Firewalld GUI, also known as firewall-config, offers a user-friendly interface for managing the Firewalld service on Fedora Linux. This guide will demonstrate how to install Firewalld GUI and running on your Fedora system. It’s a straightforward procedure, enhancing the overall experience of configuring and monitoring your firewall settings.
Below are some of the key features that make Firewalld GUI an indispensable tool for network administrators and users who prefer graphical interfaces:
- Simplified Management: Easily adjust firewall settings without delving into complex command lines.
- Real-Time Updates: Changes made in the GUI are instantly reflected in the Firewalld service.
- Zone Management: Effortlessly manage and assign network interfaces to different firewall zones.
- Rich Rule Configuration: Customize rules for incoming and outgoing traffic with a few clicks.
- Direct Interface Interaction: Directly modify firewall rules for services and ports.
- Viewing Active Rules: Quickly view currently active rules and make adjustments as needed.
Integrating Firewalld GUI into your Fedora environment, you gain a powerful yet accessible tool for ensuring your network’s security. The following sections will guide you through the installation and initial configuration, ensuring a smooth transition to a more intuitive firewall management.
Install FirewallD on Fedora Linux
Step 1: Confirming FirewallD Installation
Fedora Linux typically comes with FirewallD pre-installed. To verify its presence on your Fedora 36 system, execute the command below in the terminal. This command checks the installed version of FirewallD, which confirms its installation.
sudo firewall-cmd --versionThe terminal will display a version number indicating that FirewallD is installed on your system.
Step 2: Installing FirewallD if Not Present
If FirewallD is not pre-installed, you can easily install it using the following DNF command:
sudo dnf install firewalld -yThis command installs the FirewallD package and includes the -y flag to confirm the installation automatically.
Step 3: Enable Firewalld
Once FirewallD is installed or confirmed present, the next step is enabling the service. For enhanced security, it is crucial to have FirewallD enabled at system startup and running immediately.
The command below sets FirewallD to start on boot and also initiates it right away:
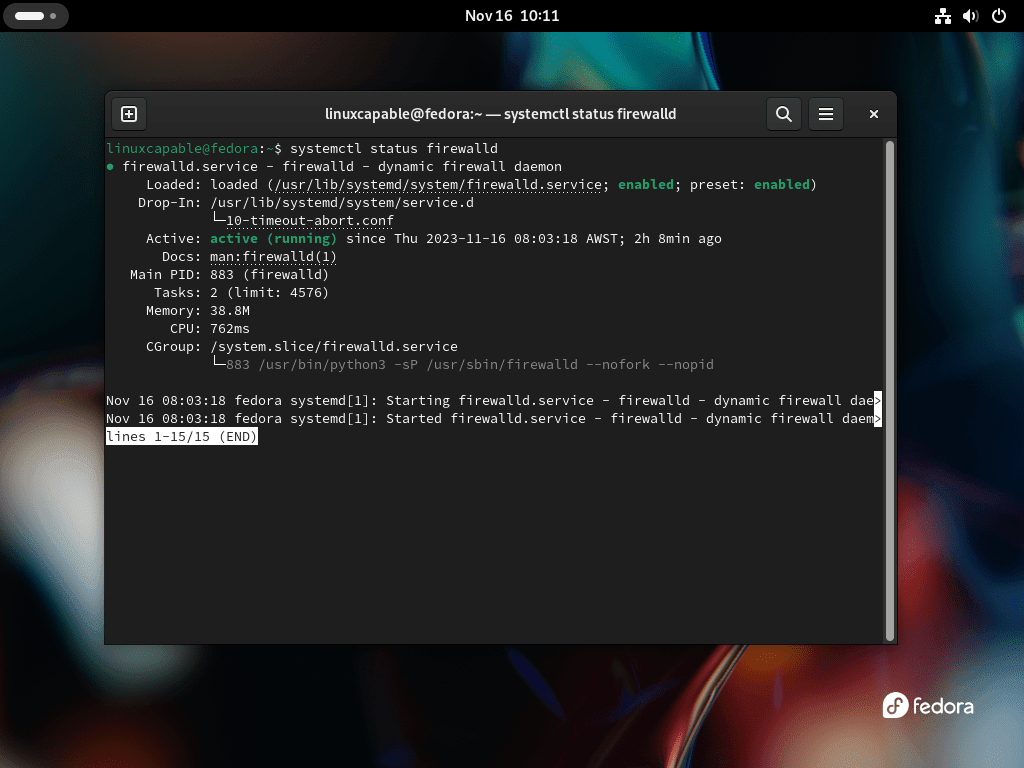
sudo systemctl enable firewalld --nowAfter enabling, it’s essential to verify that FirewallD is running smoothly. The following command checks the status of FirewallD, providing information on whether it is active and running without errors:
systemctl status firewalldWith the successful execution of these steps, you ensure that FirewallD is installed and actively protecting your Fedora system.
Install FirewallD GUI on Fedora Linux
Step 1: Install FirewallD GUI on Fedora via DNF Command
To enhance the user experience with an intuitive graphical interface, Fedora Linux users can install the FirewallD GUI. This interface simplifies the process of managing firewall settings. The necessary packages are available in Fedora’s default appstream. Initiate the installation with this command:
sudo dnf install firewall-configThis command installs firewall-config, the graphical user interface for FirewallD, making it more accessible for users who prefer a GUI over command-line interactions.
