If you’re looking for a lightweight yet feature-rich desktop environment for your Ubuntu system, LXQt could be an excellent choice. This guide will focus on how to install LXQt on Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy Jellyfish or Ubuntu 20.04 Focal Fossa, offering you a different experience from the default GNOME desktop environment.
Why Consider LXQt on Ubuntu?
- Performance: LXQt is designed to be lightweight, making it suitable for systems with limited resources. Despite its low memory footprint, it offers a smooth user experience.
- Customization: LXQt features a modular design, allowing users to add plugins and tailor the desktop to their liking.
- User-Friendly Interface: LXQt provides a straightforward, classic interface, which may appeal to those who prefer simplicity over the modern look of GNOME.
- Compatibility: Built on the Qt framework, LXQt works well with all major Linux distributions, making it easy for users who switch between different Linux environments.
- Functionality: LXQt supports multiple window managers and offers advanced settings to control your desktop environment precisely.
If you’re intrigued by what LXQt has to offer, stay tuned. The upcoming guide will provide step-by-step instructions for installing LXQt on Ubuntu 22.04 or 20.04. This method also applies to other Ubuntu releases that haven’t reached their end of life.
Section 1: Install LXQt on Ubuntu Linux
Step 1: Updating Ubuntu System Before LXQt Installation
Starting with a fully updated system is crucial, ensuring the latest software and security patches are installed. This reduces the risk of potential conflicts during the LXQt installation. The following commands are used to achieve this:
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgradeThe first command, sudo apt update, refreshes your system’s package lists, ensuring that Ubuntu is aware of the latest versions of software available. The second command, sudo apt upgrade, will subsequently upgrade all outdated software on your system.
Step 2: Installing LXQt via APT Command on Ubuntu
LXQt is conveniently available in Ubuntu’s repositories, simplifying the installation process. Its lightweight nature ensures that download and installation are considerably faster than other desktop alternatives. Here’s how you install LXQt on your system:
sudo apt install task-lxqt-desktopIn this command, sudo is used for executing the command with root privileges. apt install is the command for installing software, and task-lxqt-desktop is the package name for the LXQt desktop environment.
For minimal server installations, LXQt can be installed with the following command:
sudo apt install lxqtDuring the installation process, you’ll encounter the “Configuring sddm” screen. SDDM (Simple Desktop Display Manager) is the display manager and login screen that LXQt uses. To continue, press the TAB key to highlight <Ok> and press ENTER.
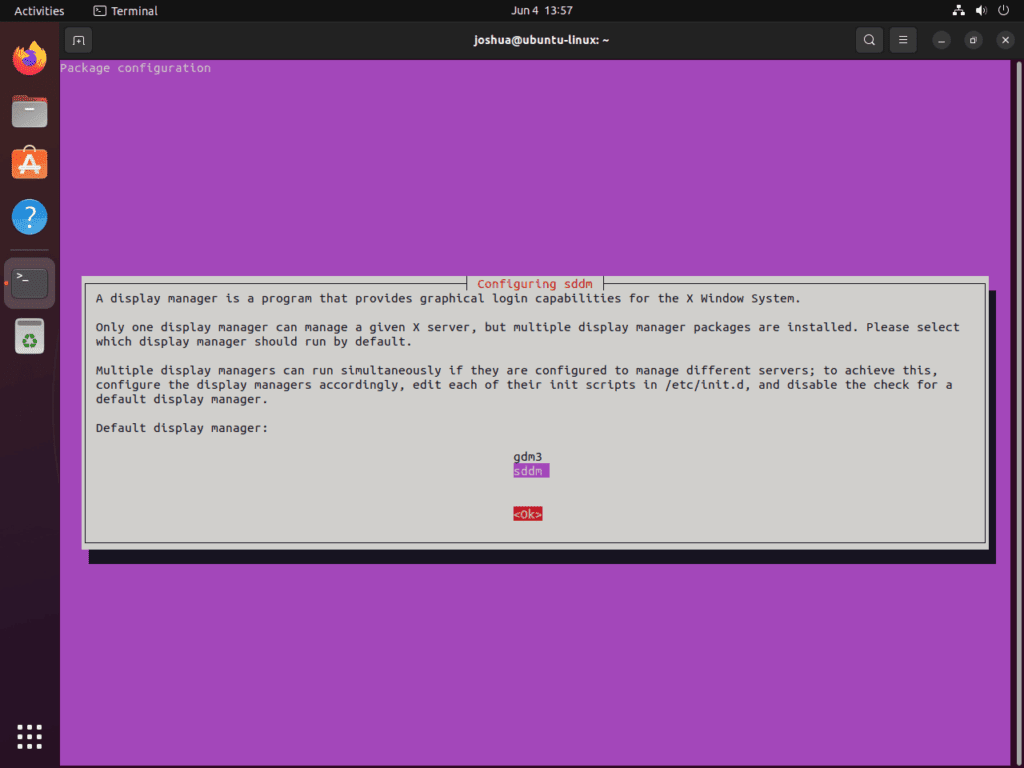
Step 3: Rebooting the System
Upon successful installation of LXQt, reboot your system to finalize the changes. Rebooting allows your system to initialize LXQt properly and ensures its proper functioning. Here’s how you can reboot your system using the terminal:
sudo rebootSection 2: Accessing LXQt on Ubuntu
Step 1: Navigating the Login Screen with LXQt on Ubuntu
After your system restarts following the LXQt installation, you will encounter your login screen. By default, LXQt should be automatically selected as your desktop environment. If this is not the case, you can manually select LXQt.
