Tasksel simplifies the process of installing predefined collections of software packages on Ubuntu, making it ideal for setting up web servers, database servers, or desktop environments with a single command. Instead of manually installing each component of a LAMP stack or SSH server, Tasksel bundles everything together and handles the configuration automatically. By the end of this guide, you will have Tasksel installed and ready to deploy complete server environments or desktop configurations through its interactive menu interface.
This guide supports Ubuntu 22.04 LTS and 24.04 LTS installations. Tasksel is available in Ubuntu’s default repositories, so commands shown work identically on both supported LTS releases.
Update Ubuntu Before Tasksel Installation
First, update your system to ensure all existing packages are current. This step helps prevent potential conflicts during the Tasksel installation.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeInstall Tasksel via APT Command
Tasksel is available in Ubuntu’s default repositories, so installation requires only a single command. To install Tasksel, enter the following in your terminal:
sudo apt install tasksel
Verify the Installation
After installation completes, confirm that APT recognizes Tasksel by checking its package status:
apt-cache policy taskselThe output confirms the installed version and repository source:
tasksel:
Installed: 3.75ubuntu1
Candidate: 3.75ubuntu1
Version table:
*** 3.75ubuntu1 500
500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble/main amd64 Packages
100 /var/lib/dpkg/status
Version numbers differ between Ubuntu releases: Ubuntu 24.04 LTS ships version 3.75ubuntu1, while Ubuntu 22.04 LTS uses 3.68ubuntu2. Your output will reflect your specific release.
Test Tasksel with Dry Run
Additionally, you can test Tasksel’s functionality using the -t flag, which performs a dry run without actually installing any packages:
sudo tasksel -tRunning this command opens the Tasksel interface and allows you to select a task. The system performs a simulated installation, demonstrating the process without deploying any software packages. This is useful for exploring available tasks before committing to an installation.
Launch and Use Tasksel
With Tasksel now on your system, you can launch it to install software task groups. Because Tasksel modifies system packages, it requires root privileges.
Open the Tasksel Interface
To launch the interactive Tasksel menu, run the following command:
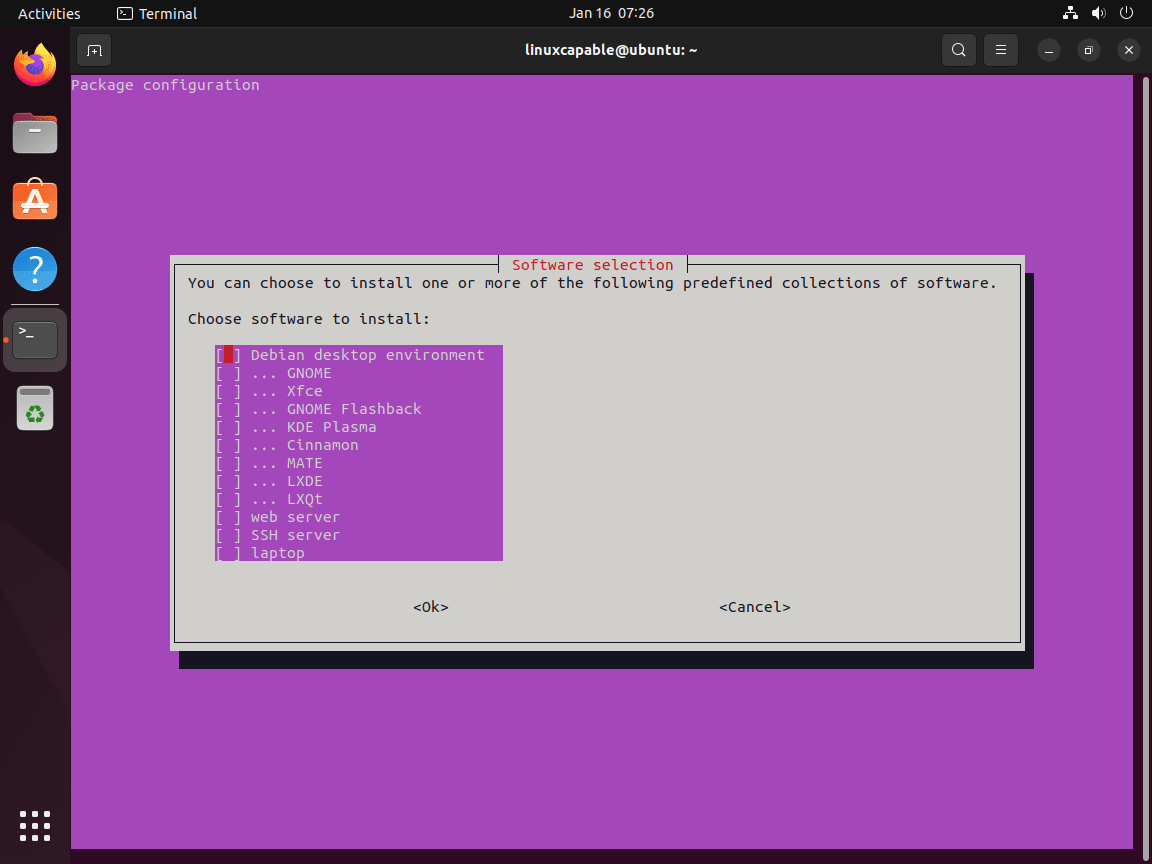
sudo taskselThis opens a text-based interface showing all available task groups. On Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, the available tasks include:
┌───────────────────────┤ Software selection ├────────────────────────┐ │ You can choose to install one or more of the following predefined │ │ collections of software. │ │ │ │ Choose software to install: │ │ │ │ [ ] KDE Plasma │ │ [ ] Cinnamon │ │ [ ] MATE │ │ [ ] LXDE │ │ [ ] LXQt │ │ [ ] web server │ │ [ ] SSH server │ │ [ ] laptop │ │ │ │ <Ok> <Cancel> │ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
Select and Install a Task
In the Tasksel menu, use the arrow keys to navigate to your desired task. Press the spacebar to select it (an asterisk appears next to selected items), then press Tab to highlight the “Ok” button and Enter to confirm your selection.
