download speeds.
Download and upgrade to Fedora 39 From Fedora 38
With these essential pre-upgrade steps completed, you’re now ready to upgrade your Fedora system to version 39. Follow the subsequent sections for a step-by-step guide on upgrading the Fedora Workstation and Fedora Server using CLI commands.
Step 1: Install the DNF-plugin-system-upgrade Package on Fedora
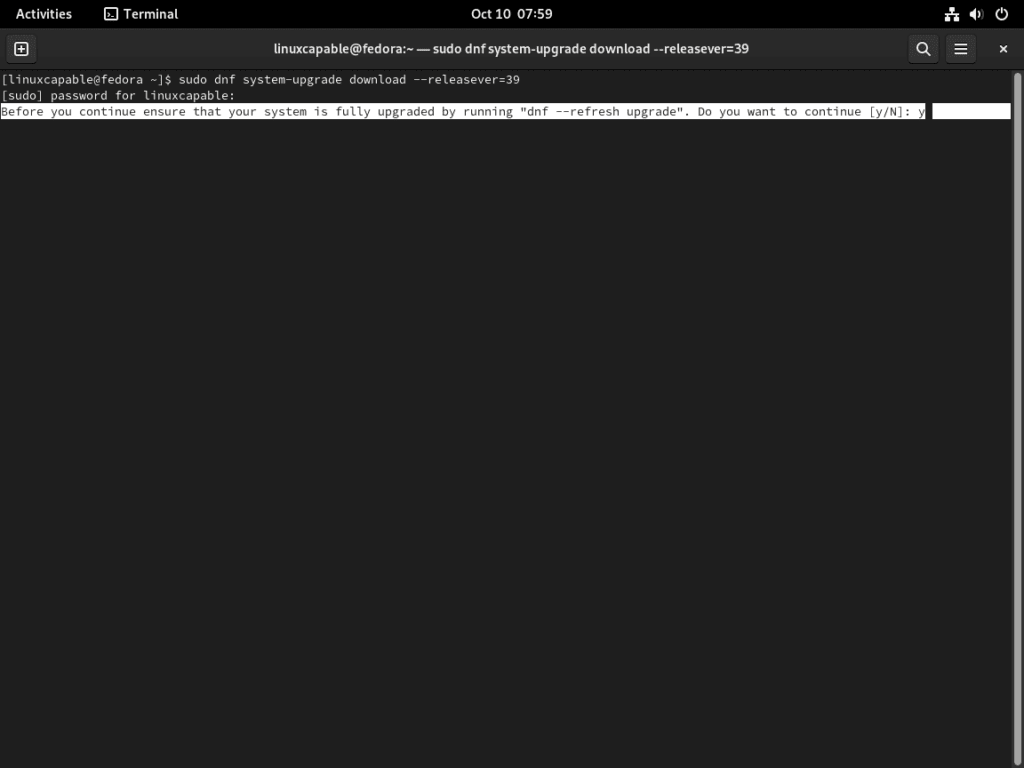
First, open your Fedora terminal and make sure the dnf-plugin-system-upgrade package is installed on your system. This package should be installed by default, but running the following command ensures it’s present:
sudo dnf install dnf-plugin-system-upgradeStep 2: Download the Fedora 39 Release
Now it’s time to download the Fedora 39 release using the system-upgrade command. Enter the following command in the terminal:
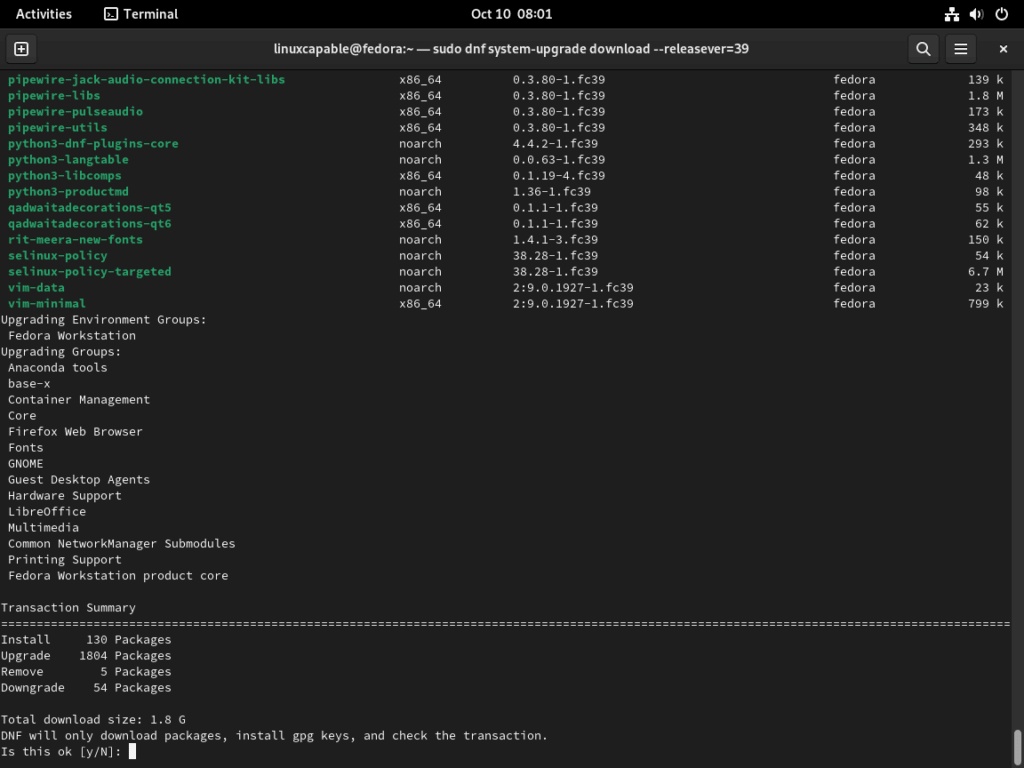
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=39This command downloads all the necessary packages for the upgrade process. Note that this may take some time, depending on your internet connection speed and the number of packages to be downloaded.
