This guide demonstrates how to install Neofetch on Linux Mint 21, 20 using the command-line terminal.
Neofetch stands out as a versatile and efficient tool for displaying system information in Linux environments. Primarily used in server settings, it offers a wealth of features that cater to the needs of users, system administrators, and developers alike. Its functionality and ease of use make it a popular choice across various Linux distributions.
Key Features of Neofetch:
- Quick System Overview: Displays essential system information like OS, kernel, CPU, and memory.
- Customization Options: Allows users to tailor the display to their preferences.
- Lightweight and Fast: Ideal for servers and systems where resource efficiency is crucial.
- Cross-Platform Utility: Compatible with numerous Linux distributions.
- Developer-Friendly: Outputs information in a format easy to integrate into scripts and tools.
Neofetch’s ability to provide detailed system information with minimal effort makes it an invaluable tool in your Linux toolkit. Whether you are managing a server or just curious about your system’s details, Neofetch delivers this information in a user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing manner. Let’s dive into the installation process on Linux Mint.
Install Neofetch on Linux Mint 21, 20 via APT
Update Linux Mint Before Neofetch Installation
To ensure a smooth installation of Neofetch, begin by updating your Linux Mint system. Updating and upgrading your existing packages is a crucial step to maintain compatibility and avoid conflicts. This process updates your system with the latest versions of all packages, enhancing stability and security. Open your terminal and execute the command:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgradeThis command first updates the list of available packages and their versions (apt update) and then installs newer versions of the packages you have (apt upgrade).
Install Neofetch via APT Command
Once your system is updated, you can proceed to install Neofetch. Neofetch is included in the official repositories of Linux Mint and Ubuntu, ensuring a reliable and secure installation. To install Neofetch, input the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt install neofetchThis command utilizes the APT (Advanced Package Tool) package manager to download and install Neofetch.
Neofetch Terminal Commands on Linux Mint 21, 20
Basic Neofetch Command
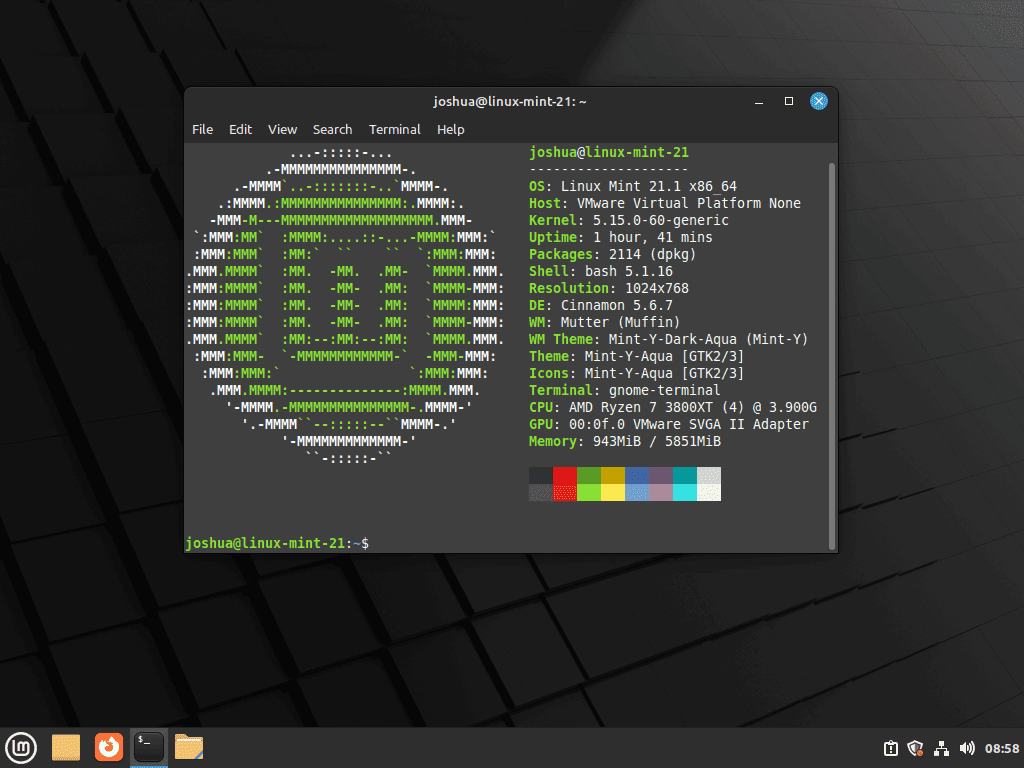
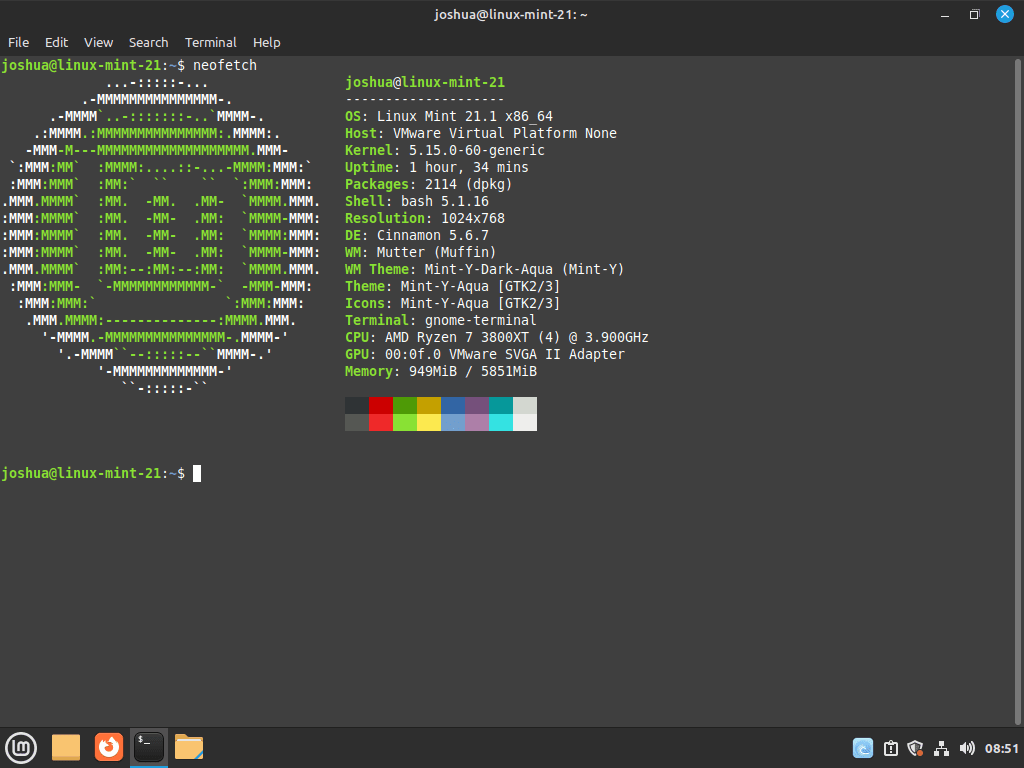
The command neofetch is the simplest way to run Neofetch. It displays your system information in a colorful ASCII art format. This output includes essential details like OS name and version, kernel version, CPU type and speed, GPU information, and memory usage.
neofetchExample output:
Disable ASCII Art in Output
Use the --off option with Neofetch to skip the ASCII art display. This command is helpful for those who prefer a straightforward, text-only overview of their system’s information.
