This guide will demonstrate how to install Okular on Ubuntu 24.04, 22.04, or 20.04 LTS utilizing the command-line terminal with three different methods: APT with Ubuntu’s default repository, which for many users will be the first option, and either Snapcraft with CLI commands or the Flatpak package manager utilizing the Flathub for alternative updated versions.
Okular stands as a versatile, user-friendly document viewer developed by the KDE community, offering extensive support for various file formats, including PDF, ePub, DjVu, and many others. Its rich set of features makes it an indispensable tool for anyone looking to view, review, and annotate documents efficiently. Beyond mere document viewing, Okular provides functionalities such as text highlighting, note-taking, and form-filling, making it a top choice for students, professionals, and casual users alike. The application’s adaptability across multiple Linux distributions and integration capabilities elevate the user experience to new heights.
Key highlights of Okular include:
- Broad File Format Support: From PDFs to comic book formats, Okular handles a wide array of document types.
- Annotation Tools: It offers comprehensive annotation capabilities, including highlights, notes, and stamps.
- Customizable Viewing Options: Users can tailor their viewing experience with various modes and themes.
- Accessibility Features: Includes features like text-to-speech and magnification for users with visual impairments.
With Okular, engaging with digital documents becomes more interactive and productive, thanks to its blend of powerful features and intuitive interface. Whether you’re reviewing a technical paper, signing a document, or just reading your favorite comic book, Okular ensures a seamless experience.
Now, let’s move forward to installing Okular on your Ubuntu system, ensuring you can take full advantage of this exceptional document viewer without delay.
Install Okular on Ubuntu via APT
Update Ubuntu Packages are Updated Before Okular Installation
We must lay the groundwork before we embark on the installation journey by ensuring our Ubuntu packages are up-to-date. This practice not only maintains the overall health of your system but also preempts any potential software conflicts that could occur during the installation process.
You can swiftly accomplish this task using the Terminal, an interface allowing you to interact with the system using text commands. Here is the command you should enter:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeInstall Okular on Ubuntu via APT Command
Once your system is updated, we’re ready to install Okular. The Ubuntu default APT repository offers a stable and secure version of Okular, which makes it a highly recommended option for installation. While it might not always be as up-to-date as the Flatpak version, the APT repository is known for its robust, tried-and-true packages.
To install Okular from the APT repository, you’ll need to execute the following command in your Terminal:
sudo apt install okularUpon running this command, your system will reach out to the Ubuntu repositories, fetch the Okular package, and proceed with the installation. Once the process is complete, you will have successfully installed Okular on your Ubuntu system through the APT repository.
As we continue, we’ll explore alternate methods of installation, which can come in handy depending on your specific requirements.
Install Okular on Ubuntu via Snap
Snapcraft, commonly referred to as ‘Snap’, offers another pathway to install Okular. It’s a universal package manager created by Canonical (the maker of Ubuntu) that simplifies the installation process and ensures you always have the latest version of an application. It should be available on your Ubuntu desktop by default unless it has been previously removed.
Enabling Classic Snap Support on Ubuntu for Okular
To kick things off, we need to ensure that Snap can handle ‘classic’ packages. A ‘classic’ Snap has more permissions on the host system than regular Snaps, which allows it to function just like a traditionally packaged application. Not all applications require this, but it’s prudent to enable classic support to have the broadest compatibility.
We’ll create a symbolic link (symlink), essentially a shortcut that points from one location to another in the filesystem. This enables the Snap package manager to find and handle classic Snaps.
To create this symlink, input the following command:
sudo ln -s /var/lib/snapd/snap /snapHere’s the breakdown for those who may be interested:
sudogrants the command administrative privileges, as creating a symlink at the system level requires these permissions.ln -sis the part of the command that creates a symbolic link./var/lib/snapd/snapis the source directory that houses the Snap core files./snapis the target directory where the symlink will be created.
Install the Snap Core
Once classic support is enabled, installing the Snap core is next. The Snap core provides the foundations for any Snap package to run properly on your system, and it helps avoid any potential issues.
Use the following command to install the Snap core:
sudo snap install coreThis command follows the same pattern as before: sudo for administrative privileges, snap install to instruct the system to install a Snap package, and core being the specific package to install.