During the process, a message will prompt you about package installation, upgrade, downgrade, and download size.
Review the information and press y to continue with the installation.
You must reboot your system once the package download is complete to initiate the final installation process.
To do so, enter the following command in the terminal:
Enter the following command in the terminal:
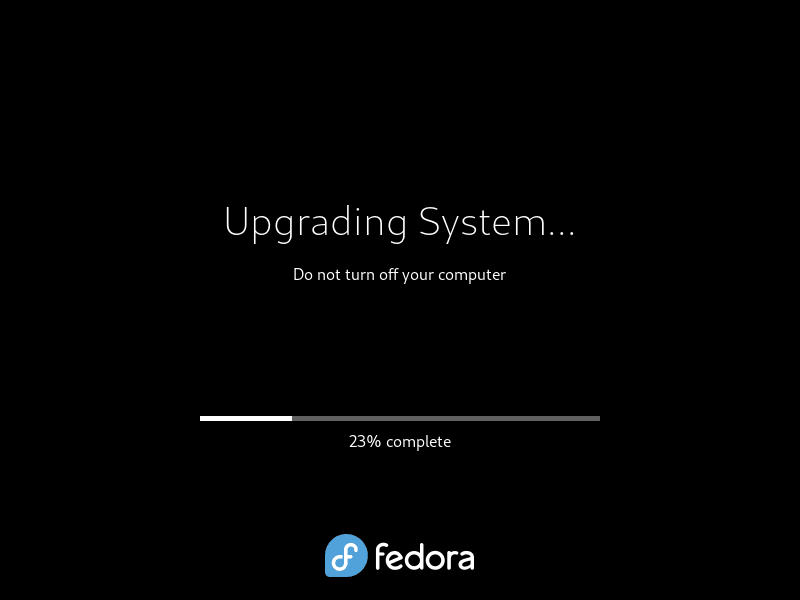
sudo dnf system-upgrade rebootThe system will reboot, and a progress bar will indicate the final installation progress.
Step 3: Monitor the Upgrade Progress and Complete the Upgrade
After the system reboots, a progress bar will appear to indicate the final installation progress. Monitor the progress bar to ensure the upgrade is progressing as expected.
Once the upgrade is complete, Fedora will return you to the login screen. Log in to your system to start using Fedora 39.
Log in to Fedora 39 and Verify Fedora Upgrade
After completing the upgrade to Fedora 39 and logging in, you’ll notice some changes to the user interface. These include a new default background, updated icons, and a refreshed wallpaper.