For example, to install an SSH server:
- Navigate to “SSH server” using the arrow keys.
- Press spacebar to select it.
- Press Tab to move to “Ok” and press Enter.
Tasksel then automatically installs all packages required for that task. For more detailed SSH configuration options, see our guide on installing and enabling SSH on Ubuntu.
Install Tasks from Command Line
Alternatively, you can install tasks directly from the command line without opening the interactive interface. First, list all available tasks:
tasksel --list-tasksThe output shows each task’s status (u for uninstalled, i for installed) and name:
u kde-desktop KDE Plasma u cinnamon-desktop Cinnamon u mate-desktop MATE u lxde-desktop LXDE u lxqt-desktop LXQt u web-server web server u ssh-server SSH server u laptop laptop
To install a specific task directly, use the install command with the task name:
sudo tasksel install ssh-serverThis approach is particularly useful for scripted deployments or when you already know which task you need.
Verify Task Installation
After installing a task, verify that the services are running correctly. For example, after installing the SSH server task, check the service status:
sudo systemctl status sshFor a web server task, you would check Apache’s status:
sudo systemctl status apache2The output should show “active (running)” to confirm the service started successfully. For comprehensive web server setup including virtual hosts and SSL, see our guide on installing Apache on Ubuntu.
Troubleshoot Common Tasksel Issues
Debconf Frontend Errors in Minimal Installations
When running Tasksel on minimal Ubuntu installations or Docker containers, you may see warnings about the debconf frontend:
debconf: unable to initialize frontend: Dialog debconf: falling back to frontend: Readline
These warnings occur because minimal systems do not include the dialog package (which provides the text-based UI) by default. To resolve this, install the dialog package:
sudo apt install dialogAfter installing dialog, Tasksel will display its graphical interface correctly. Standard Ubuntu desktop and server installations typically include this package by default.
Remove Tasksel from Ubuntu
If you no longer need Tasksel, you can remove it from your system. Removing Tasksel does not affect any software you installed using it—those packages remain installed independently.
To remove Tasksel and its data package, run:
sudo apt remove tasksel tasksel-dataNext, remove any orphaned dependencies that APT installed alongside Tasksel:
sudo apt autoremoveFinally, verify that Tasksel has been removed:
apt-cache policy taskselThe output should confirm that APT no longer lists Tasksel as installed:
tasksel:
Installed: (none)
Candidate: 3.75ubuntu1
Version table:
3.75ubuntu1 500
500 http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu noble/main amd64 Packages
Conclusion
You now have Tasksel installed and configured on Ubuntu, ready to deploy complete server environments or desktop configurations through its interactive or command-line interface. The tasksel install command is particularly useful for quickly provisioning new servers with SSH access, web server capabilities, or database functionality. For production deployments, consider combining Tasksel with manual configuration to fine-tune services like Nginx or MySQL according to your specific requirements.