Install Okular on Ubuntu via Snap Command
With the preparations complete, we’re now ready to install Okular using Snap. Thanks to the universality of Snap, this command is as straightforward as it comes.
Input the following command to install Okular:
sudo snap install okularAs before, sudo grants administrative privileges, snap install instructs the system to install a Snap package, and okular is the specific package we’re installing.
Once this command completes, you will have successfully installed Okular on your Ubuntu system using the Snapcraft package manager.
Install Okular on Ubuntu via Flatpak and Flathub
In this section, we’ll dive into another method of installing Okular: using the Flatpak package manager. Flatpak is a universal package management system for Linux that makes applications available across a variety of Linux distributions. It operates in a sandbox environment, isolating applications from the main system, which enhances system security and stability.
Note: If your system doesn’t already have Flatpak installed, you can follow our step-by-step guide on “How to Install Flatpak on Ubuntu” to get up and running with the most recent supported version of Flatpak.
Enabling Flathub for Okular on Ubuntu
Our first step in this journey is to enable the Flathub repository. Flathub is a vibrant app store that hosts a multitude of Flatpak applications. It’s like an ever-expanding library, ensuring you have a vast variety of applications, including Okular.
To add the Flathub repository to your Flatpak configuration, execute the following command:
sudo flatpak remote-add --if-not-exists flathub https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepoIn this command:
sudogrants administrative privileges needed for adding a repository.flatpak remote-addis the command to add a new repository to Flatpak.--if-not-existsis a safety mechanism that prevents Flatpak from returning an error if Flathub is already added to the configuration.flathubis the name assigned to the repository.https://flathub.org/repo/flathub.flatpakrepois the URL of the Flathub repository.
Once you’ve run this command, your system is set to fetch and install applications from Flathub.
Install Okular on Ubuntu 22.04 or 20.04 via Flatpak
With Flathub at our disposal, we’re all set to install Okular. The Flatpak version of Okular can be fetched directly from the Flathub repository, which ensures you’re getting the latest version of the application.
Enter the following command to install Okular:
flatpak install flathub org.kde.okular -yIn this command:
flatpak installinstructs the system to install a Flatpak package.flathubpoints to the repository that the package will be fetched from.org.kde.okularis the specific package we’re installing.-yis an optional parameter that automatically answers ‘yes’ to any prompts, streamlining the install process.
Once the process is complete, you’ll have successfully installed Okular via Flatpak and Flathub.
Launching Okular on Ubuntu
Congratulations on successfully installing Okular! Now, let’s shift gears and focus on how to launch this versatile document viewer on your Ubuntu Linux system. There are several ways to start using Okular, depending on your preferred method and the package management system used for installation.
Launching Okular from the Terminal on Ubuntu
To begin with, you can launch Okular directly from your Terminal. This method can be handy when you’re already operating within the terminal environment. The command to start Okular is as straightforward as:
okularRunning this command searches for the Okular application within your system and initiates it promptly.
If you installed Okular using Snapcraft, the command to launch Okular is slightly different:
snap run okularIn this command, snap run instructs the Snapcraft system to execute the application following it, in this case, okular.
For those who installed Okular via Flatpak, the command to start Okular takes a different form:
flatpak run org.kde.okularHere, flatpak run prompts the Flatpak system to execute the specified application, identified by org.kde.okular.