Step 2: KDE-Specific FirewallD GUI Installation
A specialized version of the FirewallD GUI is available for users operating on the KDE desktop environment. This version is tailored to integrate seamlessly with the KDE interface. To install this KDE-specific FirewallD control panel, execute the following command:
sudo dnf install plasma-firewall-firewalld -yThis command installs plasma-firewall-firewalld, ensuring a consistent and integrated experience for KDE users managing their firewall settings.
Run FirewallD GUI on Fedora Linux
Launching FirewallD GUI
After successfully installing the FirewallD GUI on your Fedora Linux system, you can initiate the interface to start configuring your firewall settings. To open the FirewallD GUI, navigate through the following steps:
- Click on ‘Activities’ at the top left corner of your screen.
- Select ‘Show Applications’ to view all installed applications.
- Locate and click on ‘Firewall’ to open the FirewallD GUI.
Exploring Firewall Settings
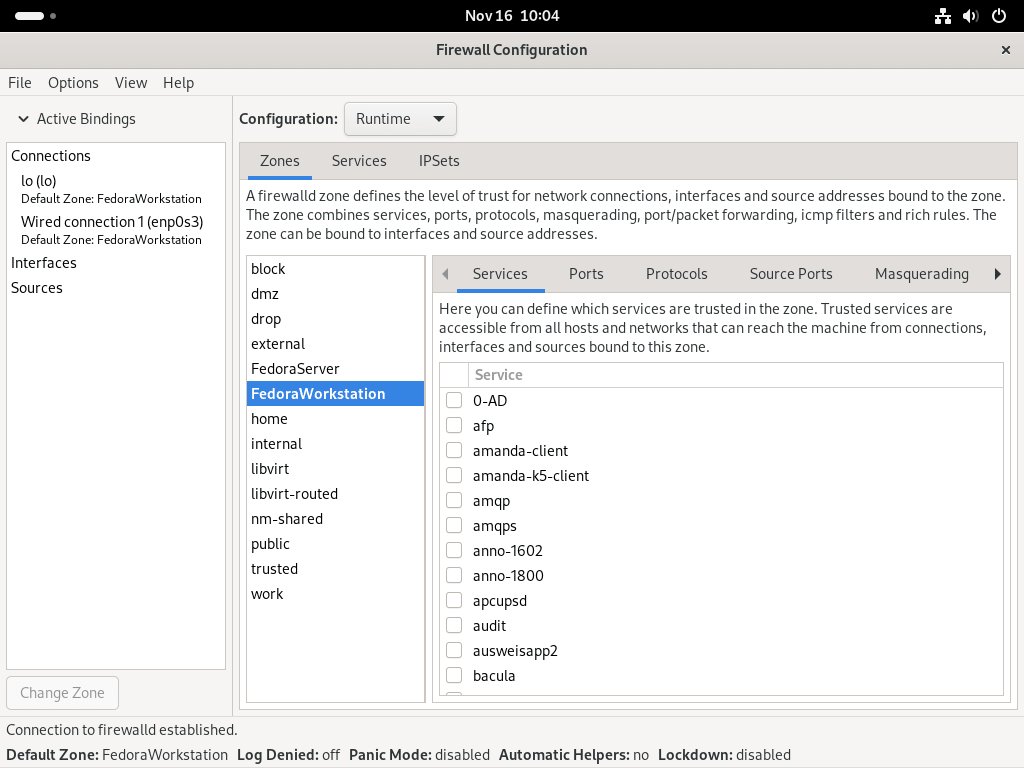
With the FirewallD GUI open, you now have the opportunity to explore and modify various firewall settings. The initial screen typically displays the ‘public’ zone, the default zone for most network interfaces. Within the GUI, you will find options to manage:
- Services: Configure which services are allowed through the firewall.
- Ports: Specify which ports are open for incoming and outgoing traffic.
- Protocols: Define rules based on different network protocols.
Additionally, the ‘View’ menu and ‘Options’ provide further customization and settings, enhancing your control over the firewall configuration.
Managing Firewalld GUI on Fedora Linux
Remove Firewalld GUI
In some scenarios, users may uninstall the FirewallD GUI from their Fedora Linux system. The removal process is straightforward, whether for system optimization, preference for command-line tools, or other reasons.
Standard Environment
For those using the standard FirewallD GUI (firewall-config), the following DNF command will uninstall the graphical interface:
sudo dnf remove firewall-config
This command removes the firewall-config package, effectively uninstalling the FirewallD GUI from your system.
KDE Environment
KDE desktop environment users who have installed the KDE-specific version of the FirewallD GUI can uninstall it using a similar DNF command:
sudo dnf remove plasma-firewall-firewalldThis command targets the plasma-firewall-firewalld package, removing the KDE-integrated FirewallD GUI.
Conclusion
In this guide, we’ve journeyed through the essential steps for installing and managing Firewalld GUI on Fedora Linux. From confirming the presence of Firewalld to installing the GUI and even removing it when necessary, we’ve explored the key actions to streamline your firewall management. Remember, while the GUI offers a user-friendly interface, keeping your firewall configurations up-to-date is crucial for system security. As a final recommendation, regularly review your firewall settings and stay informed about best practices in network security. This way, you’ll maintain a robust defense against potential network threats.