neofetch --offExample output:
Plain-Text Output for Scripting
Combining --off with --stdout in the Neofetch command outputs the system information to the terminal’s standard output in plain text. This format is particularly useful for scripting or when you need to pipe the output to other programs.
neofetch --off --stdoutExample output:
Overview of Neofetch Command Options
Following from the examples, here is a detailed overview of Neofetch commands:
neofetch: Shows system information with ASCII art.neofetch --off: Outputs system details in plain text, excluding ASCII art.neofetch --color_blocks: Enhances output readability with color blocks.neofetch --ascii_distro: Shows your Linux distribution’s logo in ASCII art.neofetch --cpu_temp: Reveals the current CPU temperature.neofetch --memory_display: Presents memory usage as a progress bar.neofetch --battery_display: Useful for laptops, shows battery status.neofetch --gtk2: Details the installed GTK2 theme.neofetch --gtk3: Provides information about the installed GTK3 theme.neofetch --wm: Informs about the active window manager.neofetch --wm_theme: Displays the theme used by the window manager.neofetch --kernel_shorthand: Shows a concise version of the kernel version.neofetch --song: Displays the song playing in a music player, if any.neofetch --uptime_shorthand: Presents system uptime in a brief format.neofetch --distro_shorthand: Offers a shortened display of the distribution name.neofetch --kernel_display: Gives detailed kernel information.neofetch --color_blocks_off: Turns off color blocks in the output.neofetch --no_cpu_brand: Omits the CPU brand from the display.neofetch --backend: Shows the backend used for gathering system information.neofetch --config: Reveals the location of the Neofetch configuration file.neofetch --config_file: Allows specifying a different configuration file.neofetch --help: Provides help and usage information for Neofetch.
Each of these commands adds a layer of customization to how Neofetch displays system information, catering to different preferences and requirements of users, whether for aesthetic purposes or practical applications such as system monitoring and scripting.
Managing Neofetch on Linux Mint 21, 20
Remove Neofetch From Linux Mint
To uninstall Neofetch from your Linux Mint system, a simple terminal command is all that’s required. This action is useful when you no longer need the application or are streamlining your system’s applications.
Execute the following command in your terminal to remove Neofetch:
sudo apt remove neofetchConclusion
And there you have it! We’ve journeyed through the ins and outs of Neofetch on Linux Mint, covering everything from installation to customization and even how to uninstall it. Remember, Neofetch is more than just a tool for displaying system info; it’s a customizable piece of your Linux toolkit. Whether you’re a server admin or a casual user, it’s a fantastic way to keep an eye on your system’s health and show off its specs with style.