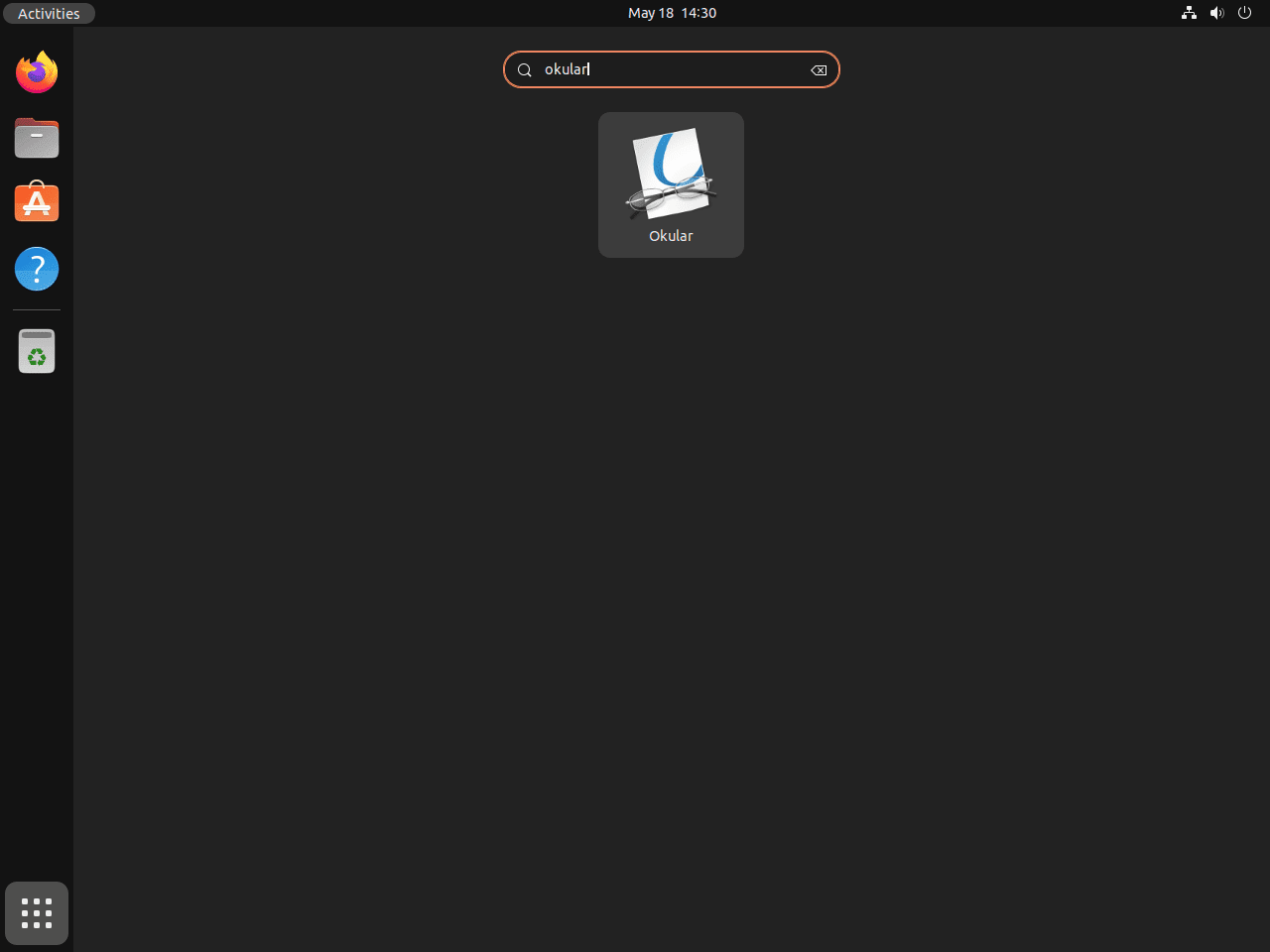
Launching Okular from the Ubuntu Desktop
While running Okular from the Terminal is efficient, it’s not always the most practical or user-friendly method, especially if you frequently interact with a graphical desktop environment.
To launch Okular from your desktop:
- Click on ‘Activities’ located at the top-right corner of your desktop.
- Select ‘Show Applications’.
- Search for ‘Okular’ in the application list.
First-Time Tips with Okular on Ubuntu
Now that you have successfully installed Okular on Ubuntu Linux, here are some first-time tips on getting started with the software:
General Tips for Okular on Ubuntu
- Explore the Interface: Familiarize yourself with Okular’s layout and where the different tools and options are located. Understanding the interface will greatly enhance your efficiency.
- Keyboard Shortcuts: Make use of keyboard shortcuts to navigate through documents quicker. For example,
Ctrl+Fallows you to search within the document, andCtrl+Shift+Nopens a new window. - Document Preview: Utilize the Thumbnails panel for a quick preview of document pages. This feature is especially useful for lengthy documents.