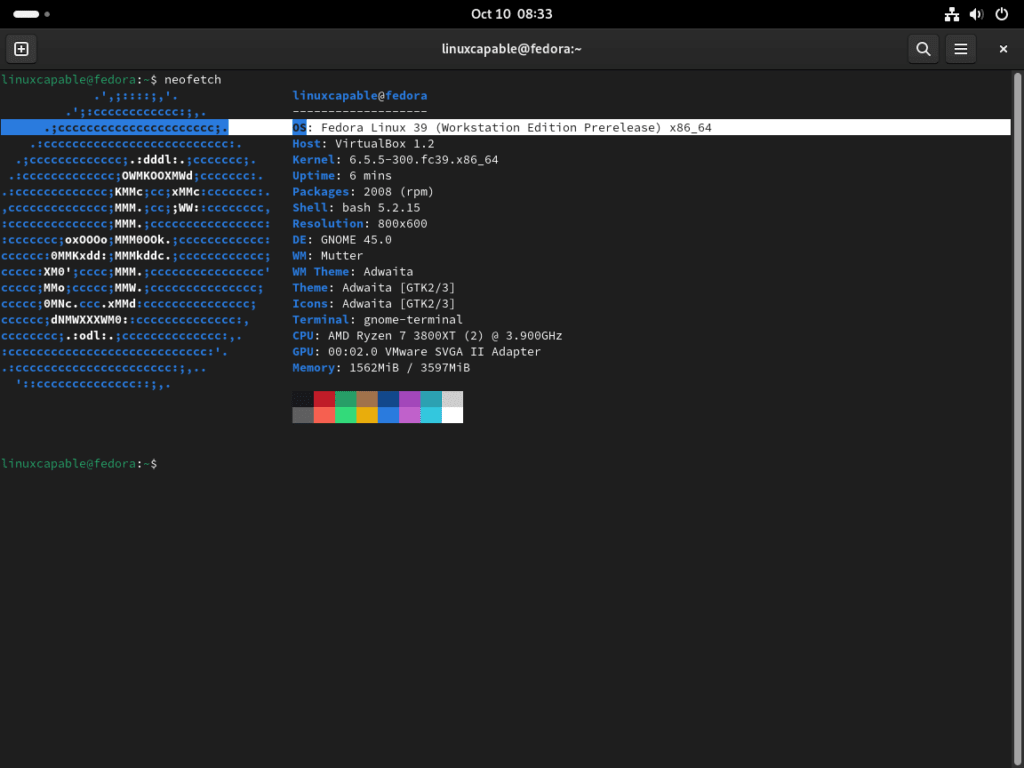
Fedora 39 Post Upgrade Cleanup (Optional and Situational)
After upgrading to Fedora 39, performing some cleanup tasks is an excellent idea to ensure your system runs smoothly and efficiently. This section will guide you through the recommended post-upgrade cleanup steps.
Step 1: Remove Old and Obsolete Packages From Fedora 39
First, clean up your system by removing any old and obsolete packages. To do this, run the following command in the terminal:
sudo dnf system-upgrade cleanThis command will remove any leftover data from the upgrade process, ensuring your system is free from unnecessary files.
Step 2: Remove Broken Symlinks on Fedora 39
Removing broken symlinks on your system can help prevent potential issues and maintain a clean filesystem. To remove broken symlinks, run the following command:
sudo find /usr -type l -xtype l -deleteIf you’d like to view a list of all broken symlinks before cleaning them up, you can use the following command to display them:
sudo symlinks -r /usr | grep danglingThis command will show you all the broken symlinks, allowing you to review them before removing them with the previous command.
Step 3: Change the Hostname (Optional) on Fedora 39
Finally, if you want to change the hostname of your Fedora system, you can use the following command:
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname --static fedora-39Replace fedora-39 with the desired hostname for your system. This step is optional but helpful if you’d like to customize your system’s hostname.
Troubleshooting Fedora 39 Upgrade Issues
Sometimes, you might encounter issues during the Fedora 39 upgrade process. This section will discuss common problems and their potential solutions to help you overcome these obstacles and successfully upgrade your system.
Step 1: Use the –allowerasing Option
If you face conflicts during the upgrade, you can try adding the --allowerasing option to your upgrade command. This allows DNF to remove packages that might be causing conflicts during the upgrade. To use this option, enter the following command in the terminal:
sudo dnf system-upgrade download --releasever=38 --allowerasingStep 2: Re-sync Your Fedora 38 System
If the --allowerasing option doesn’t resolve the issue, you might need to re-sync your Fedora 38 system using the following command:
sudo dnf distro-syncThis command will synchronize your system with the latest Fedora 38 package versions, which might help to resolve any conflicts you are experiencing.
Step 3: Reset SELinux (Last Resort)
If you’ve exhausted all other options and are still encountering issues, you might consider resetting SELinux.
This step should only be used as a last resort and only if you’ve previously adjusted SELinux permissions.
To reset SELinux, enter the following command in the terminal:
sudo fixfiles -B onbootThis command will reset SELinux and apply any necessary changes during the next system boot.
Retry the Upgrade Process
Once you’ve tried the troubleshooting steps mentioned above, you can re-run the upgrade commands from the beginning of the guide to restart the upgrade to Fedora 39.
Conclusion
Upgrading to Fedora 39 from Fedora 38 is a prudent step forward, embracing various technical advancements and user-experience enhancements. Through our discussion, we’ve navigated the upgrade steps and addressed tips to tackle common issues you might encounter. With its updated software suites and improved system capabilities, Fedora 39 stands as a testament to Fedora’s ongoing commitment to delivering a modern and user-friendly operating environment.




Hello, there is a small typo, it still mentions releasever=38:
sudo dnf system-upgrade download –releasever=38
It should be
sudo dnf system-upgrade download –releasever=39
Thanks for the great guide!
i appreciate the message on the typo, it’s fixed.
thanks again 🙂