To choose LXQt, locate the desktop environment selection option in the top left-hand corner of the login screen. Click on this dropdown and select “LXQt” as your desktop environment. This will replace the default choice of “GNOME (Wayland).”

Step 2: Understanding the Initial Appearance with LXQt on Ubuntu
When you first log in to LXQt, the appearance of your login screen may resemble a Debian interface. This can initially seem confusing, given that you are running Ubuntu. However, there’s no need for concern; this occurrence can be attributed to Ubuntu’s lineage.
Ubuntu is fundamentally built upon Debian; hence, certain aspects of Debian’s aesthetic design can manifest in Ubuntu, particularly when installing alternative desktop environments like LXQt. It’s important to remember that this initial appearance can be customized and adjusted to your liking in subsequent steps, offering a truly tailored desktop experience.
Section 3: Tips on Getting Started with LXQt on Ubuntu
LXQt can be a powerful addition to your Linux workflow, offering many customization options to enhance your user experience. To aid you in settling into LXQt, we’ll explore some helpful tips and tricks specific to the software’s Linux-based installations.
Setting a Desktop Background
Unlike many desktop environments, LXQt typically has no background set by default. This blank canvas provides an excellent opportunity to make the desktop truly yours. To set a background, right-click anywhere on the desktop and select “Desktop Preferences.” From here, you can browse your system for your preferred wallpaper image.
Configuring the Panel
The LXQt panel is a versatile tool, allowing you to access various features swiftly. However, the default configuration might not align perfectly with your workflow. To customize the panel, right-click on an empty area and select “Configure Panel.” This opens the panel settings, where you can modify its location, size, and more.
Managing Windows
Windows management in LXQt is highly configurable, which can significantly improve your productivity. Accessing the “Openbox Settings” in the LXQt configuration center lets you fine-tune window behavior to your liking, including focusing, placing, and resizing windows.
Personalizing LXQt Themes
LXQt allows for extensive theme customization, allowing you to alter the look and feel of your desktop environment. To explore this, head to “LXQt Settings”> “Appearance.” Here, you can customize LXQt themes to suit your aesthetic.
Remember, the beauty of LXQt lies in its flexibility and versatility. Don’t be afraid to play around with the settings and configurations. These tips are just a starting point. The more you experiment, the more you can mold LXQt to fit your needs and preferences. Enjoy your exploration of LXQt on Ubuntu Linux!
Section 4: Managing LXQt on Ubuntu
Navigating a system equipped with LXQt can sometimes necessitate a switch back to the GNOME Desktop Environment and its default display manager, GDM. This process involves moving away from LXQt and the LightDM display manager it uses. In this section, we will guide you through the procedure for this transition.
Switching Default Display Managers with LXQt on Ubuntu
Reverting to GNOME from LXQt starts with resuming the display manager selection screen, similar to what you encountered during the LXQt installation process. This can be achieved by running the following command in your terminal:
sudo dpkg-reconfigure sddmThis command initiates the SDDM display manager’s configuration process, allowing you to select an alternate default option, such as GDM, for GNOME. Please note it is essential to reboot your system whenever you switch display managers or desktop environments to ensure all changes are accurately incorporated.
sudo rebootUninstalling LXQt on Ubuntu
There might be situations where you decide to uninstall LXQt. Maybe you’re keen on trying out another desktop environment or want to revert to your previous configuration. If you find yourself in this position, you can remove LXQt as follows:
Run the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt-get remove lxqt*The command will expel LXQt and any associated files from your system, returning your desktop environment to its prior state.
Following the LXQt removal, it’s probable that you’ll need to reinstall the GNOME Desktop Environment. The process of LXQt uninstallation might have led to the removal of some packages that GNOME relies on. Hence, to reinstall GNOME, update your package list and install the ubuntu-gnome-desktop package:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install ubuntu-gnome-desktopFinally, to ensure all modifications are correctly applied, reboot your system:
sudo rebootConclusion: Installing LXQt on Ubuntu Linux
Exploring LXQt as an alternate desktop environment on Ubuntu Linux has offered insightful revelations. The installation and management of LXQt are, in essence, simplistic processes, even for users who might not be too familiar with Linux distributions. This desktop environment’s lightweight characteristics, easy installation, and efficient performance make it a compelling choice, especially for systems striving for optimal performance. By understanding the necessary commands for installation, login, and potential uninstallation, we’ve covered the basics of managing LXQt on a Ubuntu Linux system.