- Configure Default View Settings: Adjust the default zoom level, page layout, and other viewing preferences from the Settings menu to suit your needs.
Customization Tips for Okular
- Theme and Appearance: Customize the appearance of Okular to match your desktop environment. You can change the color scheme and font settings under Settings > Configure Okular.
- Annotation Tools Setup: Tailor the annotation tools to your liking. You can customize the color, size, and opacity of annotation tools for a more personalized note-taking experience.
- Memory and Performance: In the settings, you can adjust memory usage options to optimize performance, especially useful for older hardware.
- Document-Specific Settings: Remember, Okular allows you to save document-specific settings such as annotations, bookmarks, and the last page read, making it easier to pick up where you left off.
Navigation and Usability Tips
- Advanced Search: Beyond basic text search, Okular supports searching by annotations, bookmarks, and even metadata. This feature is invaluable for research and studying.
- Split View: Use the split view feature to view different sections of a document simultaneously. This can be activated from the View menu.
- Bookmark Pages: For lengthy documents, use bookmarks to easily navigate back to important pages. You can manage bookmarks via the Bookmarks menu.
- Presentation Mode: Make use of the presentation mode for PDFs during meetings or lectures. It provides a clean, distraction-free way to display documents.
Accessibility Features
- Text to Speech: Okular supports text-to-speech functionality, which can be a great aid for users with visual impairments or for those who prefer auditory learning.
- Magnification Tool: Use the magnification tool to zoom into specific areas of a document without changing the overall zoom level.
- High Contrast Themes: For users who require high contrast for better readability, Okular supports various high contrast themes that can be activated from the settings.
- Keyboard Navigation: Navigate through the document, annotations, and the Okular interface itself using keyboard shortcuts to improve accessibility.
Exploring these tips, you’ll be well on your way to mastering Okular on your Ubuntu system. Remember, the more you use Okular, the more you’ll discover its full potential to enhance your document viewing and annotation experience.
Managing Okular on Ubuntu
Being proficient in managing your software is as crucial as knowing how to use it. This section will guide you through the procedures to update and uninstall Okular on Ubuntu Linux, providing necessary insights at each stage.
Update Okular
One of the benefits of software updates is getting access to the latest features, improved security, and bug fixes. Ubuntu’s system regularly checks for updates and notifies you about them. However, in certain scenarios, these notifications may not appear. That’s when you need to take the reins and manually check for updates using the Terminal. Here’s how you do it based on the installation method you followed:
APT Update Terminal Command for Okular on Ubuntu
For installations done via the APT package manager, enter the following command in your Terminal:
sudo apt updateThis command updates the package list on your Ubuntu system, including Okular.
Flatpak Update Terminal Command for Okular on Ubuntu
For those who have installed Okular using Flatpak, you can update your software with the following command:
flatpak updateThis command checks for updates in your Flatpak applications and installs them.
Snap Update Terminal Command for Okular on Ubuntu
If you have used Snap to install Okular, update it using the command below:
sudo snap refreshThis command will update all your Snap applications, including Okular.
Remove Okular from Ubuntu
There might come a time when you no longer require Okular on your Ubuntu system. Here’s how to uninstall it based on your original installation method:
APT Remove Terminal Command for Okular
To remove Okular installed via the APT package manager, use the following command:
sudo apt remove okularFlatpak Remove Terminal Command for Okular
If Okular was installed using Flatpak, use the following command to remove it:
flatpak remove --delete-data org.kde.okular -ySnap Remove Terminal Command for Okular
For Okular installed via Snap, you can uninstall it using the following command:
sudo snap remove okularClosing Thoughts
In this guide, we walked you through installing Okular on Ubuntu Linux, covering everything from using APT and Snapcraft to exploring Flatpak options for those seeking the latest versions. We also shared some first-time tips to kickstart your journey with Okular, focusing on customization, navigation, and making the most out of its robust features for document viewing and annotation. As a final recommendation, dive into Okular’s settings to tailor the experience to your needs, and don’t shy away from experimenting with different tools and features to find what works best for you. Remember, the goal is to make your document handling as efficient and pleasant as possible, so take these tips, explore, and make Okular your own.